Unveiling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Topographic Map Of Panama
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of Panama
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of Panama
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of Panama. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of Panama
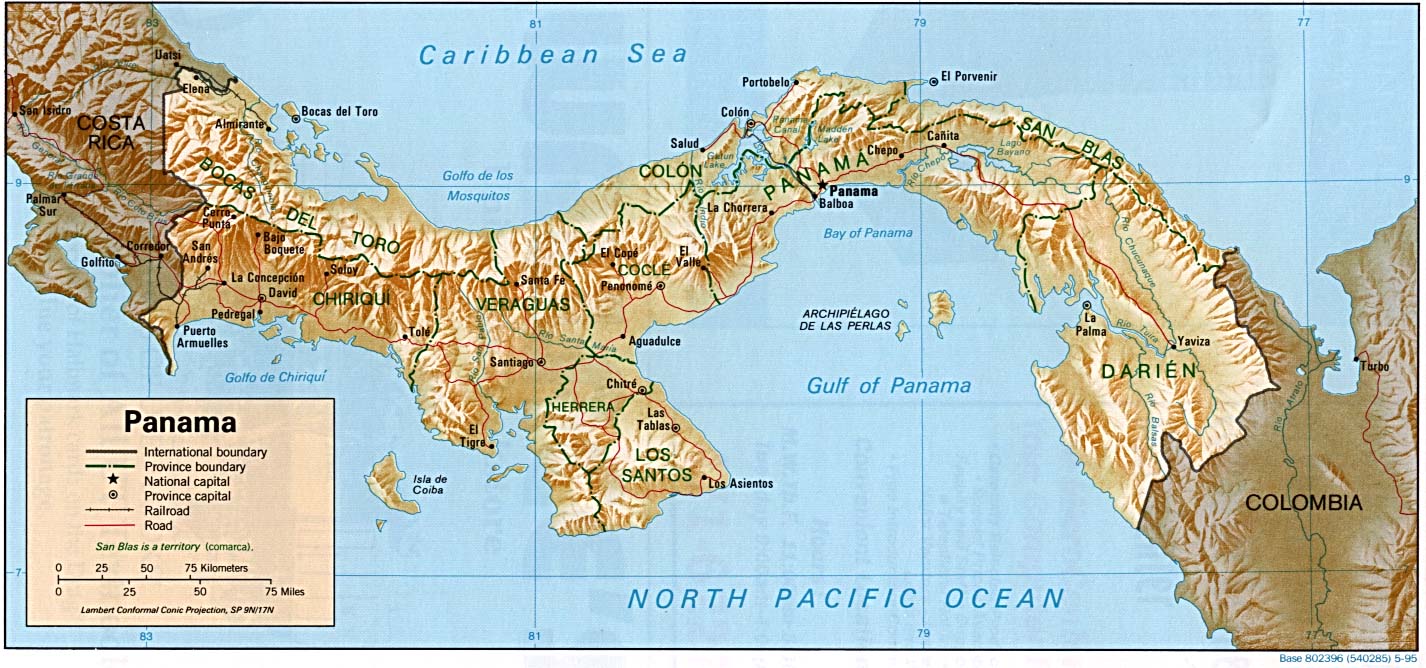
The Republic of Panama, a slender nation bridging North and South America, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from the lush rainforests of Darién to the towering peaks of the Cordillera Central. This intricate geographical mosaic is meticulously captured in its topographic map, a vital tool for understanding and navigating the country’s physical features.
Understanding the Terrain: Deciphering the Topographic Map
A topographic map is a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, showcasing not only the shape of the land but also its elevation. Panama’s topographic map, like any other, utilizes contour lines to depict these elevations. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the land’s ups and downs.
The Importance of Elevation: Unveiling the Landscape’s Secrets
Elevation plays a crucial role in shaping the Panamanian landscape. The country’s topography is characterized by a distinct north-south divide. The north is dominated by the lowlands of the Caribbean coast, while the south features the higher elevations of the Cordillera Central, a mountain range extending through the country’s heart. This elevation gradient influences various aspects of Panama’s natural environment:
- Rainfall: The higher elevations of the Cordillera Central receive significantly more rainfall than the lowlands, creating a distinct difference in vegetation and ecosystems.
- Climate: The higher altitudes experience cooler temperatures compared to the lowlands, resulting in different climatic zones.
- Biodiversity: The variation in elevation fosters a remarkable diversity of habitats, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
- Water Resources: The mountains are the source of numerous rivers and streams, providing vital water resources for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
Navigating the Terrain: Practical Applications of the Topographic Map
The topographic map of Panama serves as an indispensable tool for various purposes, including:
- Planning and Development: Understanding the terrain helps in planning infrastructure projects, urban development, and resource management.
- Conservation Efforts: The map assists in identifying and protecting critical ecosystems, biodiversity hotspots, and fragile areas.
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and adventurers rely on topographic maps for navigation, identifying trails, and assessing the difficulty of routes.
- Disaster Management: The map aids in understanding flood risks, landslide hazards, and other natural disasters, facilitating effective preparedness and response.
Beyond Elevation: Exploring Additional Information on the Topographic Map
While elevation is the primary focus, Panama’s topographic map provides additional information crucial for understanding the country’s geography:
- Hydrography: The map showcases the network of rivers, lakes, and streams, providing insights into water flow and distribution.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and mangroves, are represented on the map, revealing the country’s diverse ecosystems.
- Land Use: The map indicates areas dedicated to agriculture, urban development, and other human activities, providing a glimpse into land use patterns.
- Transportation: Roads, railways, and waterways are depicted on the map, highlighting the country’s transportation infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Topographic Map of Panama
1. What is the highest point in Panama?
The highest point in Panama is Cerro Tacarcuna, located in the Cordillera Central, with an elevation of 3,475 meters (11,401 feet).
2. How can I access a topographic map of Panama?
Topographic maps of Panama are available from various sources, including:
- Government agencies: The National Geographic Institute (IGN) of Panama provides detailed topographic maps.
- Online mapping services: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer topographic layers for Panama.
- Specialty map vendors: Companies specializing in outdoor recreation and mapping offer topographic maps.
3. Are there different scales for topographic maps of Panama?
Yes, topographic maps of Panama are available in various scales, each providing different levels of detail:
- Large-scale maps: These maps provide detailed information about small areas, useful for hiking and local planning.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover larger areas with less detail, suitable for regional planning and overview.
4. What are the benefits of using a topographic map for hiking in Panama?
Topographic maps are essential for hiking in Panama, providing crucial information about:
- Elevation changes: Identifying steep slopes, ridges, and valleys for safe navigation.
- Trail locations: Locating trails and assessing their difficulty levels.
- Water sources: Identifying potential water sources along the trail.
- Potential hazards: Recognizing potential hazards like cliffs, ravines, and landslides.
5. How can I learn to read a topographic map?
Learning to read a topographic map requires understanding contour lines and their relationship to elevation. Various resources are available, including:
- Online tutorials: Websites offer step-by-step guides and interactive lessons.
- Books and guides: Numerous publications provide comprehensive explanations of topographic maps.
- Workshops and courses: Outdoor recreation organizations often offer workshops and courses on map reading.
Tips for Using the Topographic Map of Panama
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a map scale suitable for your intended purpose, whether it’s hiking a specific trail or planning a larger project.
- Familiarize yourself with map symbols: Understand the symbols used to represent various features, such as elevation, water bodies, and vegetation.
- Use a compass and GPS: Pair the topographic map with a compass and GPS for accurate navigation, especially in remote areas.
- Consider the date of the map: Ensure the map is up-to-date, as changes in the landscape can occur over time.
- Practice map reading: Regularly practice reading topographic maps to enhance your skills and improve your navigation abilities.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Panama is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the country’s diverse landscape. By deciphering its contour lines, symbols, and additional information, we gain valuable insights into the physical features, ecosystems, and human activities shaping the nation. Whether for planning development projects, protecting natural resources, or embarking on outdoor adventures, the topographic map serves as a vital guide, revealing the secrets of Panama’s intricate geography.
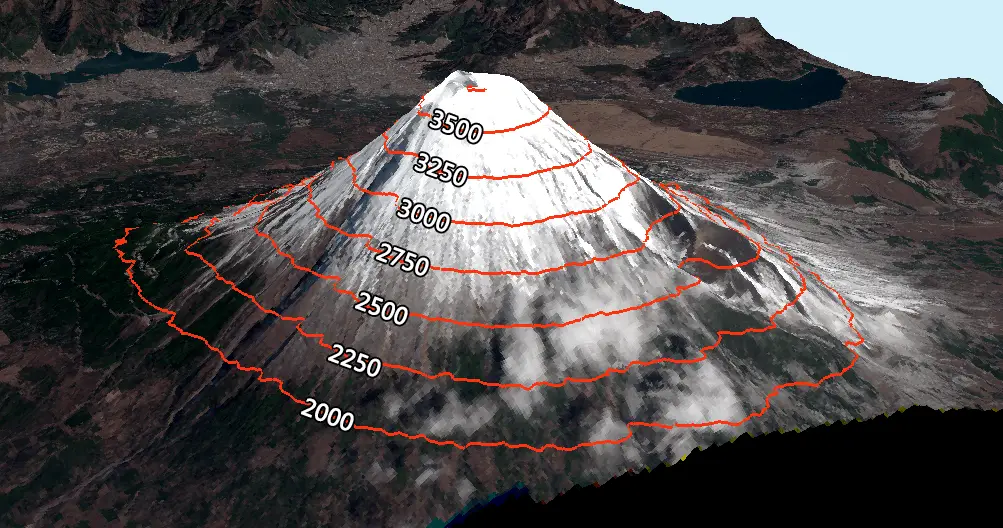
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)


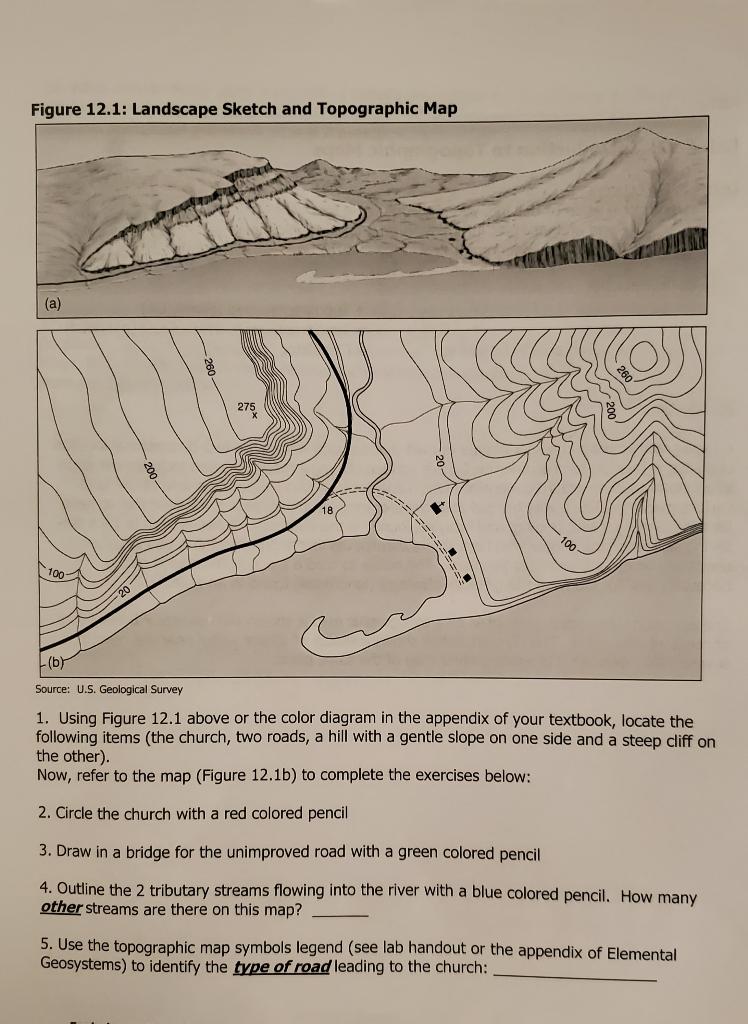
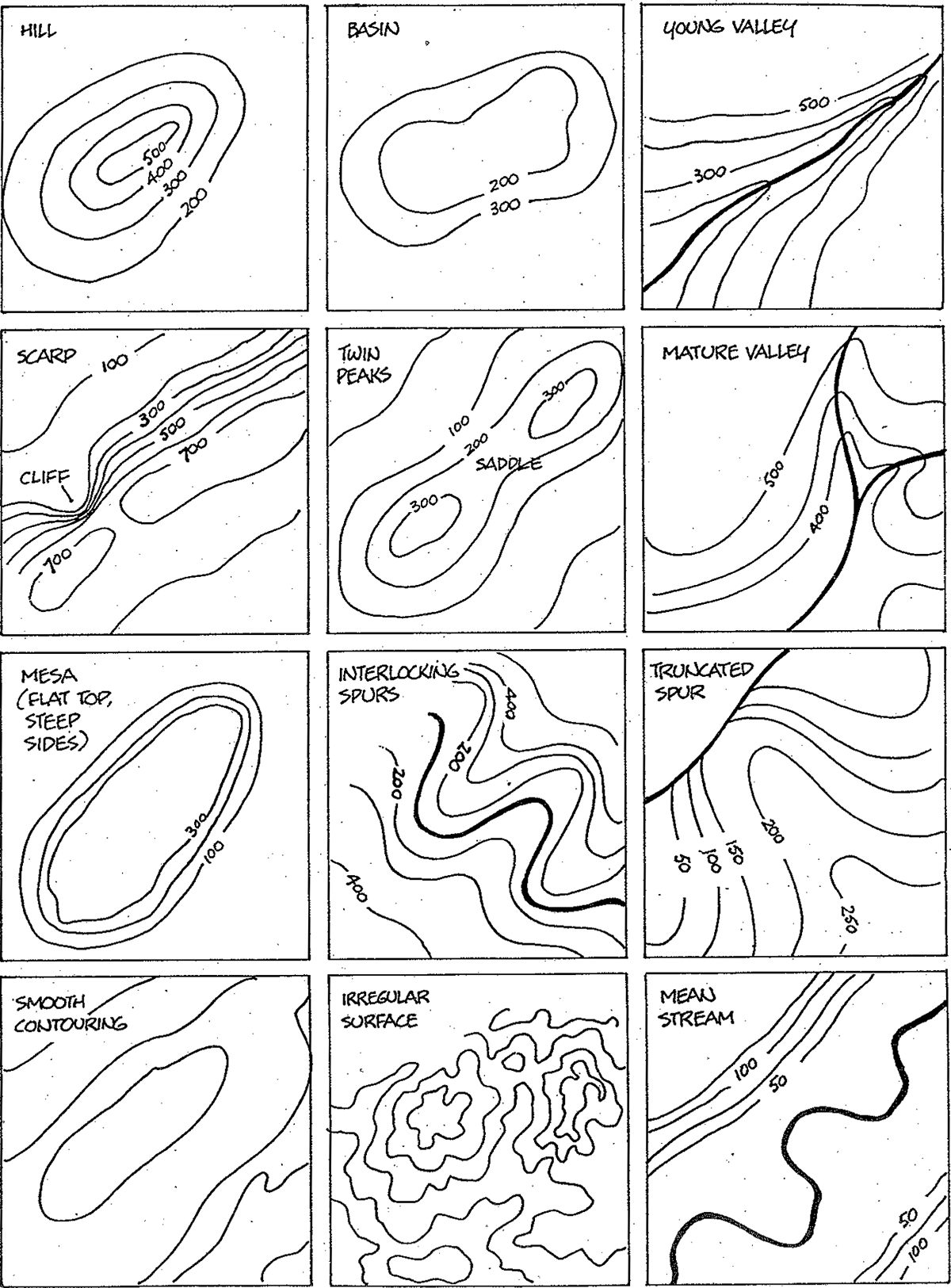

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of Panama. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!