The Alamo in 1836: A Strategic Fortress and Symbol of Texan Resistance
Related Articles: The Alamo in 1836: A Strategic Fortress and Symbol of Texan Resistance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Alamo in 1836: A Strategic Fortress and Symbol of Texan Resistance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Alamo in 1836: A Strategic Fortress and Symbol of Texan Resistance

The Alamo, a Spanish mission turned fort, stands as a powerful symbol of Texan independence and sacrifice. Its pivotal role in the Texas Revolution, particularly during the 13-day siege in February 1836, solidified its place in history and cultural memory. Understanding the Alamo’s layout and strategic importance in 1836 offers a deeper appreciation for the events that unfolded within its walls and the impact they had on the future of Texas.
The Alamo’s Strategic Location and Layout:
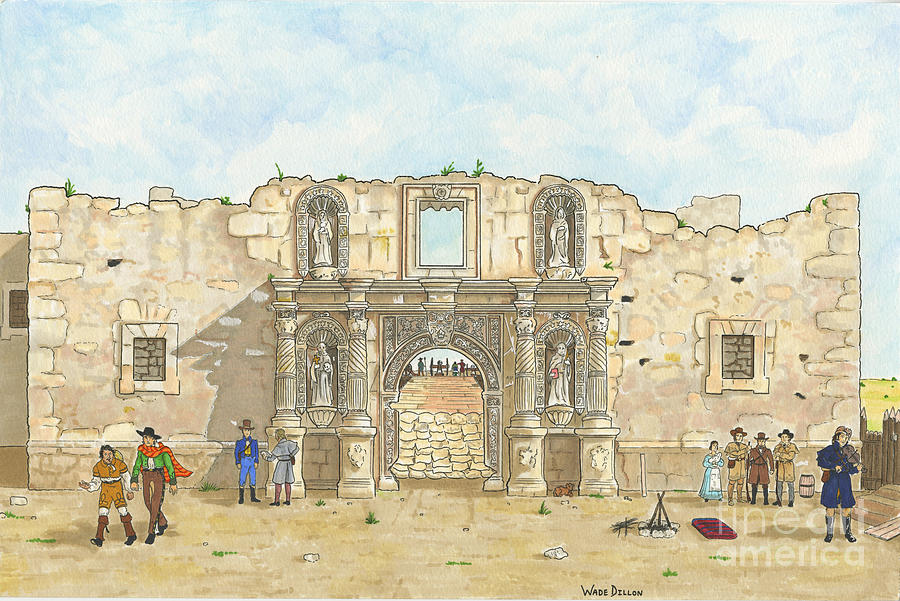
Located in San Antonio de Béxar, the Alamo’s strategic position along the San Antonio River made it a vital point of control in the region. The fort’s layout reflected its defensive purpose, encompassing a roughly rectangular compound enclosed by a sturdy wall. Within this enclosure, several structures served as barracks, living quarters, and storage spaces. The Alamo’s layout provided a crucial advantage for the Texan defenders, allowing them to concentrate their forces and resist the overwhelming Mexican army.
Key Features and Defenses:
The Alamo’s defenses were strategically designed to maximize resistance. The main entrance, located on the south side, was protected by a fortified gate and a drawbridge. The surrounding walls, constructed from adobe bricks, were thick and sturdy, offering protection against artillery fire. The fort also boasted several bastions, projecting outwards from the walls, providing flanking fire and commanding a wider field of vision. These strategic features allowed the defenders to effectively withstand the Mexican army’s initial assaults.
The Alamo’s Importance in the Texas Revolution:
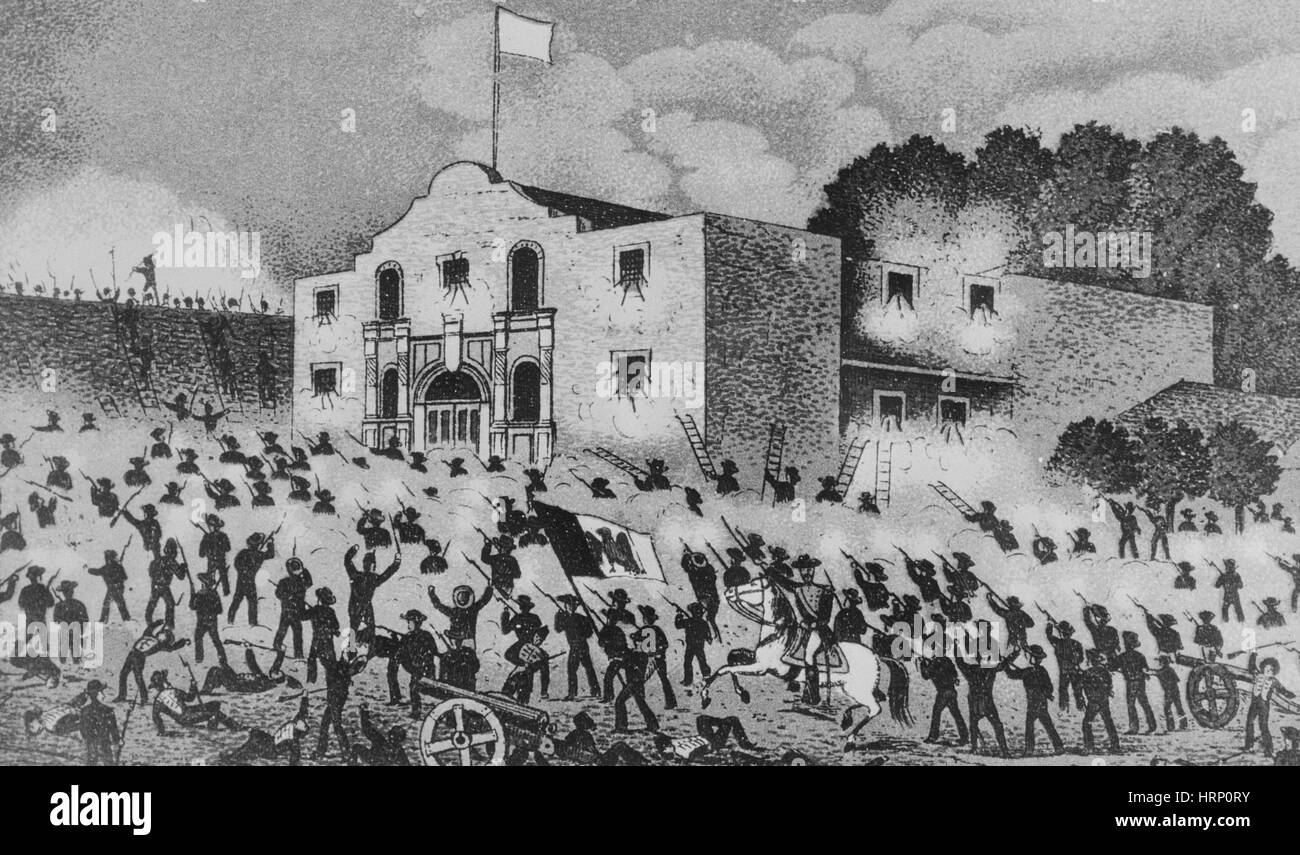
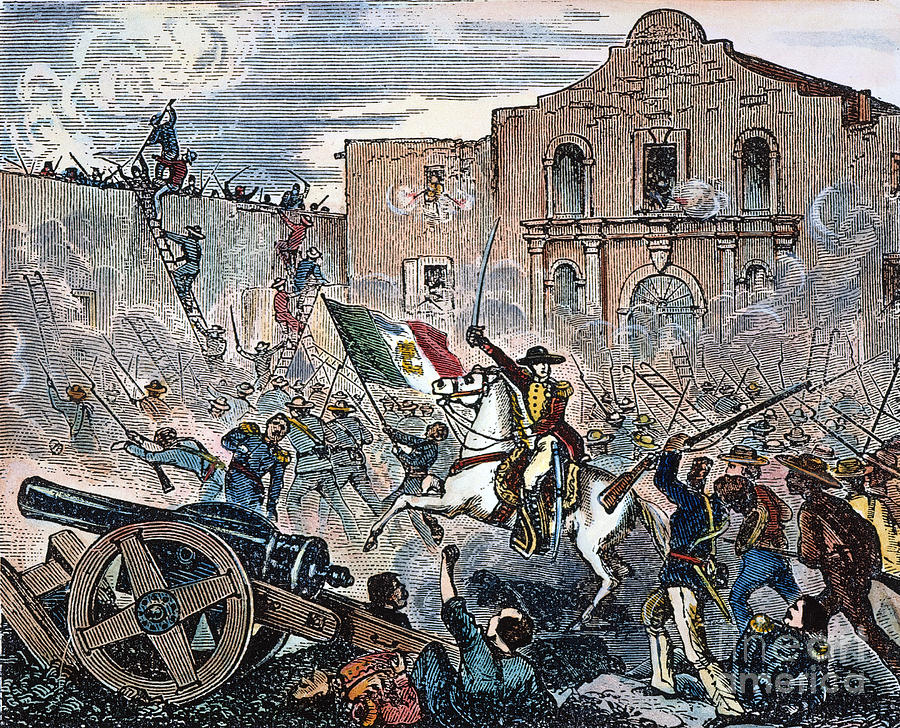
The Battle of the Alamo, fought in February 1836, stands as a defining moment in the Texas Revolution. The Texan defenders, under the command of William Barret Travis, faced a vastly superior Mexican army led by General Antonio López de Santa Anna. Despite the odds stacked against them, the Texans fought bravely, holding off the Mexican forces for 13 days.
The Alamo’s strategic location, coupled with its strong fortifications, allowed the defenders to resist the Mexican onslaught for an extended period. The defenders’ unwavering courage and determination inspired the Texans to fight for their independence, even after the tragic loss of the Alamo. The battle became a rallying cry for the Texan forces, galvanizing them to victory at the Battle of San Jacinto.
The Alamo’s Legacy and Significance:
The Alamo’s legacy extends beyond its strategic importance in the Texas Revolution. The heroic sacrifice of the defenders, including figures like William Barret Travis, James Bowie, and Davy Crockett, has become a powerful symbol of courage, resilience, and the fight for freedom. The Alamo’s story has been immortalized in countless books, movies, and historical accounts, solidifying its place in American and Texan cultural memory.
Beyond the Battle:
While the Alamo’s role in the Texas Revolution is undeniable, it’s important to acknowledge its complex history and significance. The site has been a source of debate and controversy, particularly regarding its role in the larger context of Texas history and the treatment of Native Americans. Understanding the Alamo’s history requires acknowledging the various perspectives and narratives surrounding it.
FAQs:
Q: What was the significance of the Alamo’s location in San Antonio de Béxar?
A: The Alamo’s location along the San Antonio River made it a strategic point of control in the region. Its proximity to the city allowed the defenders to access resources and provided a strategic advantage in defending against Mexican forces.
Q: How did the Alamo’s layout contribute to its defense?
A: The Alamo’s layout, featuring a rectangular compound enclosed by a strong wall, allowed the defenders to concentrate their forces and maximize their defensive capabilities. The bastions and fortified gate further enhanced the fort’s defensive strength.
Q: What were the key events during the 13-day siege of the Alamo?
A: The 13-day siege witnessed fierce battles, constant bombardment, and relentless Mexican assaults. The defenders held their ground bravely, inflicting heavy casualties on the Mexican forces. The siege culminated in a final, desperate stand by the Texan defenders, who fought to the last man.
Q: What was the impact of the Alamo’s fall on the Texas Revolution?
A: The Alamo’s fall, though a tragic loss, served as a rallying cry for the Texan forces. The defenders’ sacrifice inspired the Texans to fight for their independence with renewed fervor, ultimately leading to victory at the Battle of San Jacinto.
Q: What are some of the historical controversies surrounding the Alamo?
A: The Alamo’s history has been subject to debate and controversy, particularly regarding its portrayal in popular culture and its role in the treatment of Native Americans. Understanding the Alamo’s history requires acknowledging the various perspectives and narratives surrounding it.
Tips for Visiting the Alamo:
- Plan your visit in advance: The Alamo is a popular tourist destination, so booking your tickets online and planning your visit in advance is recommended.
- Take a guided tour: Guided tours provide valuable insights into the Alamo’s history, architecture, and significance.
- Explore the surrounding area: San Antonio offers a rich history and culture, with attractions such as the River Walk, the Spanish Governor’s Palace, and the Pearl District.
- Respect the site: The Alamo is a sacred site, and visitors are expected to show respect for its history and the sacrifices made by those who fought there.
Conclusion:
The Alamo stands as a testament to the spirit of Texan independence and sacrifice. Its strategic importance in the Texas Revolution, the heroic deeds of its defenders, and its enduring legacy continue to resonate with visitors from around the world. Understanding the Alamo’s history, its layout, and its role in the events of 1836 provides a deeper appreciation for this iconic landmark and its enduring significance.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/battle-of-the-alamo-large-56a61be45f9b58b7d0dff502.jpg)





![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Alamo in 1836: A Strategic Fortress and Symbol of Texan Resistance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
























































![Atlas del Reino de Tonga [Geography and History of Tonga] - Geografia e](http://www.vidiani.com/maps/maps_of_australia_and_oceania/maps_of_tonga/large_detailed_political_map_of_tonga_with_cities_for_free.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)