Unveiling The Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide To The Seismology World Map
Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide to the Seismology World Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide to the Seismology World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide to the Seismology World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide to the Seismology World Map

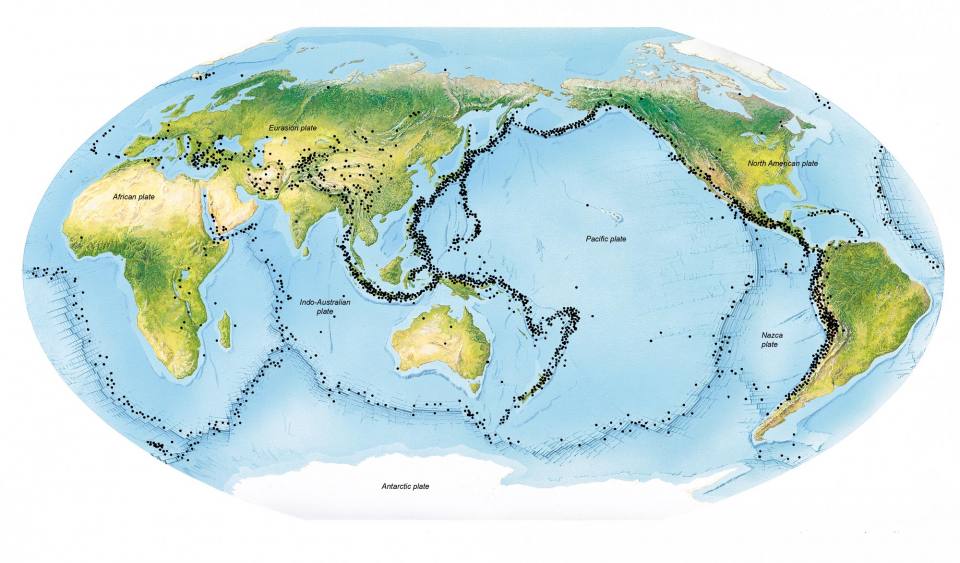
The Earth, despite its seemingly solid exterior, is a dynamic and restless planet. Beneath the surface, tectonic plates constantly shift and collide, generating powerful forces that manifest as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain ranges. Understanding these forces and their distribution is crucial for mitigating their impact on human lives and infrastructure. This is where the seismology world map emerges as a vital tool, offering a visual representation of seismic activity and its global implications.
Understanding the Seismic Landscape:
The seismology world map is not merely a static depiction of earthquake locations. It serves as a dynamic platform for visualizing and analyzing seismic data, providing valuable insights into:
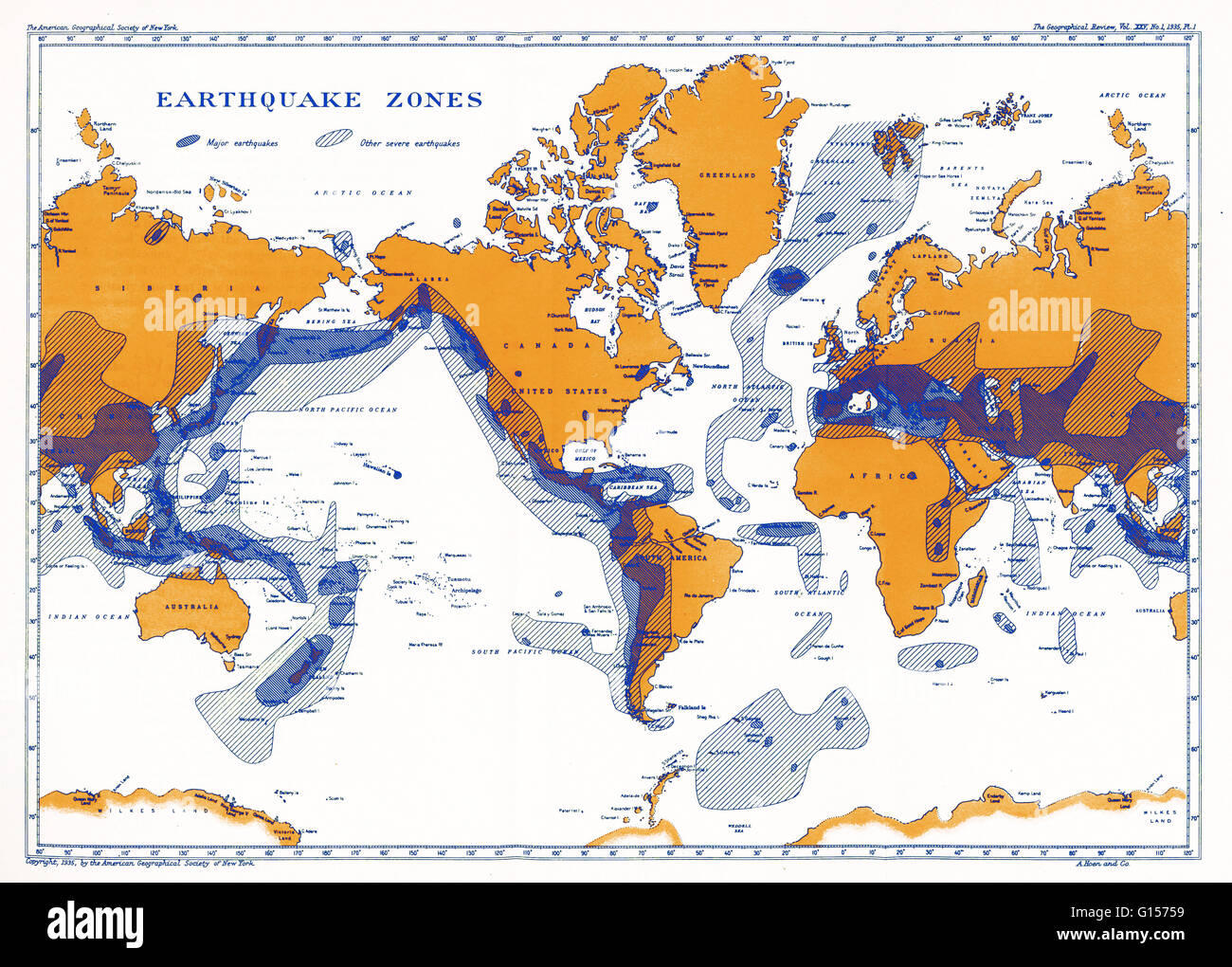
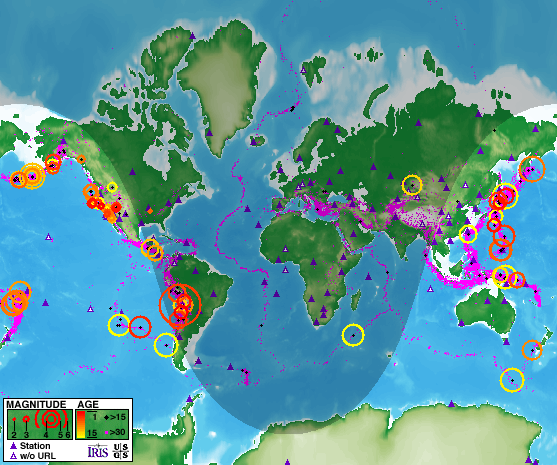
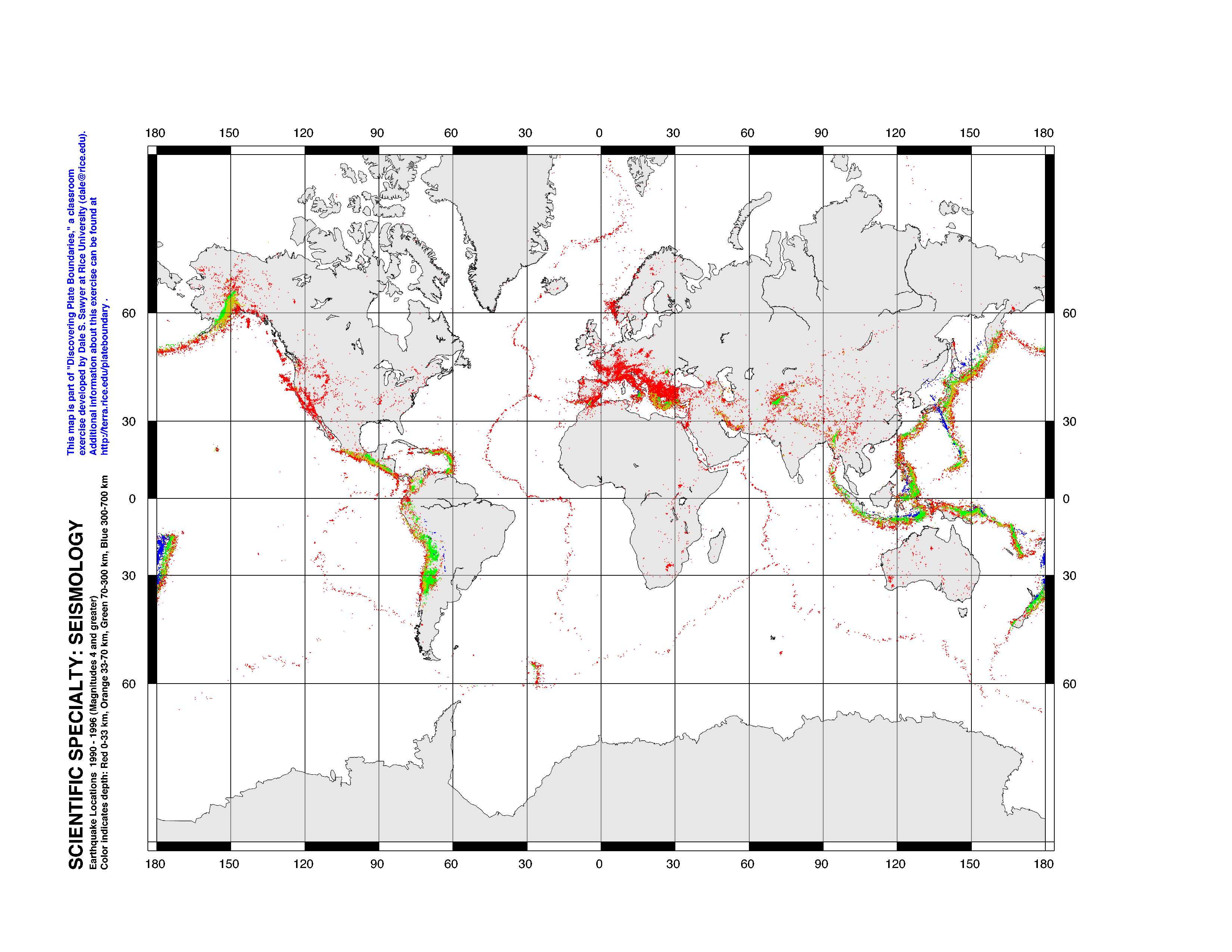
- Earthquake Distribution: The map clearly illustrates the geographical distribution of earthquakes, highlighting regions prone to seismic activity. This information is crucial for understanding the underlying geological processes and predicting future earthquake occurrences.
- Magnitude and Frequency: The map utilizes color-coding or size variations to represent the magnitude and frequency of earthquakes. This enables scientists to identify areas with higher seismic risk and understand the potential for devastating events.
- Tectonic Plate Boundaries: The map showcases the major tectonic plate boundaries, revealing the zones of intense geological activity and providing a visual framework for understanding the driving forces behind earthquakes.
- Volcanic Activity: In addition to earthquake data, the map often includes information on volcanic activity, further emphasizing the interconnected nature of these geological phenomena.
Benefits and Applications of the Seismology World Map:
The seismology world map plays a critical role in various fields, contributing to:
- Earthquake Prediction and Early Warning Systems: By analyzing historical seismic data and identifying patterns, scientists can develop models to predict future earthquake occurrences and trigger early warning systems, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
- Infrastructure Design and Construction: The map helps engineers design earthquake-resistant buildings and infrastructure, ensuring their stability and safety in seismically active regions.
- Disaster Management and Response: By providing real-time data on earthquake events, the map facilitates efficient disaster management and response efforts, aiding in coordinating rescue operations, providing aid, and minimizing the impact of disasters.
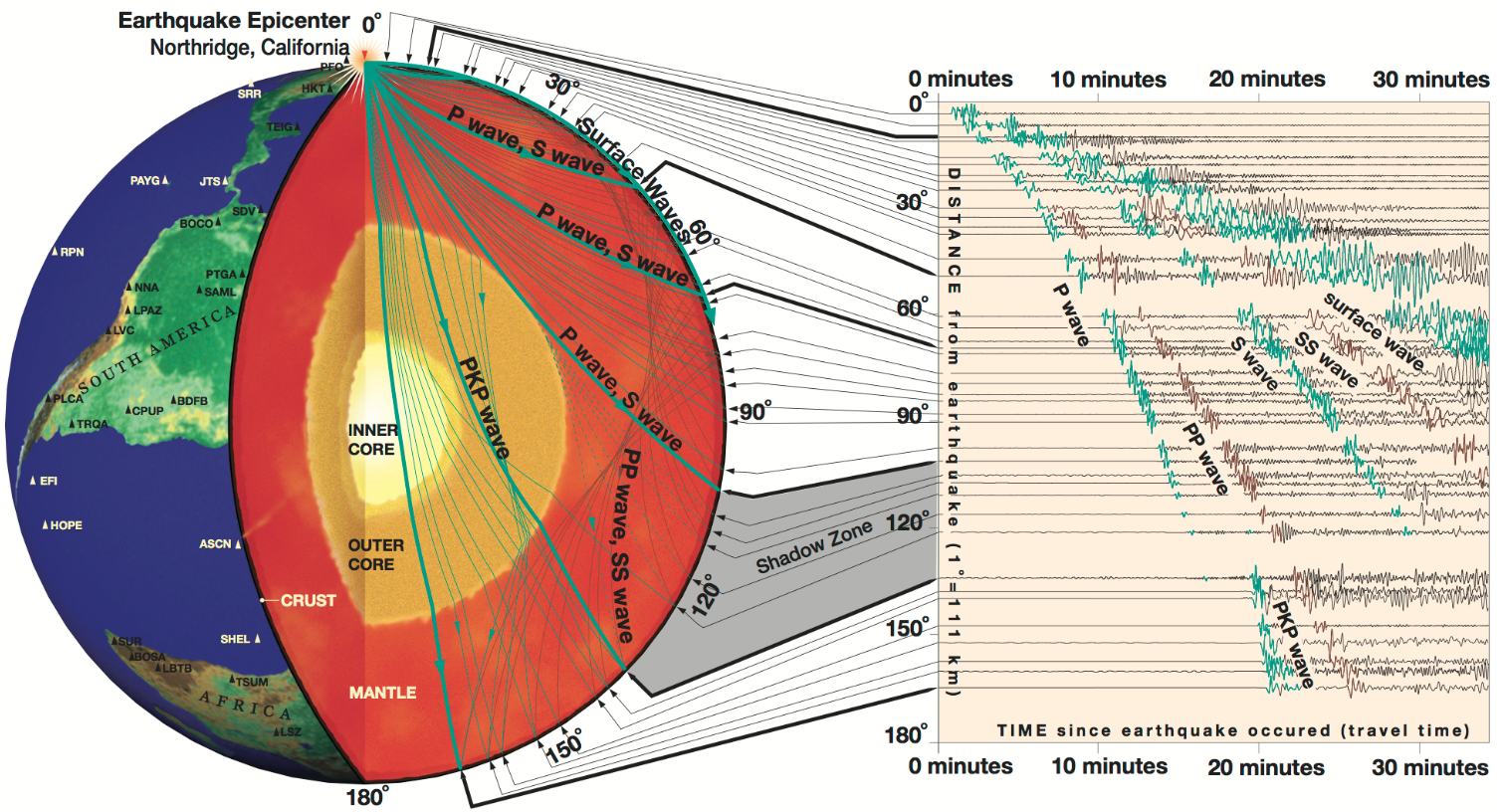
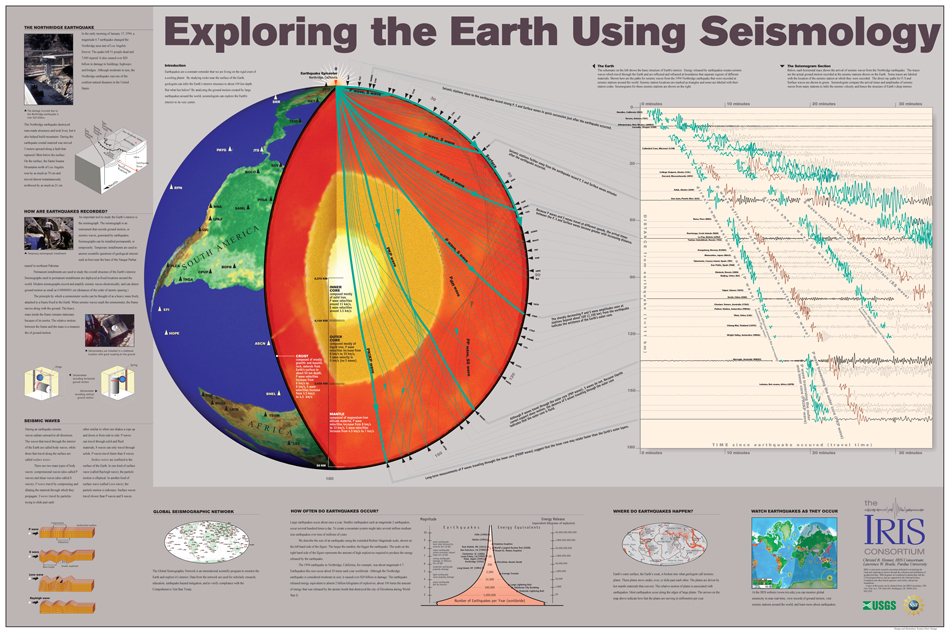
- Scientific Research and Understanding: The map serves as a valuable tool for researchers studying the Earth’s interior, tectonic plate movements, and the processes that drive seismic activity. It allows them to analyze data, identify trends, and develop new theories.
Navigating the Seismology World Map: A Guide for Users:
Navigating the seismology world map requires an understanding of its key elements:
- Legend and Data Representation: The map typically includes a legend that explains the color-coding or size variations used to represent earthquake magnitude, depth, and other relevant parameters.
- Time Scale and Data Filtering: Users can often adjust the time scale to view historical or real-time seismic data. Filtering options allow for focusing on specific regions, magnitudes, or types of events.
- Interactive Features: Many seismology world maps offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas, view detailed information about individual events, and access additional data.
FAQs: Demystifying the Seismology World Map:
1. What are the different types of seismology world maps?
Seismology world maps can be categorized based on their purpose, data sources, and level of detail. Some common types include:
- Global Earthquake Maps: These maps depict the distribution of earthquakes across the entire globe, often focusing on magnitude and frequency.
- Regional Earthquake Maps: These maps focus on specific regions, providing detailed information on seismic activity within those areas.
- Real-Time Earthquake Maps: These maps display live earthquake data, updating in real-time as new events occur.
- Historical Earthquake Maps: These maps showcase the historical occurrence of earthquakes, providing insights into long-term seismic trends.
2. How are earthquakes depicted on the map?
Earthquakes are typically represented by markers or symbols, with their size, color, or shape indicating their magnitude, depth, and other relevant parameters.
3. What are the limitations of seismology world maps?
While incredibly valuable, seismology world maps have limitations:
- Data Availability: Not all regions have comprehensive seismic monitoring networks, leading to gaps in data coverage.
- Prediction Accuracy: Predicting earthquakes with absolute accuracy remains a challenge, and the map can only provide insights based on historical data and patterns.
- Interpretation and Context: Interpreting the map requires understanding the underlying geological processes and the context of seismic activity.
Tips for Utilizing the Seismology World Map:
- Explore Different Maps: Compare data from various sources and map types to gain a comprehensive understanding of seismic activity.
- Consider the Time Scale: Analyze data over different time scales to identify long-term trends and patterns.
- Use Interactive Features: Utilize zoom, filtering, and other interactive features to focus on specific areas of interest.
- Consult Experts: When interpreting the map, consult with experts in seismology and earthquake engineering for accurate analysis and informed decisions.
Conclusion:
The seismology world map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature, revealing the distribution and intensity of seismic activity. It plays a crucial role in earthquake prediction, infrastructure design, disaster management, and scientific research. By leveraging this valuable resource, we can better prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with seismic events, promoting safety and resilience in our communities. As technology continues to advance, seismology world maps will undoubtedly evolve, offering even more comprehensive and insightful data to guide our understanding of the Earth’s restless pulse.
/worldseismap-56a368c65f9b58b7d0d1d07a.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Guide to the Seismology World Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!