Unveiling The Diverse Landscape Of Ethiopia: A Journey Through Its Physical Geography
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Ethiopia: A Journey Through its Physical Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Ethiopia: A Journey Through its Physical Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Ethiopia: A Journey Through its Physical Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Ethiopia: A Journey Through its Physical Geography
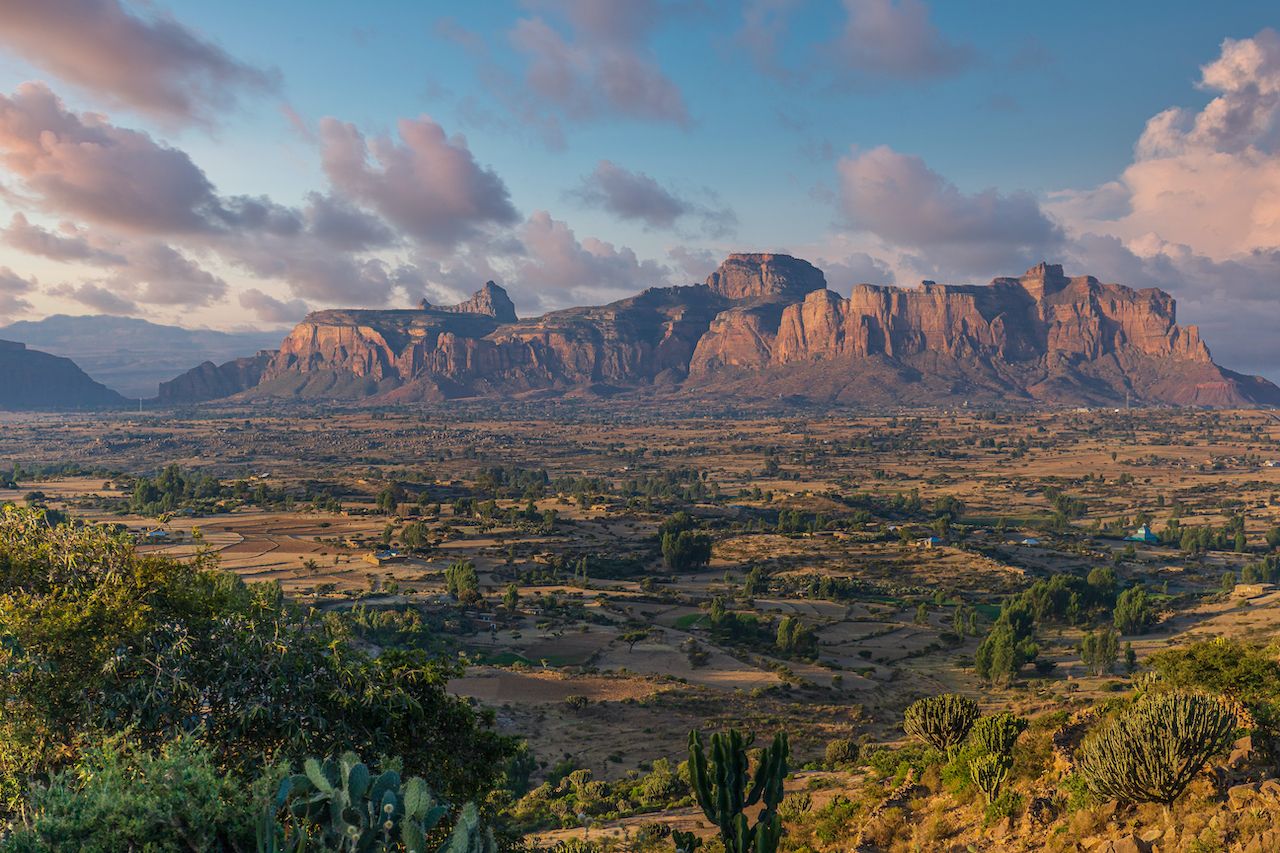

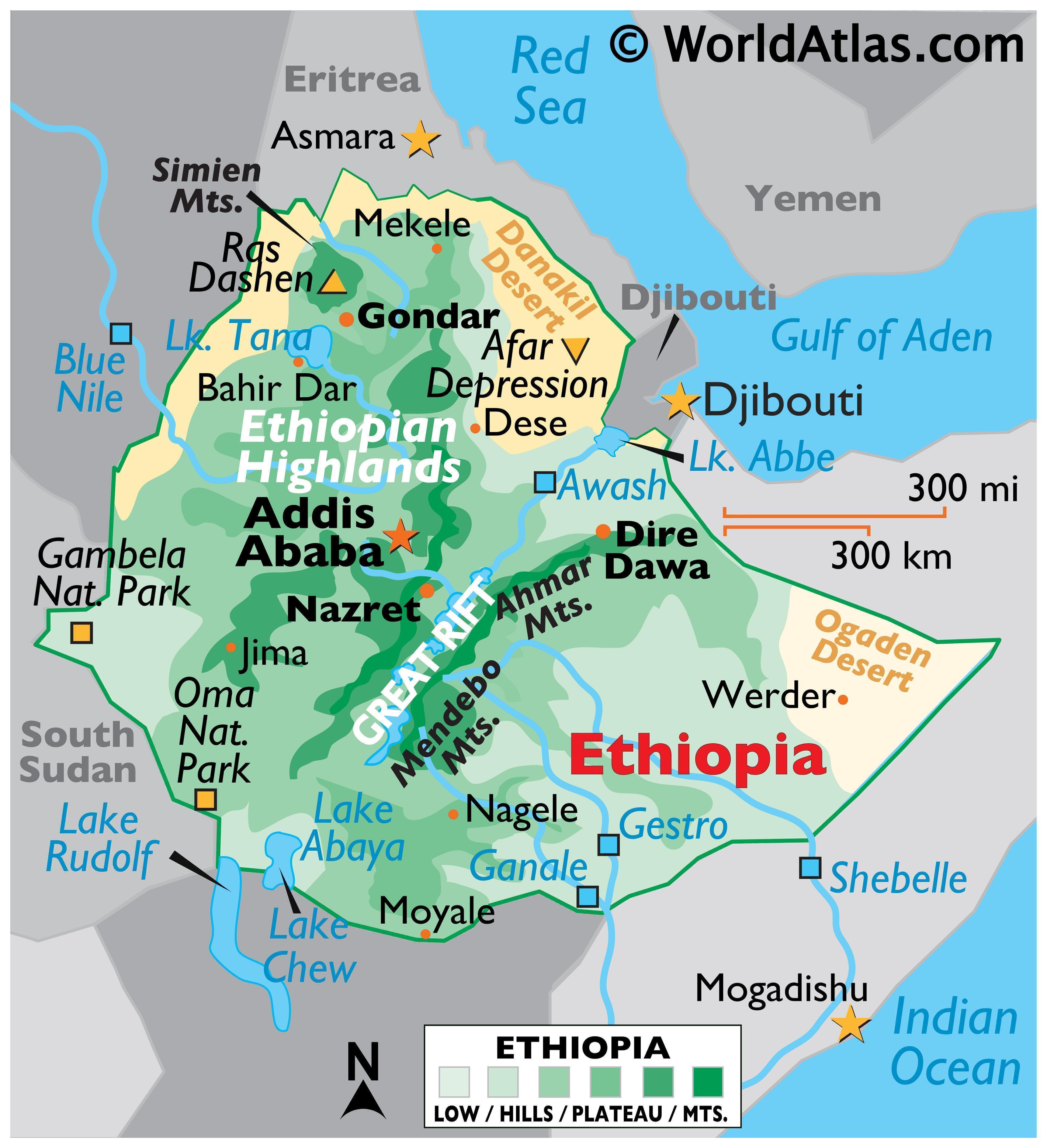
Ethiopia, a nation nestled in the Horn of Africa, boasts a captivating tapestry of physical features, each contributing to its unique character and rich biodiversity. This article delves into the intricate details of Ethiopia’s physical map, unraveling its diverse landscapes, geological formations, and the profound influence these exert on its people and environment.
A Land of Contrasts: From Mountains to Deserts
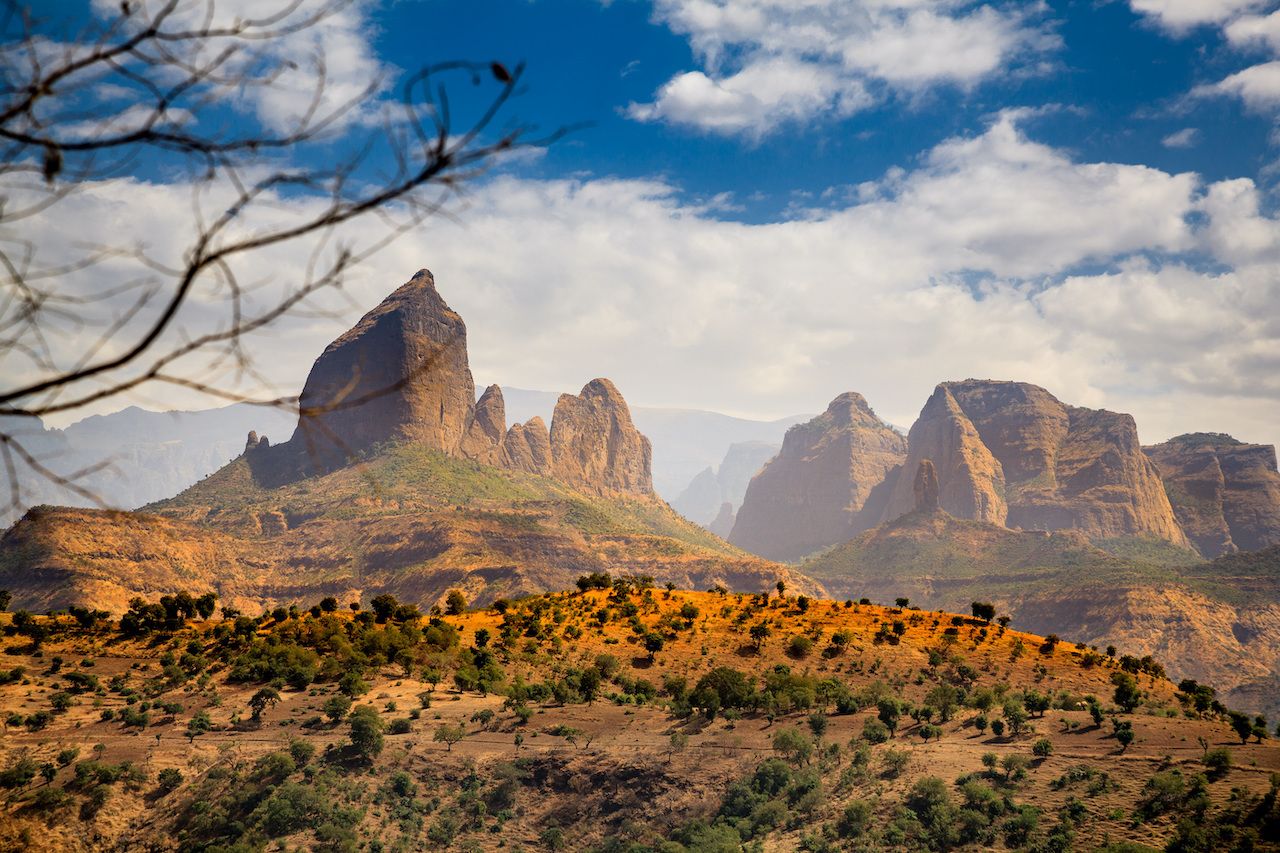
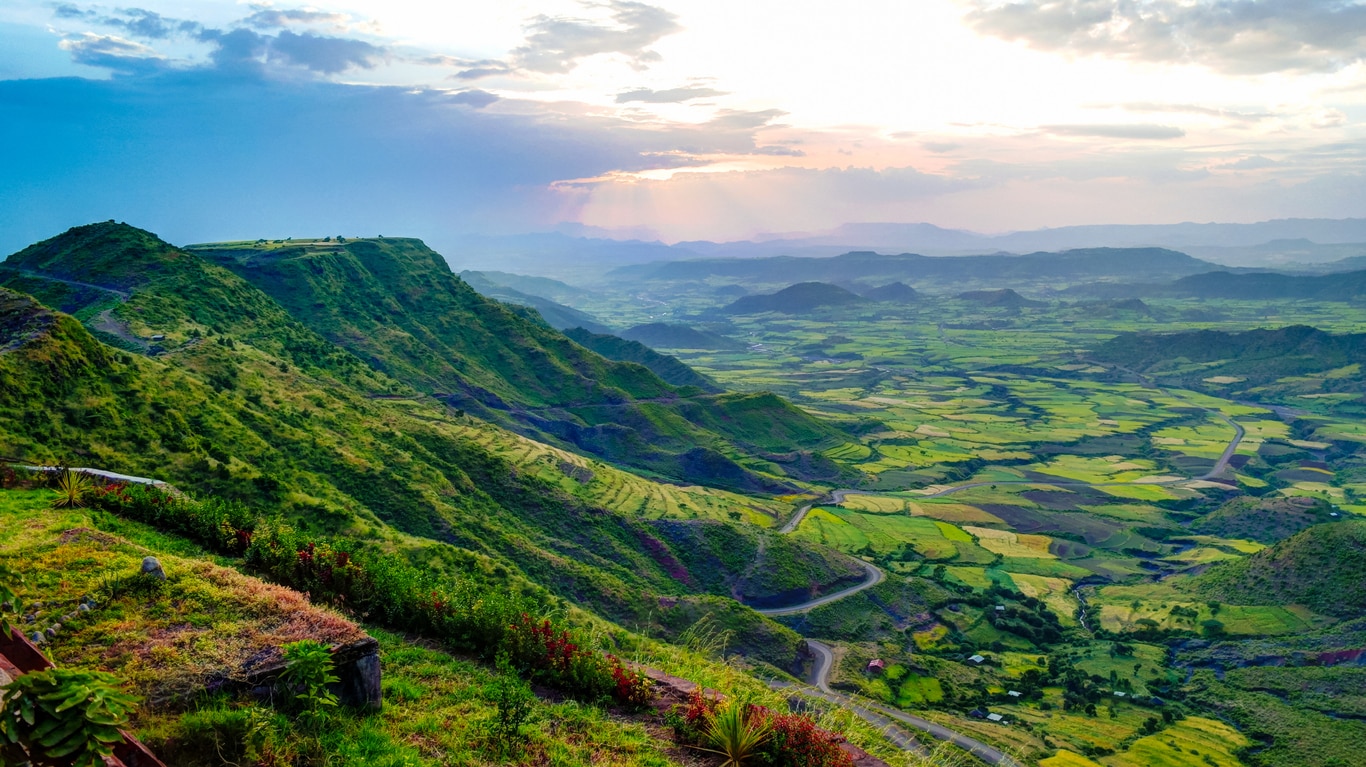
Ethiopia’s physical geography is characterized by its dramatic contrasts, showcasing a spectrum of elevations and climates. The most prominent feature is the Ethiopian Highlands, a vast plateau that dominates the country’s central and northern regions. This plateau, with its average elevation exceeding 2,000 meters, is punctuated by towering mountains, volcanic peaks, and deep valleys. The Simien Mountains National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a testament to the majestic beauty of this region, featuring towering peaks like Ras Dashen, the highest point in Ethiopia.
In stark contrast, the eastern lowlands, bordering Somalia and Djibouti, descend to the arid and hot Danakil Depression, the lowest point in Africa. This region, characterized by its volcanic activity and salt flats, is a harsh and unforgiving environment.
The Lifeblood of Ethiopia: Rivers and Lakes
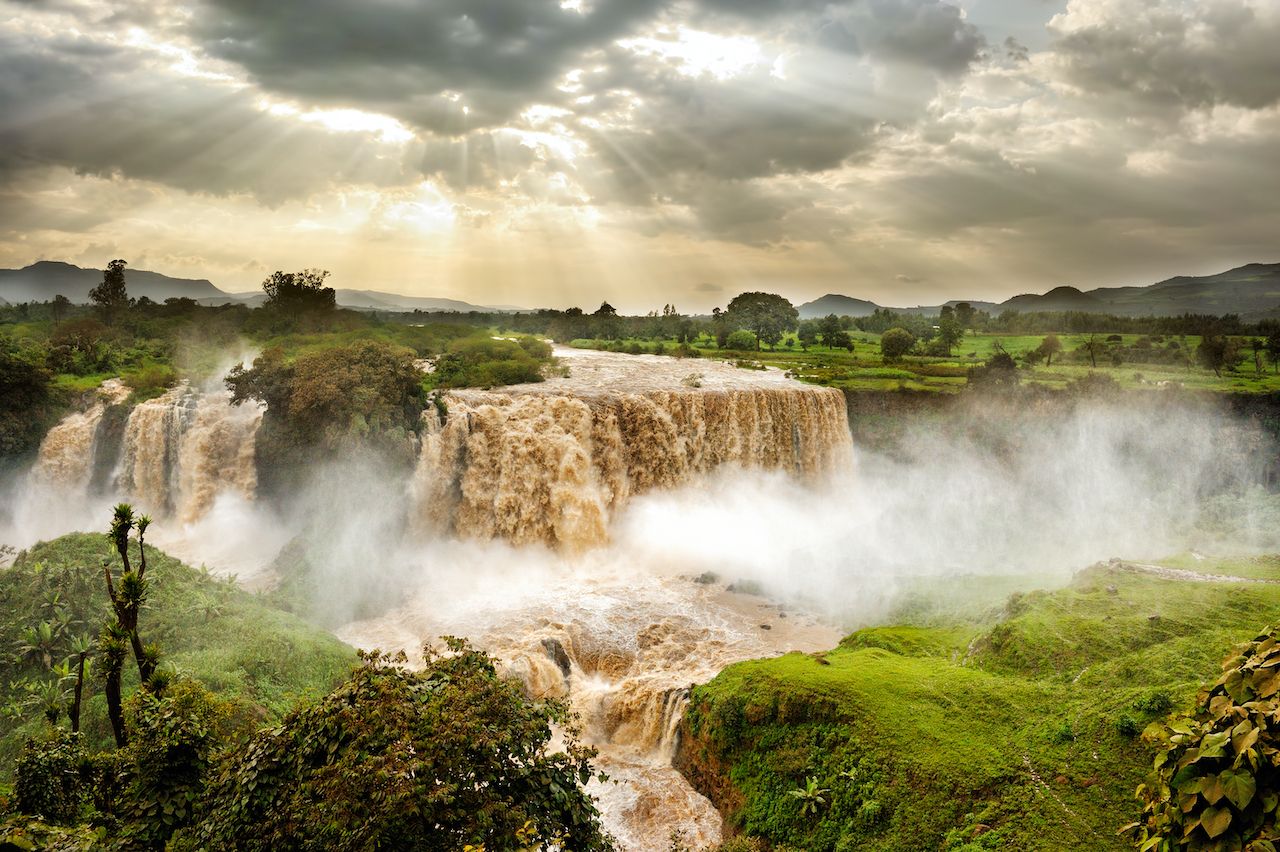
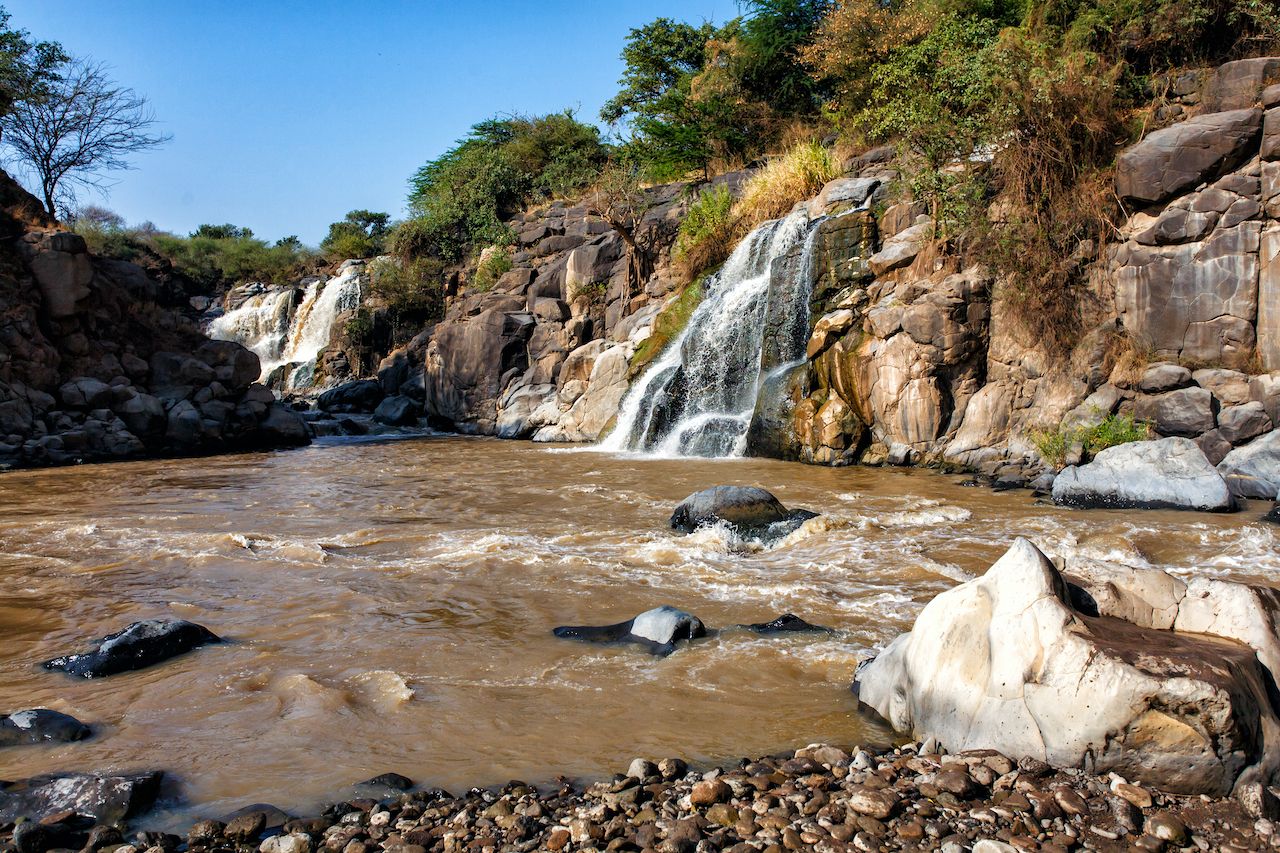
Ethiopia’s rivers and lakes play a vital role in shaping its landscape and sustaining its people. The Blue Nile, the most significant tributary of the Nile River, originates in the Ethiopian Highlands, contributing substantially to the Nile’s water flow. Other major rivers like the Awash, Omo, and Tekeze carve their way through the landscape, providing irrigation, hydropower, and vital transportation routes.
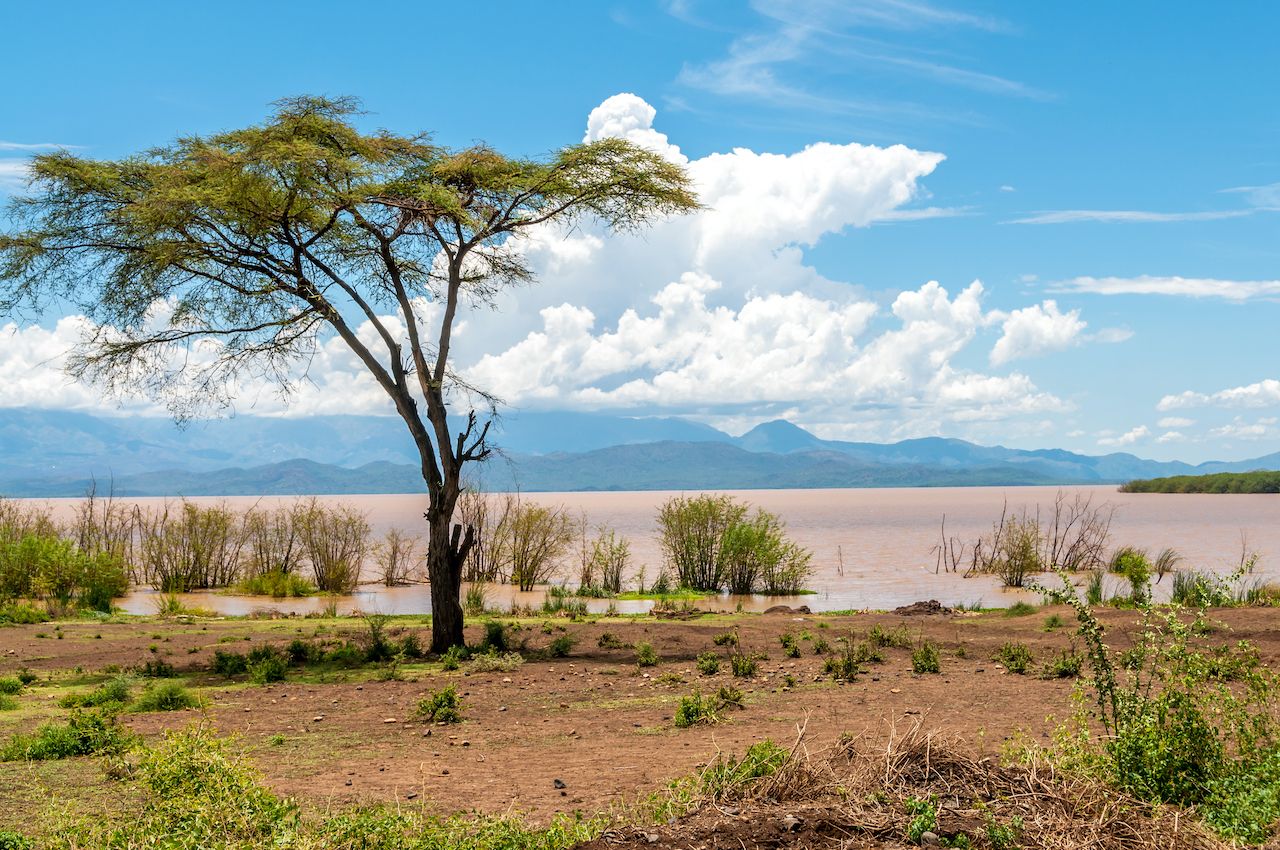
Ethiopia is also home to numerous lakes, including Lake Tana, the largest lake in the country and the source of the Blue Nile. Lake Turkana, situated on the border with Kenya, is the largest permanent desert lake in the world. These lakes are not only crucial for biodiversity and water resources but also contribute to the cultural and economic life of the communities surrounding them.
Volcanoes and Rift Valleys: Shaping the Landscape
Ethiopia’s landscape has been significantly shaped by volcanic activity and the East African Rift Valley. The Danakil Depression, with its active volcanoes like Erta Ale, showcases the ongoing geological processes shaping the region. The East African Rift Valley, a massive geological feature stretching across East Africa, runs through Ethiopia, creating a series of valleys, lakes, and volcanic formations. This rift system has profoundly influenced Ethiopia’s topography, creating diverse ecosystems and contributing to the country’s unique geological heritage.
The Influence of Physical Geography on Life in Ethiopia
Ethiopia’s physical geography has a profound impact on its people and their way of life. The highlands provide fertile soil for agriculture, supporting a diverse population of farmers and pastoralists. The lowlands, despite their harsh conditions, are home to communities that have adapted to the arid environment, practicing traditional forms of agriculture and livestock herding.
The country’s diverse physical features have also contributed to the development of distinct cultures and traditions. The highlands, with their dense population and fertile soil, have fostered a rich agricultural heritage, while the lowlands, with their nomadic communities, have developed unique traditions related to livestock herding and desert survival.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Ethiopia’s Physical Geography
While Ethiopia’s physical geography offers a diverse and beautiful landscape, it also presents challenges. The mountainous terrain can be challenging for transportation and communication, while the arid lowlands face the threat of desertification and water scarcity. However, Ethiopia’s physical features also present opportunities. The country’s abundant water resources can be harnessed for hydropower generation, contributing to its energy needs and economic development. The diverse landscapes also offer potential for tourism, attracting visitors seeking adventure and cultural experiences.
FAQs about the Physical Map of Ethiopia:
1. What is the highest point in Ethiopia?
The highest point in Ethiopia is Ras Dashen, located in the Simien Mountains, with an elevation of 4,533 meters.
2. What is the lowest point in Ethiopia?
The lowest point in Ethiopia is the Danakil Depression, which lies at an elevation of approximately 116 meters below sea level.
3. What are the major rivers in Ethiopia?
The major rivers in Ethiopia include the Blue Nile, the Awash, the Omo, and the Tekeze.
4. What are the major lakes in Ethiopia?
The major lakes in Ethiopia include Lake Tana, Lake Turkana, and Lake Abaya.
5. What is the East African Rift Valley?
The East African Rift Valley is a massive geological feature that runs through Ethiopia, creating a series of valleys, lakes, and volcanic formations.
6. What is the impact of Ethiopia’s physical geography on its people?
Ethiopia’s physical geography has a profound impact on its people, shaping their livelihoods, cultures, and traditions.
7. What are the challenges and opportunities presented by Ethiopia’s physical geography?
Ethiopia’s physical geography presents both challenges, such as transportation difficulties and water scarcity, and opportunities, such as hydropower potential and tourism.
Tips for Understanding the Physical Map of Ethiopia:
-
Use a physical map: A physical map is essential for understanding the topography and geographical features of Ethiopia.
-
Study the elevation: Pay attention to the elevation of different regions, as it influences climate, vegetation, and human settlements.
-
Identify major rivers and lakes: Understand the role of rivers and lakes in shaping the landscape and supporting life.
-
Explore the Rift Valley: Learn about the formation and impact of the East African Rift Valley on Ethiopia’s physical geography.
-
Research the different ecosystems: Explore the diverse ecosystems found in Ethiopia, from the highlands to the lowlands.
Conclusion:
The physical map of Ethiopia reveals a land of captivating contrasts, showcasing a diverse tapestry of landscapes, geological formations, and ecosystems. From the towering peaks of the Simien Mountains to the arid plains of the Danakil Depression, Ethiopia’s physical geography has shaped its history, culture, and way of life. Understanding its physical features is crucial for appreciating the unique character of this fascinating country and for recognizing the challenges and opportunities it presents for its future development.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Ethiopia: A Journey Through its Physical Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!