Unlocking The Land Of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps Of Israel In The Old Testament
Unlocking the Land of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament
Related Articles: Unlocking the Land of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Land of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Land of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament
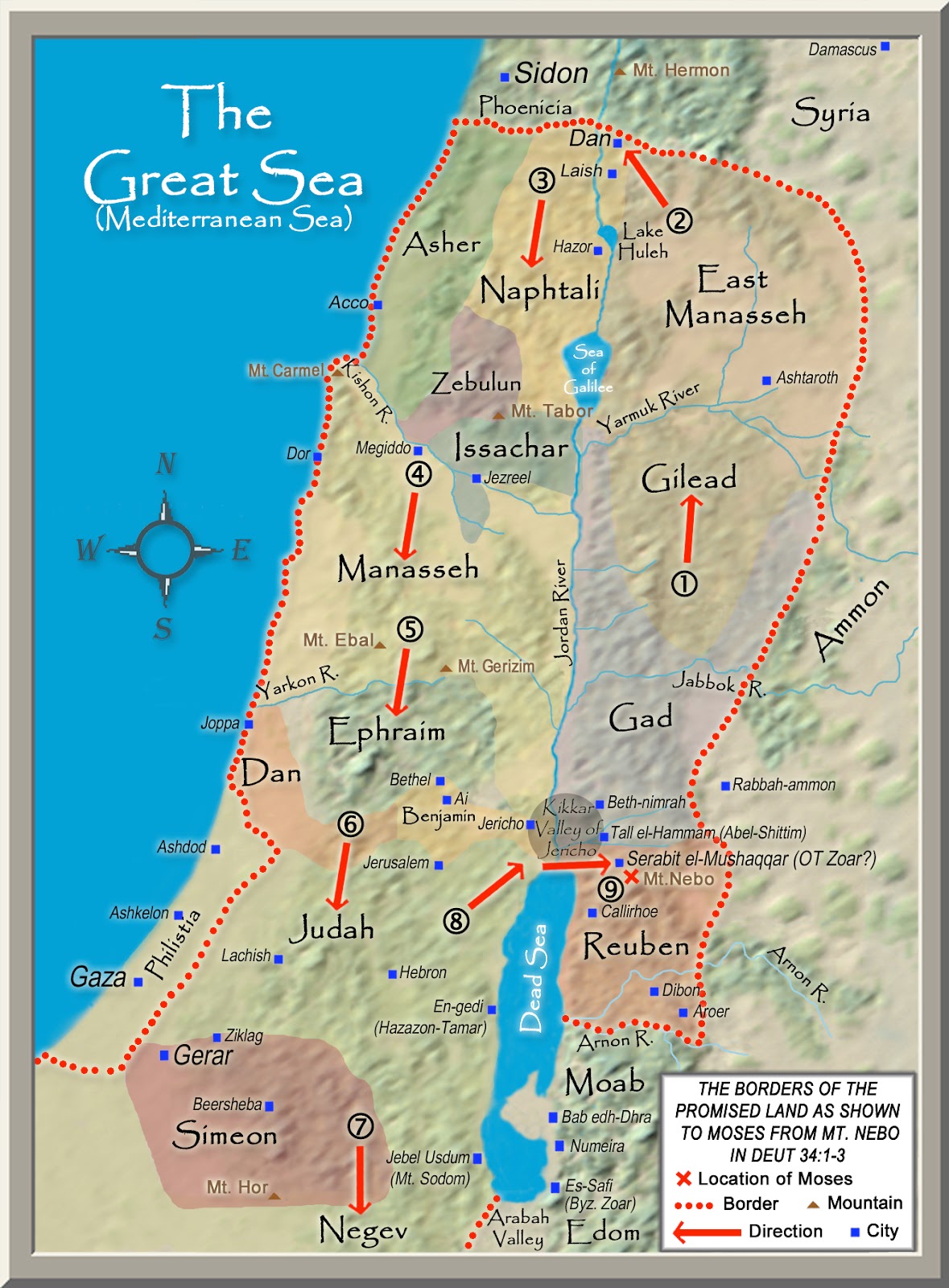
The Old Testament, a cornerstone of Jewish and Christian faith, is deeply intertwined with the geography of ancient Israel. The land, described as a "promised land" flowing with milk and honey, served as the stage for pivotal events, shaping the narratives of faith, history, and cultural identity. Understanding the geographical context of the Old Testament requires delving into the ancient maps that depict the land and its various regions. These maps, though not always precise or complete, offer invaluable insights into the lives, journeys, and struggles of the biblical characters and the development of the Israelite nation.
Mapping the Promised Land: A Historical Perspective
The concept of mapping the land of Israel has a long and rich history, dating back to ancient times. While the Old Testament itself does not contain detailed maps, it provides abundant geographical references and descriptions that allow scholars and historians to piece together a picture of the land.
Early Maps: From Texts to Visual Representations
The earliest attempts at mapping Israel were primarily based on textual descriptions found in the Bible and other ancient sources. The Book of Numbers, for instance, meticulously details the boundaries of the land promised to the Israelites, including the names of specific cities, rivers, and geographical features.
The Importance of the Tabernacle and Temple
The central location of the Tabernacle, and later the Temple in Jerusalem, played a crucial role in shaping the geography of ancient Israel. These sacred sites served as the focal point of religious life, drawing pilgrims from across the land and solidifying Jerusalem’s status as the spiritual heart of the nation.
The Rise of Cartography: Visualizing the Land
As cartography advanced, the first visual representations of ancient Israel emerged. These early maps, often found on ancient pottery, coins, and other artifacts, provided a rudimentary understanding of the land’s layout. While lacking precise details, they offer a glimpse into the visual perceptions of the land held by those living in the region.
The Impact of the Roman Empire
The Roman conquest of Judea in the first century CE had a significant impact on the mapping of ancient Israel. Roman cartographers produced detailed maps of the region, incorporating existing knowledge with their own observations, resulting in more accurate and comprehensive representations. These maps were used for administrative purposes, facilitating Roman control and governance.
Mapping the Journey: Tracing the Paths of the Israelites
The Old Testament is replete with stories of journeys and migrations, providing valuable information for reconstructing the paths taken by the Israelites. The account of the Exodus, for example, details the journey of the Israelites from Egypt to the Promised Land, highlighting the significance of key locations like Mount Sinai and the Red Sea.
Beyond the Physical Landscape: Mapping the Cultural and Historical Landscape
The maps of ancient Israel are not merely geographical representations; they also reflect the cultural and historical landscape of the time. The boundaries of the land, for example, were not merely physical lines but also represented the limits of the Israelite kingdom and its influence.
Modern Reconstructions: Combining Ancient Sources with Modern Technology
Today, scholars and historians utilize a combination of ancient sources, archaeological evidence, and modern technology to create detailed and accurate reconstructions of ancient Israel. These maps provide a valuable tool for understanding the biblical narrative and its historical context.
The Importance of Ancient Maps for Understanding the Old Testament
Studying ancient maps of Israel is crucial for understanding the Old Testament for several reasons:
- Contextualizing the Narrative: Maps provide a visual representation of the land in which the biblical stories unfolded, enhancing our understanding of the characters, their journeys, and the events that shaped their lives.
- Reconstructing History: Maps help us reconstruct the political and social landscape of ancient Israel, providing insights into the interactions between different tribes, kingdoms, and empires.
- Interpreting the Text: By understanding the geographical references in the Old Testament, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the symbolism and meaning embedded within the text.
FAQs about Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament:
1. Are there any accurate maps of ancient Israel from the time of the Old Testament?
While there are no fully accurate maps from the period, scholars can reconstruct a reasonably accurate picture of the land based on textual descriptions and archaeological evidence.
2. How do modern maps of ancient Israel differ from those created in the past?
Modern maps benefit from advanced technology, archaeological discoveries, and a deeper understanding of the historical and cultural context. They are more detailed and accurate than their earlier counterparts.
3. What are the limitations of using ancient maps to study the Old Testament?
Ancient maps were often limited in their scope and accuracy. They may not reflect the full extent of the land, the precise locations of cities, or the details of geographical features.
4. How do ancient maps help us understand the significance of Jerusalem in the Old Testament?
Maps highlight Jerusalem’s central location within the land, its strategic importance, and its status as a religious center. They also illustrate the city’s growth and development throughout history.
5. What are some of the key geographical features mentioned in the Old Testament?
Key features include the Jordan River, the Sea of Galilee, the Dead Sea, the Negev desert, and the mountains of Judea and Samaria.
Tips for Studying Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament:
- Consult Scholarly Resources: Utilize academic publications and websites specializing in biblical geography and archaeology.
- Compare Different Maps: Compare maps created by different scholars and historians to identify areas of agreement and disagreement.
- Relate Maps to the Text: Use maps to visualize the locations and journeys described in the Old Testament, enhancing your understanding of the narrative.
- Consider the Historical Context: Remember that ancient maps were created in specific historical contexts and may reflect the biases and perspectives of their creators.
Conclusion
Ancient maps of Israel offer a unique window into the world of the Old Testament. They provide a tangible link to the past, allowing us to visualize the land where biblical stories unfolded, the journeys of the Israelites, and the challenges they faced. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of the text, the historical context, and the enduring significance of the land of Israel in the history of faith and culture.


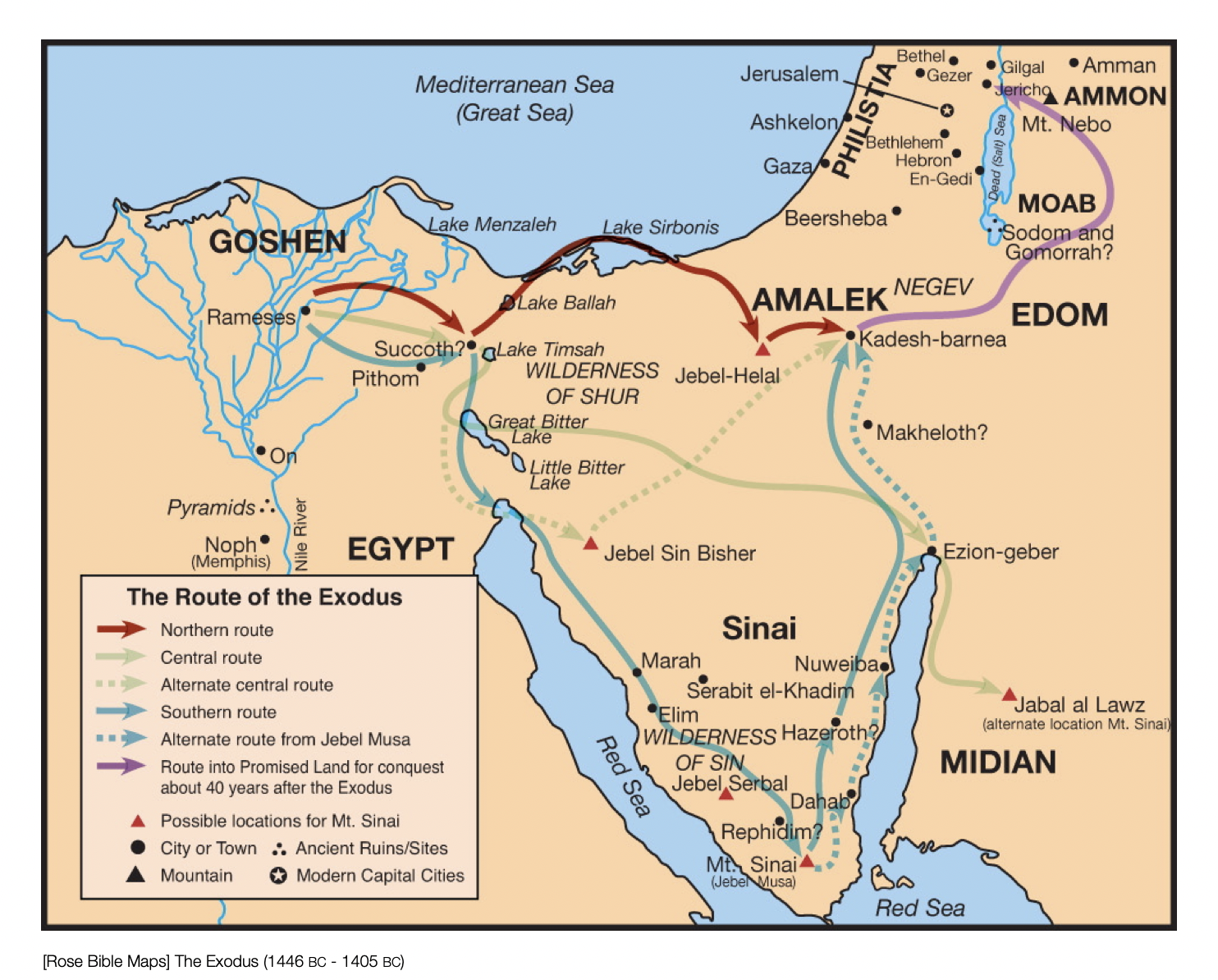




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Land of Promise: A Journey Through Ancient Maps of Israel in the Old Testament. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!