Unveiling The Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide To 3D Topographic Maps
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps
- 3.1 The Evolution of Topographic Mapping: From Flat to Form
- 3.2 Exploring the Depths of 3D Topographic Maps: Benefits and Applications
- 3.3 Unveiling the Complexity: Data Acquisition and Processing
- 3.4 Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Key Concepts
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of 3D Topographic Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: Charting the Future of Terrain Visualization
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps
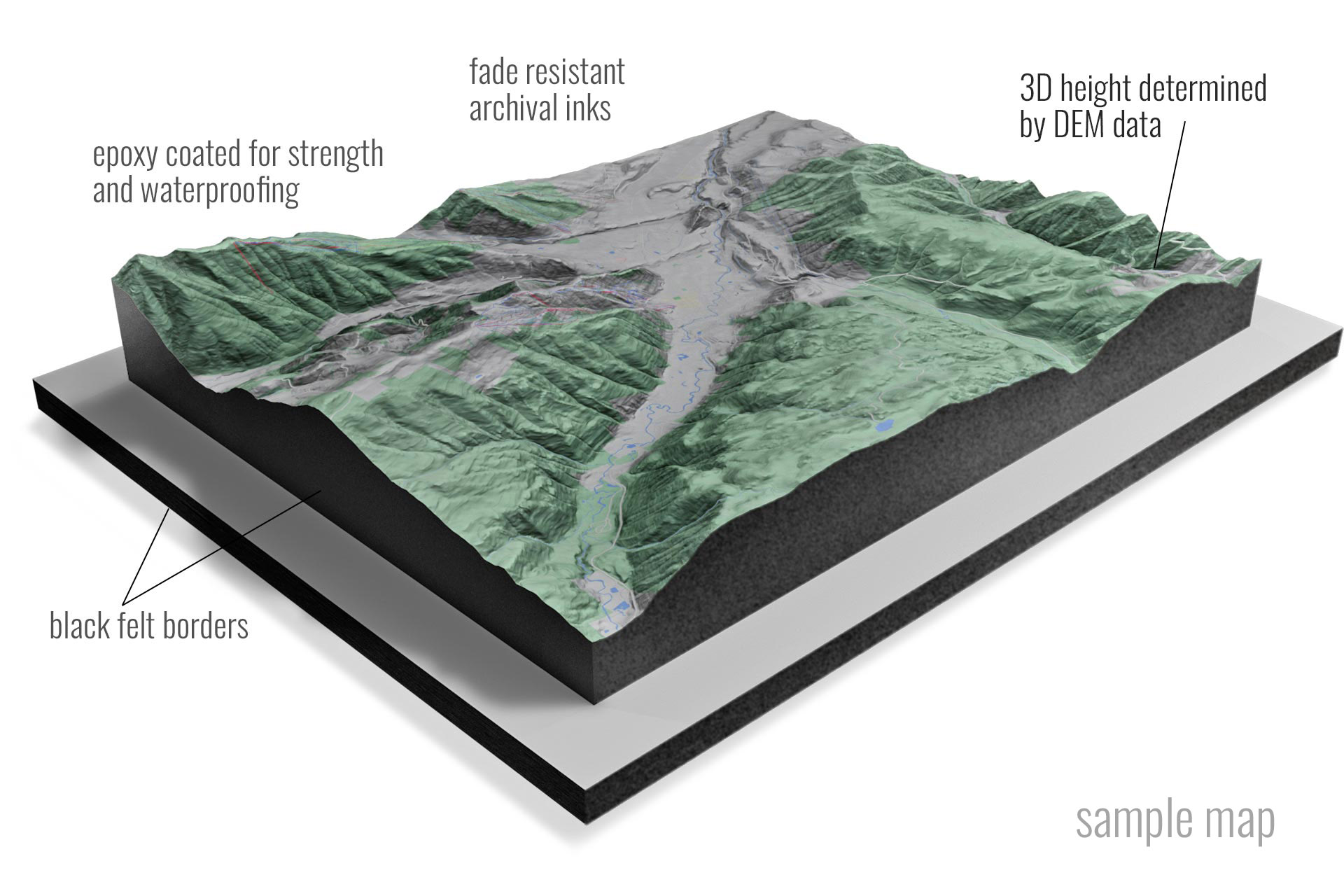
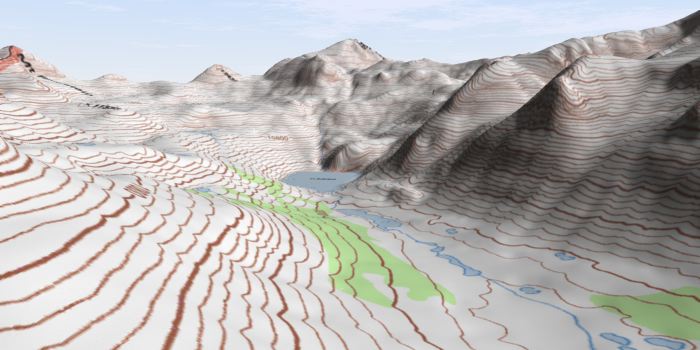
The Earth’s surface is a tapestry of intricate topography, a landscape sculpted by geological forces over millennia. Understanding this topography is crucial for a wide range of disciplines, from urban planning and environmental management to disaster preparedness and military operations. Traditionally, two-dimensional topographic maps provided a static representation of the land, but the advent of 3D technology has ushered in a new era of visualization and analysis, offering unparalleled insights into the Earth’s physical form.
The Evolution of Topographic Mapping: From Flat to Form
For centuries, topographic maps relied on two-dimensional representations, depicting elevation through contour lines, which connect points of equal height. While effective in conveying basic terrain information, these maps lacked the visual depth and immersive experience that 3D technology offers.
The transition to 3D topographic maps marked a significant leap forward. These maps utilize computer-generated models, leveraging data from various sources like aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground-based surveys. This data is processed and transformed into a three-dimensional representation of the terrain, allowing for a more comprehensive and realistic visualization of the landscape.
Exploring the Depths of 3D Topographic Maps: Benefits and Applications
The benefits of 3D topographic maps extend far beyond mere aesthetics. They provide a powerful tool for:
1. Enhanced Visualization and Analysis: 3D models offer a more intuitive and engaging way to understand terrain features. Users can rotate, zoom, and interact with the map, gaining a deeper understanding of the land’s intricacies, including elevation changes, slope gradients, and surface features. This improved visualization facilitates informed decision-making in various fields.
2. Accurate Terrain Modeling: 3D topographic maps provide a highly detailed and accurate representation of the terrain, capturing subtle elevation variations and surface features that might be missed in 2D maps. This accuracy is crucial for applications requiring precise measurements and calculations, such as infrastructure development, environmental impact assessment, and geological studies.
3. Immersive Experience: 3D topographic maps offer an immersive experience that allows users to "walk" through the landscape virtually. This immersive quality enhances the understanding of spatial relationships, facilitating better planning and analysis, particularly in complex terrain environments.
4. Integration with Other Data: 3D topographic maps can be integrated with other data sources, such as weather patterns, population density, and infrastructure networks. This integration allows for a holistic view of the landscape, enabling more informed decision-making in areas like urban planning, disaster management, and resource allocation.
5. Diverse Applications: 3D topographic maps find applications in a multitude of fields, including:
- Urban Planning: Analyzing terrain for optimal development, infrastructure placement, and urban renewal projects.
- Environmental Management: Identifying areas prone to erosion, flooding, and pollution, enabling effective mitigation strategies.
- Disaster Preparedness: Simulating natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and landslides, informing emergency response plans.
- Military Operations: Planning and executing military maneuvers, understanding terrain features for tactical advantage.
- Archaeology: Reconstructing ancient landscapes and understanding historical settlements.
- Education: Providing interactive and engaging learning experiences about geography and topography.
Unveiling the Complexity: Data Acquisition and Processing
The creation of 3D topographic maps involves a complex process of data acquisition and processing:
1. Data Acquisition: Data sources for 3D topographic maps include:
- Aerial Photography: High-resolution aerial images captured from aircraft or drones.
- Satellite Imagery: Images captured from satellites orbiting Earth, providing wide-area coverage.
- Ground-Based Surveys: Direct measurements of elevation and terrain features using surveying equipment.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): A remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D models.
2. Data Processing: The acquired data undergoes rigorous processing steps:
- Image Orientation and Rectification: Aligning and correcting the captured images to ensure accurate spatial representation.
- Point Cloud Generation: Converting images and LiDAR data into a dense point cloud, representing millions of individual points in 3D space.
- Surface Reconstruction: Creating a continuous surface model from the point cloud, representing the terrain in a smooth and accurate manner.
- Texture Mapping: Applying photographic textures to the 3D model, enhancing visual realism and providing context.
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Key Concepts
To fully appreciate the capabilities of 3D topographic maps, it is essential to understand key concepts:
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM): A digital representation of terrain elevation, typically represented as a grid of elevation values.
- Point Cloud: A collection of individual points in 3D space, representing the terrain with high accuracy.
- Mesh: A network of interconnected polygons that form a continuous surface, approximating the terrain.
- Texture: A digital image applied to the 3D model to provide visual detail and context.
- Orthophoto: A georeferenced aerial image that has been corrected for geometric distortions, providing a true representation of the terrain.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the different types of 3D topographic maps?
A: 3D topographic maps can be broadly classified into:
- Terrain Models: Focus on representing the terrain’s elevation and surface features.
- Urban Models: Represent urban environments, including buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Geological Models: Depict geological formations, faults, and other subsurface features.
Q: What are the limitations of 3D topographic maps?
A: While powerful, 3D topographic maps have certain limitations:
- Data Availability: The accuracy and detail of the map depend on the availability and quality of input data.
- Data Processing Time: Processing large datasets can be time-consuming, requiring significant computational resources.
- Visual Complexity: Highly detailed 3D models can be visually overwhelming, potentially obscuring important details.
Q: How can I access and use 3D topographic maps?
A: There are various ways to access and use 3D topographic maps:
- Online Platforms: Numerous websites offer free or subscription-based access to 3D topographic data and visualization tools.
- Software Applications: Specialized software programs allow for the creation, manipulation, and analysis of 3D topographic models.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile applications provide access to 3D topographic maps and visualization tools on smartphones and tablets.
Q: What are the future trends in 3D topographic mapping?
A: The future of 3D topographic mapping is driven by advancements in:
- Data Acquisition Technologies: The development of more sophisticated sensors and drones for capturing high-resolution data.
- Processing Power: Increased computational power enables the processing of massive datasets and the creation of highly detailed 3D models.
- Visualization Techniques: Emerging technologies like virtual reality and augmented reality will enhance the immersive experience of 3D topographic maps.
Tips for Effective Use of 3D Topographic Maps
- Understand the Data Source: Be aware of the data source and its accuracy to ensure reliable analysis.
- Choose the Appropriate Visualization: Select the visualization style that best suits the purpose of the analysis.
- Explore Different Perspectives: Rotate and zoom the 3D model to gain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
- Integrate with Other Data: Combine 3D topographic data with other relevant information for a holistic view.
- Communicate Effectively: Use visualizations and annotations to clearly communicate findings and insights.
Conclusion: Charting the Future of Terrain Visualization
3D topographic maps have revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s surface, offering a powerful tool for visualization, analysis, and decision-making in a wide range of fields. As technology continues to evolve, 3D topographic maps will become even more sophisticated, providing ever-increasing insights into the intricacies of the terrain and shaping our understanding of the world around us. By leveraging the power of 3D technology, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s complex topography and harness its knowledge to build a better future.
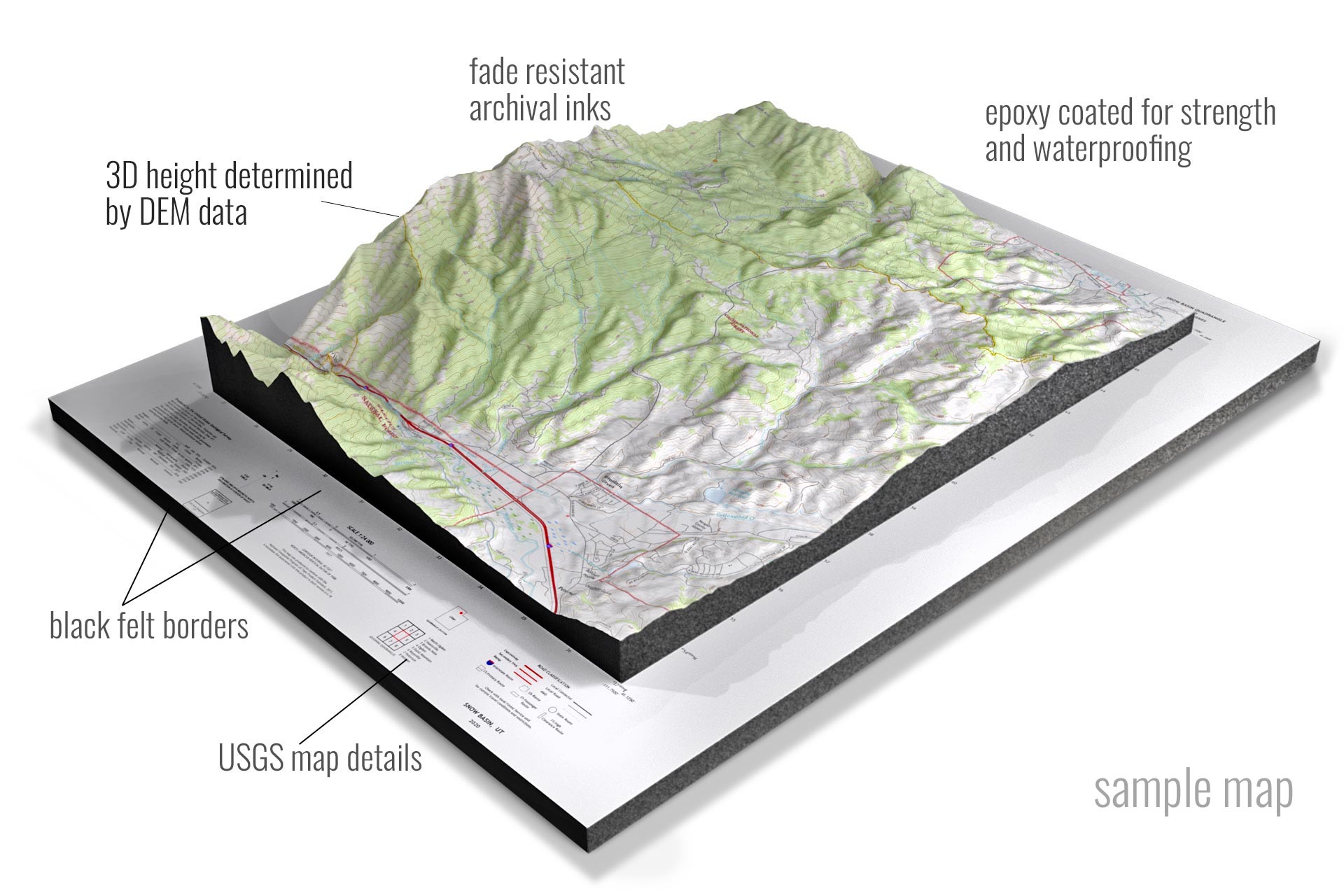




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!