Navigating the Landscape of Indigenous Lands: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Indian Tribe Territory Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Indigenous Lands: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Indian Tribe Territory Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Indigenous Lands: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Indian Tribe Territory Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Indigenous Lands: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Indian Tribe Territory Maps

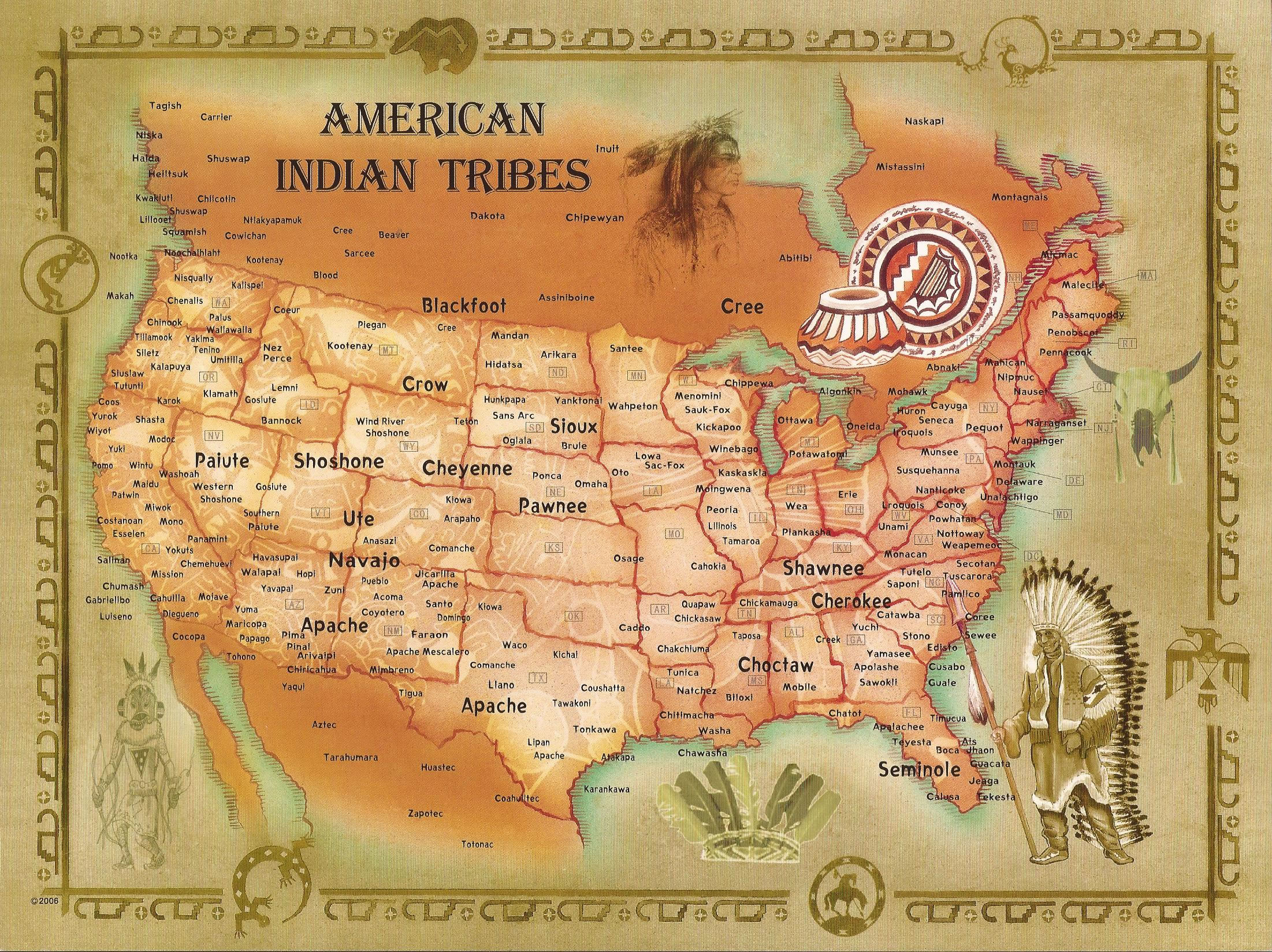
The United States is a nation built on the diverse tapestry of its indigenous peoples, each with a rich history, culture, and connection to the land. Understanding the intricate mosaic of Native American tribal territories is crucial for appreciating the nation’s history, honoring the sovereignty of indigenous communities, and fostering respectful engagement with their cultures. This guide will delve into the significance of Indian tribe territory maps, providing a comprehensive understanding of their historical context, current usage, and importance for promoting cultural awareness, social justice, and environmental stewardship.
Understanding the Historical Context
The concept of "Indian territory" is deeply intertwined with the complex and often tragic history of colonization and dispossession in the United States. Prior to European arrival, Indigenous peoples inhabited the land for millennia, establishing intricate systems of governance, resource management, and cultural practices. The arrival of European settlers, however, marked a period of forced relocation, treaty violations, and the erosion of Indigenous sovereignty.
The Indian Removal Act of 1830, for instance, resulted in the forced displacement of thousands of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands, leading to the infamous "Trail of Tears." This event, along with numerous other injustices, underscores the need to acknowledge the historical context of Indian tribe territory maps. They serve as a powerful reminder of the ongoing struggle for self-determination and the resilience of Indigenous communities in the face of historical trauma.
The Evolution of Tribal Territories: From Treaties to Recognition
The boundaries of Indian tribe territories are not static entities but rather evolving landscapes shaped by historical treaties, legal recognition, and the ongoing efforts of Indigenous nations to reclaim their ancestral lands. Treaty agreements, often negotiated under duress, played a significant role in defining the initial boundaries of tribal territories. These treaties, however, were frequently broken by the U.S. government, leading to further displacement and the loss of land.
The 20th century saw a shift in federal policy toward recognizing the sovereignty of Indigenous nations. The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, for example, granted tribes greater autonomy over their affairs and encouraged the development of tribal governments. This period also saw the establishment of the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) which, while sometimes controversial, has played a crucial role in managing federal trust lands and overseeing the administration of tribal governments.
Despite these efforts, the process of recognizing and respecting tribal sovereignty remains ongoing. The Indian Gaming Regulatory Act of 1988, for example, granted tribes the right to operate gaming facilities on their lands, providing a significant source of revenue for economic development and self-sufficiency. However, the ongoing struggle for land rights, resource management, and cultural preservation underscores the need for continued efforts to uphold the sovereignty of Indigenous nations.
The Importance of Indian Tribe Territory Maps
Indian tribe territory maps are not merely geographical representations but powerful tools for understanding the cultural, historical, and political landscape of the United States. They serve as a visual reminder of the enduring presence of Indigenous peoples and their ongoing struggle for self-determination. The maps highlight the following key aspects:
-
Cultural Heritage and Identity: Indian tribe territory maps offer a glimpse into the rich and diverse cultures of Indigenous peoples. They showcase the unique traditions, languages, and spiritual connections to the land that have been passed down through generations. By understanding the historical and cultural significance of these territories, we gain a deeper appreciation for the contributions of Indigenous communities to the fabric of American society.
-
Sovereignty and Self-Governance: The maps visually represent the sovereign status of tribal nations, emphasizing their inherent right to self-governance and control over their lands and resources. They underscore the importance of respecting tribal sovereignty and recognizing the unique legal and political status of Indigenous nations within the United States.
-
Environmental Stewardship: Indigenous peoples have a long history of sustainable resource management and environmental stewardship. Indian tribe territory maps illustrate the interconnectedness of land, culture, and identity, highlighting the importance of protecting natural resources and preserving the environment for future generations.
-
Historical Justice and Reconciliation: The maps serve as a powerful reminder of the historical injustices inflicted upon Indigenous peoples, including forced relocation, treaty violations, and the erosion of tribal sovereignty. They underscore the need for ongoing efforts to address historical wrongs and promote reconciliation with Indigenous communities.
-
Education and Awareness: Indian tribe territory maps are valuable educational tools that can foster greater understanding and awareness of Indigenous cultures, histories, and perspectives. They can be used in classrooms, museums, and community centers to engage audiences in learning about the diverse experiences of Native Americans and their contributions to American society.
Navigating the Maps: A Guide to Interpretation
Indian tribe territory maps come in various forms, each with its own unique purpose and interpretation. Here are some key elements to consider when navigating these maps:
-
Historical vs. Current Boundaries: It is important to distinguish between historical and current boundaries. While historical maps illustrate the original territories of Indigenous nations, current maps may reflect changes due to treaties, land cessions, and the establishment of reservations.
-
Tribal Sovereignty and Jurisdiction: Maps may depict areas where tribes retain sovereign jurisdiction, such as reservation lands or areas with specific treaty rights. Understanding these jurisdictional boundaries is crucial for respecting tribal sovereignty and navigating legal and cultural issues related to land use and resource management.
-
Federal Recognition: Some maps may indicate federally recognized tribes, highlighting the complex legal status of Indigenous nations within the United States. Federal recognition is a crucial element in determining the rights and responsibilities of tribes, including access to federal resources and services.
-
Cultural and Historical Significance: Maps may include information about significant cultural sites, historical landmarks, or traditional land use practices. This information can provide deeper insights into the rich cultural heritage of Indigenous peoples and their enduring connections to the land.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Indian Tribe Territory Maps
1. What is the difference between an Indian reservation and an Indian tribe territory?
An Indian reservation is a specific area of land set aside by the U.S. government for a particular tribe. It is typically located within a larger territory that historically belonged to that tribe. Indian tribe territory, on the other hand, encompasses the broader geographic area that the tribe has traditionally occupied, which may include reservations as well as other lands.
2. Are all Indian tribe territories recognized by the U.S. government?
No. While many tribes have been federally recognized, some have not. Federal recognition is a complex process, and some tribes have faced obstacles in obtaining it. However, lack of federal recognition does not diminish the sovereignty or cultural significance of a tribe.
3. How are Indian tribe territories being affected by climate change?
Climate change is having a significant impact on Indian tribe territories, affecting water resources, hunting and fishing grounds, and traditional land use practices. Indigenous communities are at the forefront of climate change impacts, and their voices are crucial for developing effective solutions.
4. What are some resources for learning more about Indian tribe territories?
There are a variety of resources available for learning more about Indian tribe territories, including:
-
The National Congress of American Indians (NCAI): The NCAI is the oldest and largest national organization representing tribal governments in the United States. Their website provides information about tribal sovereignty, legislation, and resources.
-
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA): The BIA is a federal agency responsible for administering federal trust lands and overseeing the administration of tribal governments. Their website provides information about tribal recognition, land management, and programs.
-
Tribal websites: Many tribes have their own websites that provide information about their history, culture, and current issues.
Tips for Using Indian Tribe Territory Maps Effectively
-
Consider the source: Always verify the source of the map and the date it was created to ensure accuracy and relevance.
-
Engage with tribal communities: Reach out to tribal governments or organizations to learn more about the specific territories and cultural significance of their lands.
-
Respect tribal sovereignty: Acknowledge the inherent right of tribes to self-governance and control over their lands and resources.
-
Promote cultural understanding: Use maps as educational tools to foster greater awareness and appreciation of Indigenous cultures.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Indian tribe territory maps serve as powerful reminders of the rich history, cultural diversity, and ongoing struggles of Indigenous peoples in the United States. They provide a visual representation of the enduring presence of tribal nations and their inherent right to self-determination. By understanding the historical context, current usage, and importance of these maps, we can foster greater respect for tribal sovereignty, promote cultural awareness, and contribute to a more just and equitable society. Let these maps serve as a call to action, encouraging us to engage in meaningful dialogue, support tribal self-governance, and protect the cultural heritage and lands of Indigenous communities.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Indigenous Lands: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Indian Tribe Territory Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!





















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Map_NJ_JerseyShore-56a62d5f5f9b58b7d0e04c21.png)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Map_NJ_JerseyShore_South-56a6306d5f9b58b7d0e0540e.jpg)














![Printable Detailed Interactive World Map With Countries [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Interactive-World-Map-Printable-1024x576.jpg)
![Printable Detailed Interactive World Map With Countries [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/World-Map-For-Kids-Printable.jpg?6bfec1u00266bfec1)