Unraveling The Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide To Iceland’s Earthquake Map
Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map
- 3.1 The Tectonic Dance: A Primer on Iceland’s Geological Setting
- 3.2 Unveiling the Seismic Landscape: The Iceland Earthquake Map
- 3.3 Benefits Beyond Visualization: Applications of the Iceland Earthquake Map
- 3.4 Navigating the Data: Understanding Key Features of the Iceland Earthquake Map
- 3.5 FAQs About Iceland’s Earthquake Map
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing the Iceland Earthquake Map
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Dynamic Earth
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map

Iceland, a land sculpted by fire and ice, is renowned for its dramatic landscapes, volcanic activity, and, inevitably, its seismic activity. Understanding the patterns of earthquakes in this Nordic island nation is crucial for various reasons, from safeguarding infrastructure to ensuring public safety and informing scientific research. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Iceland’s earthquake map, exploring its significance, applications, and the insights it offers into the country’s geological dynamism.
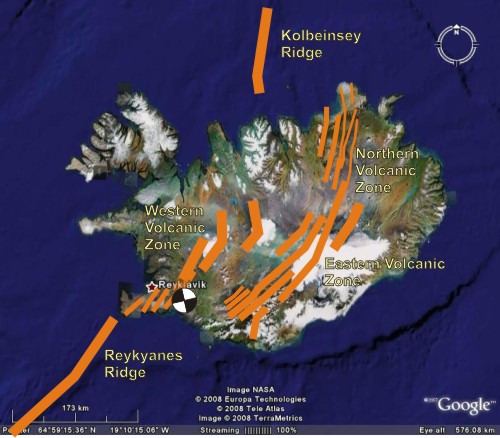
The Tectonic Dance: A Primer on Iceland’s Geological Setting
Iceland’s unique geological landscape is a direct consequence of its position atop the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent plate boundary where the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates pull apart. This separation allows molten rock, or magma, from the Earth’s mantle to rise, creating new oceanic crust and fueling Iceland’s volcanic activity.
The constant movement of these plates generates significant stress along the fault lines that crisscross the island. This stress is released through earthquakes, making Iceland one of the most seismically active regions on Earth.
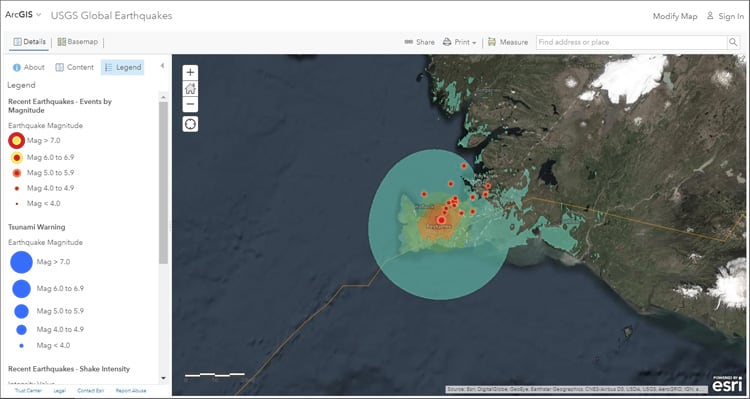
Unveiling the Seismic Landscape: The Iceland Earthquake Map
The Iceland earthquake map is a powerful visualization tool that provides a comprehensive overview of seismic activity across the country. It is a dynamic representation of earthquake occurrences, offering insights into:
- Earthquake Locations: The map pinpoints the precise locations of past earthquakes, revealing the distribution of seismic activity across Iceland. This information is crucial for identifying areas prone to earthquakes and understanding the regional variations in seismic risk.
- Earthquake Magnitudes: The map displays the magnitude of each earthquake, using a color-coded scale to differentiate between minor tremors and major events. This helps assess the potential impact of earthquakes and guide preparedness efforts.
- Earthquake Depths: The map can also depict the depth of earthquake epicenters, providing valuable information about the location of fault lines and the nature of the underlying geological structures.
- Historical Data: The map often incorporates historical earthquake data, allowing for a long-term perspective on seismic activity and trends. This historical context is essential for understanding the evolution of seismic patterns and predicting future events.
Benefits Beyond Visualization: Applications of the Iceland Earthquake Map
The Iceland earthquake map serves as a crucial resource for a wide range of stakeholders, enabling informed decision-making in various domains:
- Disaster Management: By identifying areas of high seismic activity, the map assists authorities in developing effective disaster preparedness plans, including evacuation routes, emergency response protocols, and building codes.
- Infrastructure Development: The map helps engineers and architects design structures that can withstand seismic forces, minimizing damage and ensuring the resilience of buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructure.
- Scientific Research: The map provides valuable data for researchers studying plate tectonics, seismology, and volcanism. It helps them understand the mechanisms behind earthquake generation, predict future seismic activity, and monitor the evolution of Iceland’s geological landscape.
- Public Awareness: By making seismic data readily accessible, the map fosters public awareness about earthquake hazards, encouraging preparedness and responsible behavior during seismic events.
Navigating the Data: Understanding Key Features of the Iceland Earthquake Map
The Iceland earthquake map is a valuable tool, but its effectiveness hinges on understanding its key features and interpreting the data it presents:
- Magnitude Scale: The map uses a standard magnitude scale, typically the Richter scale or the Moment Magnitude Scale, to represent earthquake intensity. Understanding the magnitude scale allows for accurate assessment of potential earthquake damage and impacts.
- Epicenter Location: The map indicates the epicenter of each earthquake, the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s origin. The epicenter is crucial for understanding the spatial distribution of seismic activity and its potential impact on surrounding areas.
- Depth: The map often includes information about the depth of the earthquake epicenter, indicating the location of the fault rupture within the Earth’s crust. This depth information is crucial for understanding the type of earthquake and its potential impact.
- Time Stamp: The map typically includes a timestamp for each earthquake, indicating the date and time of occurrence. This temporal information is essential for tracking the frequency and intensity of seismic activity over time.
FAQs About Iceland’s Earthquake Map
Q: How often are earthquakes recorded in Iceland?
A: Iceland experiences numerous earthquakes daily, ranging from minor tremors to significant events. The frequency and magnitude of these earthquakes can vary considerably depending on the location and tectonic activity in the region.
Q: Is it possible to predict earthquakes in Iceland?
A: While scientists can monitor seismic activity and identify areas prone to earthquakes, predicting the exact time and magnitude of an earthquake remains a significant challenge. Continuous monitoring and research are crucial for improving our understanding of seismic behavior and enhancing prediction capabilities.
Q: Are there any specific areas in Iceland that are more prone to earthquakes?
A: The areas most prone to earthquakes in Iceland typically coincide with the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and its associated fault lines, particularly in the south-west and north-east regions of the island. These regions are characterized by frequent volcanic activity and higher levels of seismic activity.
Q: What should I do if I experience an earthquake in Iceland?
A: If you experience an earthquake in Iceland, prioritize your safety by seeking shelter under a sturdy piece of furniture or in a doorway. Avoid windows and other areas where falling objects could pose a danger. Once the shaking subsides, check for injuries and potential damage, and follow the instructions of local authorities.
Tips for Utilizing the Iceland Earthquake Map
- Consult multiple sources: Utilize multiple earthquake maps and data sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of seismic activity in Iceland.
- Understand the scale: Familiarize yourself with the magnitude scale used on the map to accurately interpret the intensity of earthquakes.
- Track trends: Monitor the map over time to identify any patterns or trends in earthquake frequency and location.
- Stay informed: Subscribe to alerts and updates from official sources to receive timely information about earthquake events in Iceland.
Conclusion: Embracing the Dynamic Earth
Iceland’s earthquake map is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the country’s dynamic geological landscape. By providing a visual representation of seismic activity, it enables informed decision-making in various domains, from disaster management to infrastructure development and scientific research. By utilizing the map and staying informed about seismic hazards, individuals and communities can enhance their preparedness and resilience in the face of Iceland’s vibrant and ever-evolving geological landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Dynamic Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Iceland’s Earthquake Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!