Unveiling The Power Of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Unveiling the Power of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of cartography and spatial analysis, the concept of an inverted map holds significant potential, offering unique perspectives and valuable insights. This article delves into the intricacies of inverted maps, elucidating their purpose, applications, and benefits.
Understanding the Concept of Inverted Maps
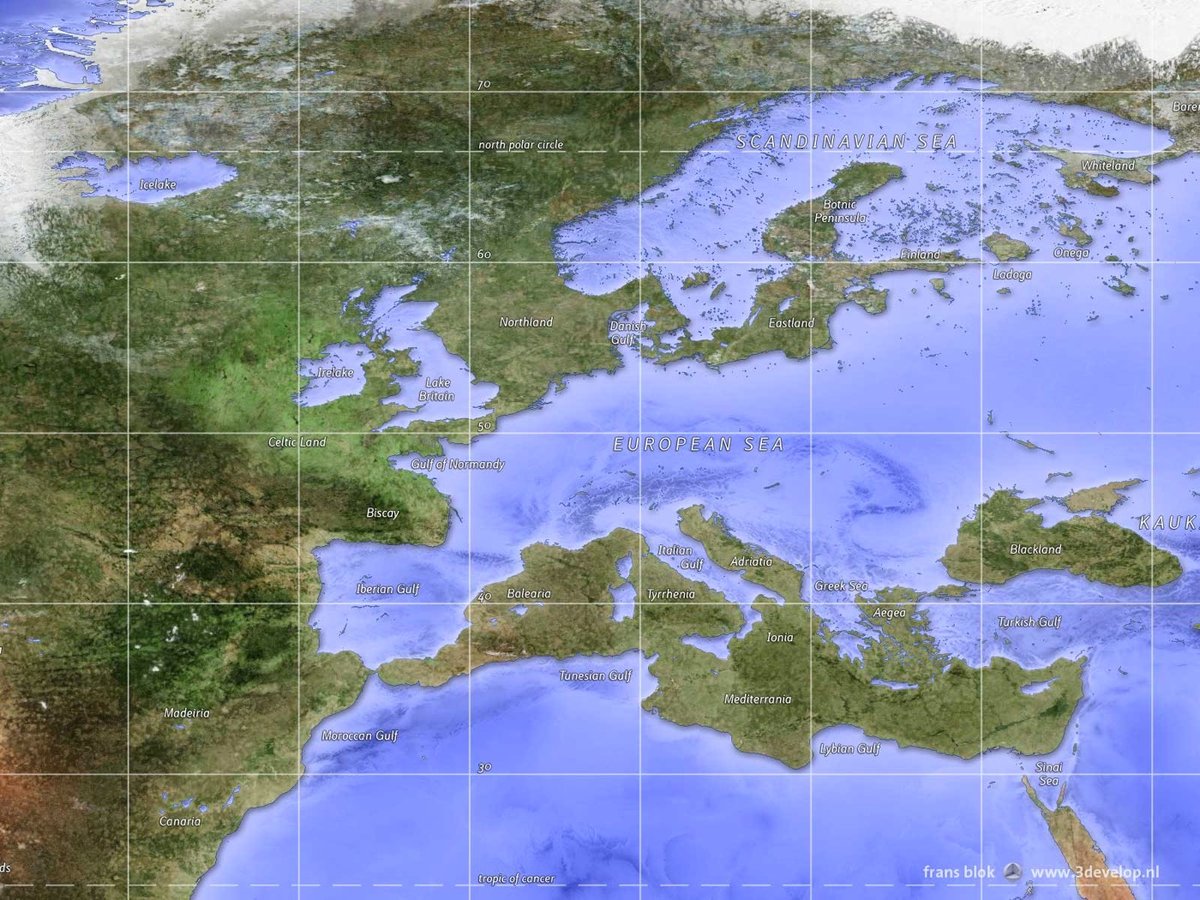
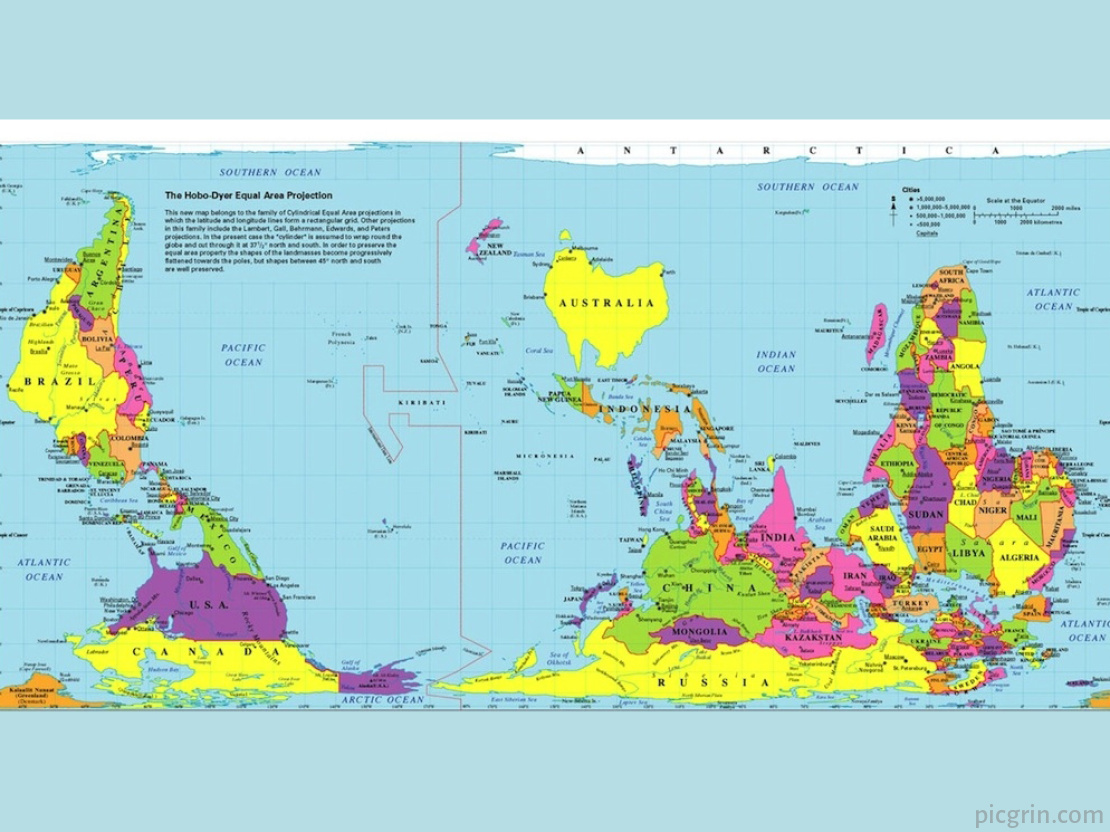
An inverted map, as the name suggests, is a visual representation of geographic data where the traditional orientation is reversed. This reversal can manifest in various forms, including:
- North-South Inversion: The most common type, where the top of the map represents south and the bottom represents north.
- East-West Inversion: The map is flipped horizontally, with east on the left and west on the right.
- Rotation: The map is rotated by a specific angle, altering the orientation of cardinal directions.
- Mirroring: The map is reflected along a vertical or horizontal axis, creating a mirror image of the original.
The Importance of Inverted Maps
While seemingly counterintuitive, inverted maps offer several advantages, particularly in specific contexts:
1. Enhancing Spatial Awareness: Inverting a map can challenge our preconceived notions of spatial relationships, forcing us to re-evaluate our understanding of geographical features and their connections. This can lead to a deeper appreciation of spatial patterns and facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of geographic data.
2. Revealing Hidden Patterns: By presenting familiar landscapes in an unfamiliar way, inverted maps can highlight previously unnoticed patterns and relationships. This can be particularly useful in identifying trends, clustering, and anomalies that might be obscured in conventional map views.
3. Promoting Creative Thinking: The unconventional nature of inverted maps encourages creative thinking and problem-solving. By breaking away from traditional perspectives, individuals can explore new ideas and develop innovative approaches to spatial analysis.
4. Facilitating Data Visualization: Inverted maps can be used to visually represent complex data sets in a more engaging and accessible manner. By altering the orientation, the map can highlight specific features or relationships that might be difficult to discern in a standard view.
5. Supporting Geographic Education: Inverted maps serve as a valuable tool for teaching geography and spatial awareness. They provide a unique perspective that can enhance student engagement and understanding of geographical concepts.
Applications of Inverted Maps
The applications of inverted maps extend beyond the realm of cartography, finding use in diverse fields:
1. Urban Planning: Inverted maps can assist urban planners in identifying spatial patterns and trends, informing decisions regarding infrastructure development, transportation planning, and urban design.
2. Environmental Studies: Environmental scientists utilize inverted maps to analyze spatial data related to pollution, climate change, and natural resource management, facilitating a better understanding of environmental challenges and potential solutions.
3. Marketing and Business: Inverted maps can aid in market research, customer segmentation, and competitor analysis, providing insights into geographical distribution, market trends, and customer preferences.
4. History and Archaeology: Historians and archaeologists can leverage inverted maps to analyze historical events, migrations, and settlements, gaining a deeper understanding of past societies and their interactions with the environment.
5. Art and Design: Inverted maps find artistic expression in graphic design, photography, and contemporary art, serving as a source of inspiration and a means of challenging conventional perspectives.
FAQs about Inverted Maps
1. Why are inverted maps used?
Inverted maps serve a variety of purposes, including enhancing spatial awareness, revealing hidden patterns, promoting creative thinking, facilitating data visualization, and supporting geographic education.
2. What are the different types of inverted maps?
Inverted maps can be classified based on the type of reversal applied, including north-south inversion, east-west inversion, rotation, and mirroring.
3. Are inverted maps accurate?
Inverted maps are accurate in terms of representing the geographic data, but their orientation differs from conventional maps. The accuracy of the data itself remains unchanged.
4. How are inverted maps created?
Inverted maps can be created using various software tools, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software and specialized mapping applications.
5. What are the limitations of inverted maps?
While valuable, inverted maps have limitations. They may be unfamiliar and require some adaptation for users accustomed to standard map orientations. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all applications and data sets.
Tips for Using Inverted Maps Effectively
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific purpose for using an inverted map and tailor the inversion method accordingly.
- Choose the appropriate inversion type: Consider the nature of the data and the desired outcome when selecting the type of inversion.
- Experiment with different orientations: Explore various inversions to identify the most insightful and effective perspective.
- Use color and symbols effectively: Enhance visualization and clarity by employing appropriate colors, symbols, and legends.
- Provide context and guidance: Offer explanations and annotations to help users interpret the inverted map and understand the spatial relationships.
Conclusion
Inverted maps offer a powerful tool for exploring geographic data and challenging conventional perspectives. By inverting the orientation, they unveil hidden patterns, facilitate creative thinking, and enhance spatial awareness. While not a replacement for traditional maps, inverted maps provide a unique lens for analyzing spatial data and gaining valuable insights. Their applications extend across diverse fields, contributing to a deeper understanding of our world and fostering innovation in spatial analysis.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Inverted Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!