The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination And Reality
The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination and Reality
Related Articles: The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination and Reality
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination and Reality. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination and Reality
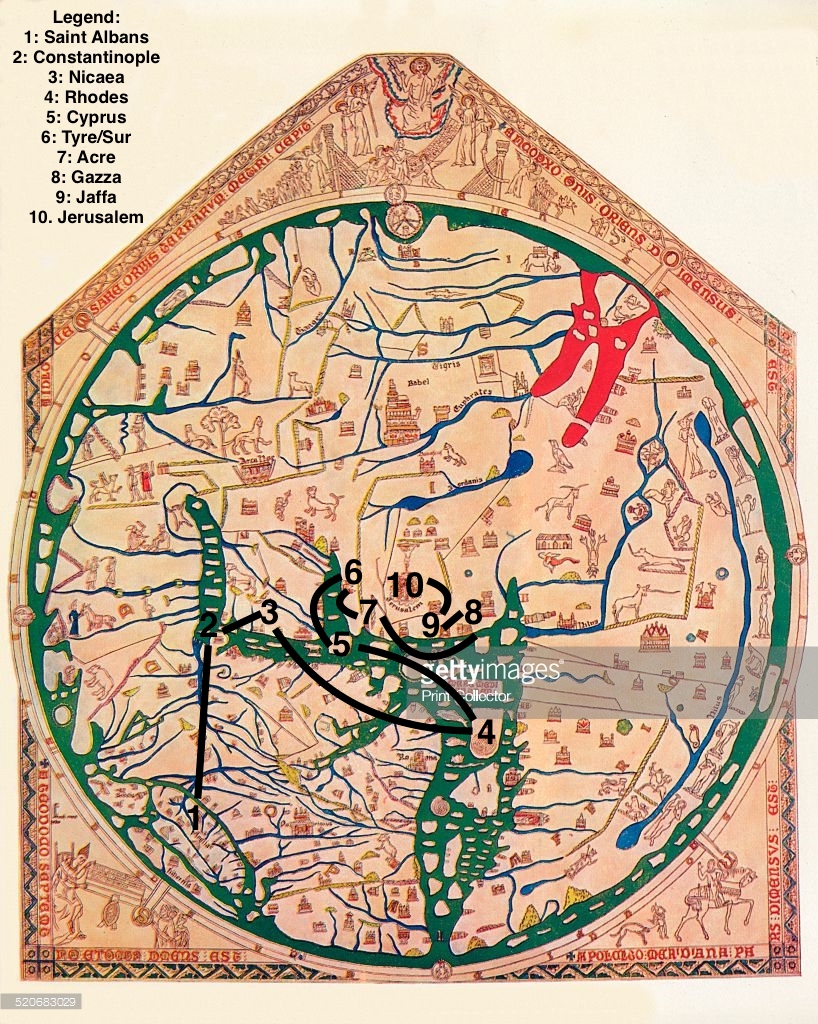
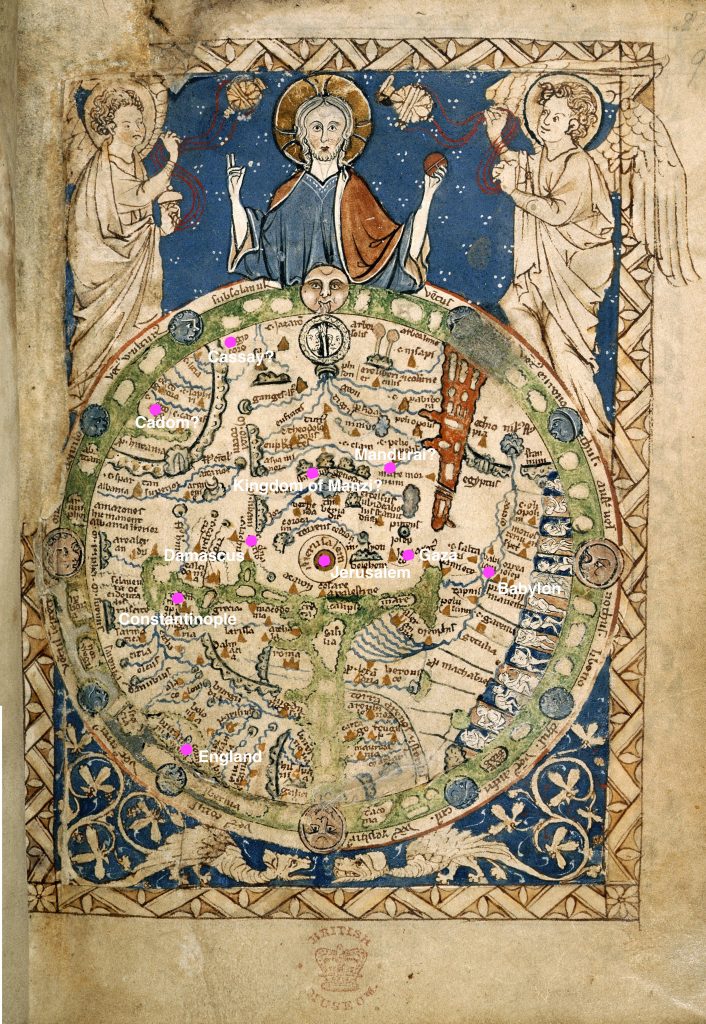
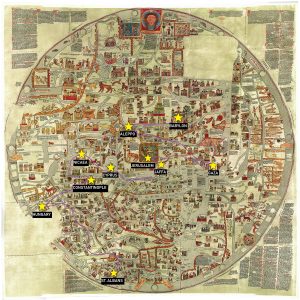
The Mandeville Map, also known as the "Mappa Mundi," is a captivating artifact of medieval cartography, offering a glimpse into the world as understood during the 14th century. While not a precise geographical representation, the map is a fascinating blend of scientific observation, religious belief, and fantastical imagination. This intricate tapestry of knowledge and folklore serves as a window into the intellectual and cultural landscape of its time.
Origins and Evolution:
The Mandeville Map, attributed to Sir John Mandeville, a fictional traveler and writer, gained widespread popularity in the 14th century. While the map’s exact origins remain debated, scholars believe it was likely based on existing cartographic traditions and influenced by various sources, including classical texts, biblical narratives, and travelers’ accounts. The map’s popularity is attributed to its accessibility, as it was widely circulated in manuscript form, making it accessible to a broad audience.
A World of Wonder and Mystery:
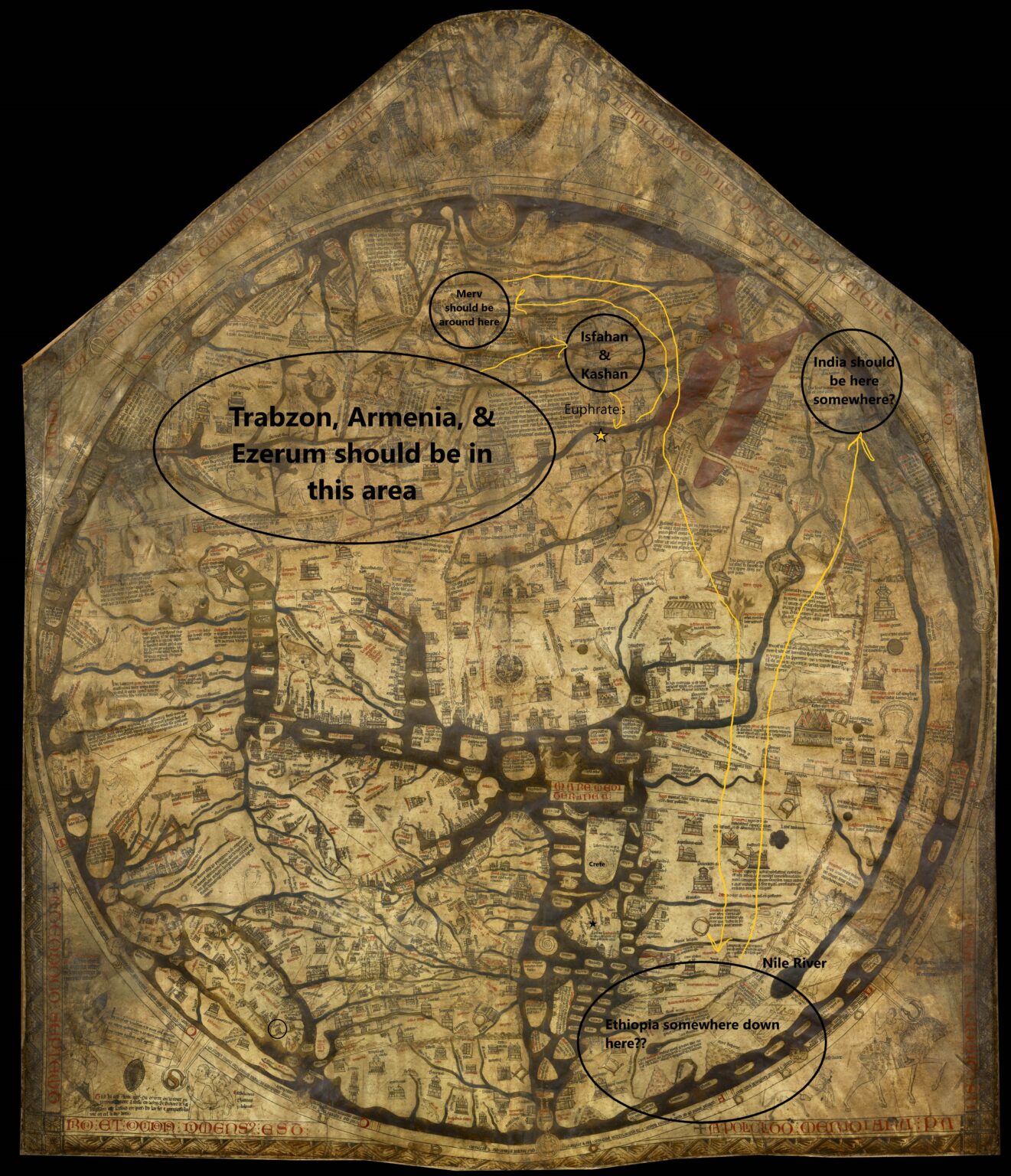
The Mandeville Map presents a world brimming with wonder and mystery. Its depiction of the Earth is circular, reflecting the prevalent geocentric model of the universe. Jerusalem, considered the center of the world, is placed prominently at the map’s heart, with the continents radiating outward. The map incorporates elements of the known world, including Europe, Asia, and Africa, alongside fantastical creatures and legendary lands.
Beyond the Familiar:
The Mandeville Map transcends the boundaries of geographical accuracy, incorporating elements of myth and folklore. The map features mythical creatures like griffins, unicorns, and dragons, alongside fantastical lands like the Land of Prester John, a legendary Christian king in the East, and the Island of Paradise, a biblical Eden-like realm. These elements reveal the medieval worldview, where the world was infused with the supernatural and the boundaries between reality and imagination were blurred.
The Importance of the Mandeville Map:
The Mandeville Map, despite its fantastical elements, played a significant role in shaping medieval understanding of the world. It served as a tool for education, stimulating curiosity and inspiring exploration. The map’s widespread circulation helped to disseminate knowledge about distant lands and cultures, fostering an interest in travel and discovery.
Beyond the Literal:
The Mandeville Map is more than just a geographical representation. It is a testament to the power of imagination and the human desire to understand the world around us. It reflects the medieval fascination with the unknown, the desire to explore the world beyond the familiar, and the search for meaning in a world often shrouded in mystery.
Analyzing the Map’s Content:
The Mandeville Map is divided into three main sections:
- The East: This section encompasses the lands east of Jerusalem, including the mythical Land of Prester John, the legendary city of Babylon, and the fabled Silk Road.
- The South: This section features Africa, with its diverse cultures and landscapes, including the Kingdom of Ethiopia and the legendary city of Timbuktu.
- The West: This section encompasses Europe, with its major kingdoms and cities, including England, France, and Rome.
The Map’s Impact on Exploration and Discovery:
The Mandeville Map, despite its inaccuracies, played a crucial role in inspiring exploration and discovery. It fueled the imagination of travelers and adventurers, encouraging them to venture beyond the known world. Its depictions of fantastical lands and creatures sparked curiosity and a desire to unravel the mysteries of the world.
The Map’s Legacy:
The Mandeville Map, despite its fantastical elements, serves as a valuable historical document, offering insights into the medieval worldview and the evolution of cartography. It remains a testament to the power of imagination and the enduring human fascination with the unknown.
FAQs about the Mandeville Map:
1. Who created the Mandeville Map?
The Mandeville Map is attributed to Sir John Mandeville, a fictional traveler and writer. The map’s actual creator remains unknown, but it is believed to have been based on existing cartographic traditions and influenced by various sources.
2. When was the Mandeville Map created?
The Mandeville Map was created in the 14th century, during a period of significant exploration and expansion in Europe.
3. What is the significance of the Mandeville Map?
The Mandeville Map is significant for its portrayal of the world as understood during the medieval period. It combines elements of reality, myth, and folklore, reflecting the intellectual and cultural landscape of its time.
4. What are some of the fantastical elements depicted on the Mandeville Map?
The Mandeville Map features mythical creatures like griffins, unicorns, and dragons, alongside fantastical lands like the Land of Prester John, a legendary Christian king in the East, and the Island of Paradise, a biblical Eden-like realm.
5. How did the Mandeville Map influence exploration and discovery?
The Mandeville Map, despite its inaccuracies, played a crucial role in inspiring exploration and discovery. It fueled the imagination of travelers and adventurers, encouraging them to venture beyond the known world.
Tips for Studying the Mandeville Map:
- Consider the historical context: The Mandeville Map reflects the medieval worldview, where the world was infused with the supernatural and the boundaries between reality and imagination were blurred.
- Focus on the map’s symbolism: The map is rich in symbolism, with each element representing a specific concept or belief.
- Compare the map to other medieval maps: Comparing the Mandeville Map to other maps of the period can provide insights into the evolution of cartography and the changing understanding of the world.
- Explore the map’s cultural significance: The Mandeville Map was a cultural artifact that reflected the values and beliefs of its time.
Conclusion:
The Mandeville Map, though not a precise geographical representation, is a fascinating window into the medieval world. It embodies a blend of scientific observation, religious belief, and fantastical imagination, reflecting the intellectual and cultural landscape of its time. The map’s enduring legacy lies in its ability to spark curiosity, inspire exploration, and illuminate the enduring human fascination with the unknown. It serves as a reminder that the world is a place of both wonder and mystery, where the boundaries between reality and imagination can be blurred, and the thirst for knowledge and discovery is a timeless human pursuit.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mandeville Map: A Journey Through Medieval Imagination and Reality. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!