Navigating the Vastness: Exploring the California Desert Region
Related Articles: Navigating the Vastness: Exploring the California Desert Region
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Vastness: Exploring the California Desert Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Vastness: Exploring the California Desert Region
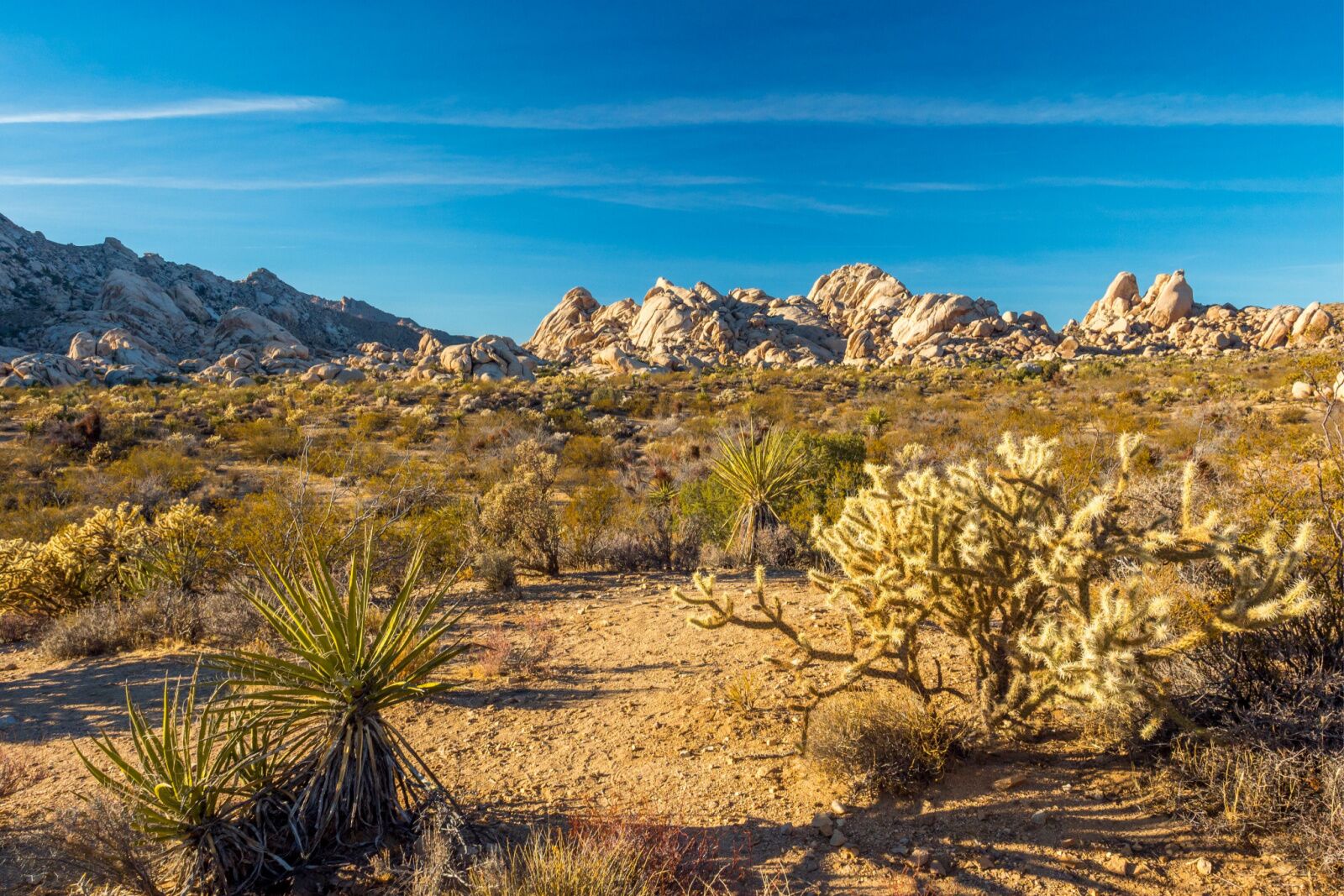

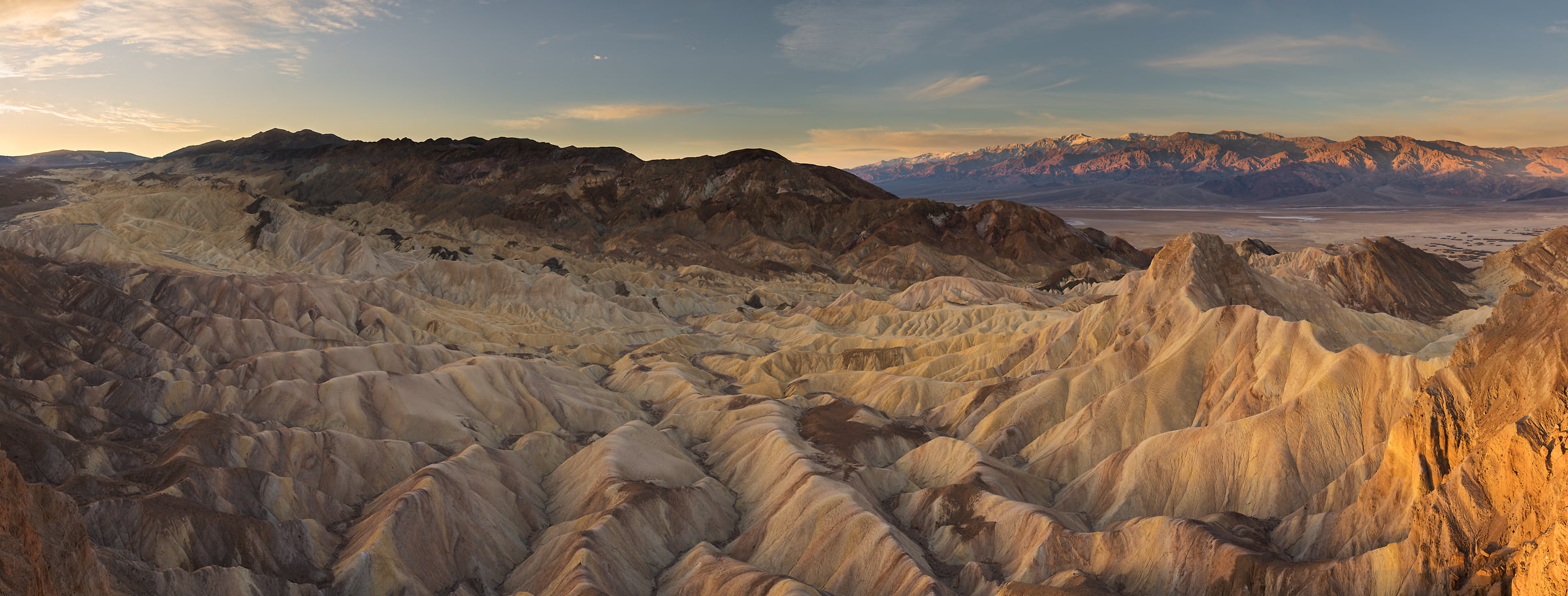
The California desert region, a captivating expanse of arid landscapes, holds a unique allure for adventurers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike. Spanning a significant portion of the state’s southeastern quadrant, this diverse ecosystem boasts a fascinating tapestry of geological formations, unique flora and fauna, and a rich history intertwined with the stories of indigenous cultures and early pioneers. Understanding the geography of this region through maps is crucial for appreciating its ecological significance, exploring its hidden treasures, and navigating its challenges.
A Geographic Overview: Unveiling the Desert’s Tapestry
The California desert region encompasses four distinct desert subregions, each with its own characteristic features and ecological dynamics:
1. The Mojave Desert: Occupying the largest portion of the region, the Mojave Desert is known for its dramatic landscapes, including the iconic Joshua Tree National Park, Death Valley National Park, and the Mojave National Preserve. Its defining feature is the presence of the Joshua tree, a unique species of yucca that thrives in this arid environment.
2. The Colorado Desert: Situated in the southeastern corner of the state, the Colorado Desert is characterized by its proximity to the Salton Sea, a large, saline lake formed by an accidental flood in 1905. The region is also home to the Anza-Borrego Desert State Park, known for its diverse flora and fauna, including bighorn sheep and desert tortoises.
3. The Sonoran Desert: Extending into Arizona, the Sonoran Desert is the hottest and driest desert in the United States. Its iconic saguaro cactus, towering over the landscape, is a symbol of this unique ecosystem.
4. The Great Basin Desert: While not technically part of the California desert region, a small portion of the Great Basin Desert extends into southeastern California. This high-elevation desert is characterized by its cold winters and unique plant communities, including sagebrush and juniper.
Maps as Guides: Navigating the Desert’s Complexity
Maps serve as indispensable tools for understanding the intricate geography of the California desert region. They provide a visual representation of the region’s topography, elevation, and key landmarks, allowing for a comprehensive grasp of its spatial relationships.
1. Topographic Maps: These maps depict the elevation changes across the desert region, highlighting mountain ranges, canyons, and other significant landforms. They are essential for planning hikes, identifying potential water sources, and understanding the overall landscape.
2. Geological Maps: Geological maps showcase the rock formations and geological history of the desert region. They provide insights into the formation of unique landforms, such as the Death Valley fault system and the San Andreas Fault, which plays a significant role in the region’s seismic activity.
3. Vegetation Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of different plant communities across the desert region, highlighting the presence of Joshua trees, creosote bushes, and other desert-adapted flora. They are useful for understanding the ecological diversity of the region and identifying areas with specific plant species.
4. Wildlife Maps: Wildlife maps provide information about the distribution of different animal species, including desert tortoises, bighorn sheep, and various bird species. They are invaluable for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers seeking to understand the region’s biodiversity and identify areas where specific species can be found.
5. Road Maps: Road maps are essential for navigating the desert region, providing information about major highways, backroads, and points of interest. They are particularly useful for travelers exploring the region by car and for accessing remote areas.
6. Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery offers a comprehensive perspective of the California desert region, showcasing its vastness and highlighting key features like the Salton Sea, the Mojave River, and the intricate network of canyons and washes.
The Importance of Maps: Unveiling the Region’s Value
Understanding the California desert region through maps is crucial for a variety of reasons:
1. Conservation and Management: Maps provide essential data for conservation efforts, allowing scientists and land managers to identify areas of ecological significance, track habitat changes, and implement effective conservation strategies.
2. Resource Management: Maps are vital for managing water resources, identifying potential geothermal energy sources, and understanding the distribution of mineral deposits within the desert region.
3. Recreation and Tourism: Maps are indispensable for planning outdoor activities, identifying hiking trails, and exploring the region’s unique natural attractions.
4. Scientific Research: Maps provide a framework for conducting scientific research, allowing researchers to map out study sites, track environmental changes, and analyze data related to the desert ecosystem.
5. Educational Value: Maps offer a valuable educational tool for students, providing a visual representation of the desert region’s geography, history, and ecology, fostering a deeper understanding of this unique ecosystem.
FAQs About the California Desert Region
Q: What is the average temperature in the California desert region?
A: The average temperature varies significantly depending on the specific location and time of year. However, the region is generally characterized by hot summers and mild winters. Temperatures can reach extreme highs in the summer, particularly in Death Valley, which holds the record for the highest recorded temperature in the world.
Q: What are the major cities located within the California desert region?
A: Major cities within the region include Palm Springs, Indio, Lancaster, and Barstow. These cities serve as gateways to the desert and offer a range of amenities for visitors and residents alike.
Q: What are some of the unique plant and animal species found in the California desert region?
A: The region is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species adapted to the harsh conditions. Notable species include the Joshua tree, creosote bush, desert tortoise, bighorn sheep, and various species of birds, reptiles, and insects.
Q: What are some of the major threats to the California desert region?
A: The California desert region faces various threats, including habitat loss due to urbanization and development, invasive species, climate change, and water scarcity. Conservation efforts are crucial for mitigating these threats and preserving the region’s unique biodiversity.
Tips for Exploring the California Desert Region
1. Prepare for Extreme Conditions: The desert region can experience extreme temperatures, so it’s essential to be prepared for hot days and cool nights. Bring plenty of water, sunscreen, and appropriate clothing.
2. Be Aware of Wildlife: The desert is home to a variety of wildlife, including venomous snakes and scorpions. Be aware of your surroundings and avoid disturbing animals.
3. Respect the Environment: Leave no trace of your visit. Pack out all trash, stay on designated trails, and avoid disturbing the fragile desert ecosystem.
4. Obtain Necessary Permits: Some areas within the desert region require permits for hiking, camping, or other activities. Ensure you have the necessary permits before venturing into these areas.
5. Check Weather Conditions: The desert climate can change rapidly, so it’s essential to check weather conditions before heading out. Be prepared for sudden changes in temperature and wind.
Conclusion: A Region of Beauty and Resilience
The California desert region, with its vast expanses of arid landscapes, unique plant and animal life, and rich history, holds a captivating allure for adventurers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike. Maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating its complexities, understanding its ecological significance, and exploring its hidden treasures. By understanding the region’s geography and appreciating its fragility, we can contribute to its preservation and ensure that this remarkable ecosystem continues to thrive for generations to come.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Vastness: Exploring the California Desert Region. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!


/mesalightrailmap_640-56a726c43df78cf77292ca01.jpg)
/light-rail-train-at-station-689232589-5a6dd528fa6bcc00373be02a.jpg)



.jpeg)









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SanDiego_Cabrillo_Statue_01072020_A7RIII_SUMANA__05-f53f753942fe4141b4f48bed01952296.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/san-diego-skyline-in-magic-hour-172674423-eff84e89947a4ee6b1dbff984c2cb6e4.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SanDiego_Cabrillo_Lighthouse_01072020_A7RIII_SUMANA__24-a389a63c5fe5448c995b3e4fff28bd82.jpg)