Navigating The Terrain: Understanding The Significance Of Map Weight In Geographic Information Systems
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems
- 3.1 The Impact of Map Weight: A Balancing Act
- 3.2 Factors Influencing Map Weight
- 3.3 Strategies for Optimizing Map Weight
- 3.4 Applications of Map Weight Optimization
- 3.5 FAQs on Map Weight
- 3.6 Tips for Managing Map Weight
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems
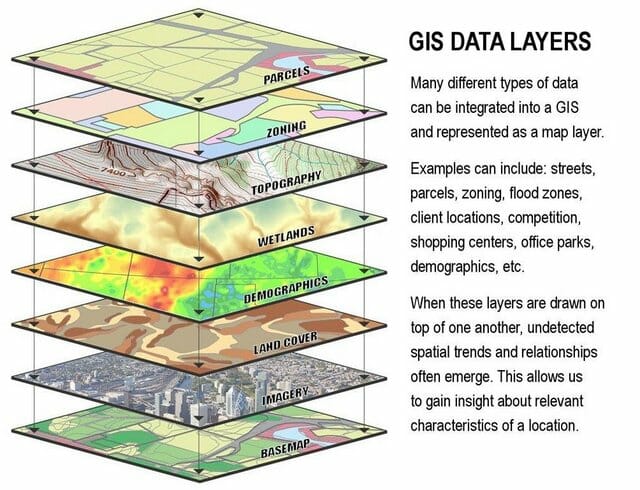
Geographic information systems (GIS) are powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing spatial data. They rely on maps as their foundation, and the weight of these maps plays a crucial role in determining the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of GIS applications. Map weight, in the context of GIS, refers to the size of the map file, which is determined by factors such as the resolution, complexity, and data density of the map.
This article delves into the intricacies of map weight, exploring its implications for GIS workflows and highlighting its significance in various applications.
The Impact of Map Weight: A Balancing Act
Map weight is a double-edged sword. While a heavier map, with a larger file size, may contain more detailed information and higher resolution, it comes with certain drawbacks:
- Storage and Transmission: Heavier maps demand more storage space, potentially straining available resources. Transmission over networks, particularly for mobile applications, can be slow and inefficient, leading to delays and frustration.
- Processing Power: Rendering and manipulating large maps require significant computational power, potentially slowing down GIS software and impacting performance.
- User Experience: Complex maps with high data density can be overwhelming for users, hindering their ability to interpret information effectively.
Conversely, lightweight maps, while offering faster processing and transmission, may lack detail, resulting in reduced accuracy and limited analytical capabilities. Therefore, achieving an optimal balance between map weight and data richness is paramount for successful GIS applications.
Factors Influencing Map Weight
Several factors contribute to the overall weight of a map:
- Resolution: The resolution of a map, measured in pixels per inch (ppi), directly impacts its file size. Higher resolution maps, with more pixels, capture finer details and result in larger file sizes.
- Data Density: The amount of data contained within a map, such as points, lines, and polygons, significantly influences its weight. Maps with dense datasets, containing numerous features, will be heavier than those with sparse datasets.
- Data Type: The type of data used in a map can also influence its weight. For instance, raster data, which represents continuous surfaces like elevation or temperature, often generates larger files compared to vector data, which represents discrete features like roads or buildings.
- Compression: Employing data compression techniques can effectively reduce map file sizes without compromising essential information.
- Map Projection: The chosen map projection, which determines how the Earth’s surface is represented on a flat map, can impact map weight. Some projections might introduce distortions that affect the overall size of the map file.
Strategies for Optimizing Map Weight
Various strategies can be employed to manage map weight effectively, striking a balance between data richness and performance:
- Data Simplification: Reducing the complexity of map features, such as simplifying line geometries or merging small polygons, can significantly reduce file size without sacrificing critical information.
- Data Generalization: Generalizing data by aggregating smaller features into larger units, such as combining multiple points into a single cluster, can effectively reduce data density and map weight.
- Data Subsetting: Extracting only the relevant data for a specific analysis or area of interest can create lighter maps, improving performance without compromising accuracy.
- Tile-based Rendering: Dividing large maps into smaller tiles, each containing a portion of the data, allows for efficient rendering and transmission, particularly for online applications.
- Data Compression: Employing lossless compression techniques, such as ZIP or GZIP, can significantly reduce file size without altering the original data.
Applications of Map Weight Optimization
The principles of map weight optimization are crucial for various GIS applications:
- Web Mapping: For web maps, optimizing map weight is essential for fast loading times and smooth user experiences, particularly on mobile devices with limited bandwidth.
- Mobile GIS: Mobile GIS applications, often deployed on devices with limited storage and processing power, require maps with optimized weight to ensure smooth performance and efficient data access.
- Real-time Analytics: In real-time applications, such as traffic monitoring or emergency response, efficient map loading and processing are crucial for timely decision-making.
- Data Visualization: When presenting data visually, striking a balance between map weight and detail is essential for clear and effective communication.
FAQs on Map Weight
Q: How does map weight affect GIS performance?
A: Larger maps with heavier file sizes require more processing power, potentially slowing down GIS software and impacting overall performance. This is particularly noticeable when manipulating or rendering maps, especially in real-time applications.
Q: What are the benefits of optimizing map weight?
A: Optimizing map weight improves performance, reduces storage requirements, enhances user experience, and facilitates efficient data transmission, particularly for web and mobile applications.
Q: How can I determine the optimal map weight for my application?
A: The optimal map weight depends on the specific application, available resources, and desired level of detail. It involves a careful balance between data richness and performance considerations.
Q: What tools can be used to optimize map weight?
A: Various GIS software packages offer tools for data simplification, generalization, subsetting, and compression, allowing for effective map weight optimization.
Tips for Managing Map Weight
- Analyze Data Requirements: Carefully assess the specific needs of your application to determine the optimal level of detail and data density required for your maps.
- Prioritize Data: Identify essential data layers and prioritize them for inclusion in your maps, eliminating unnecessary or redundant information.
- Use Data Compression: Employ lossless compression techniques to reduce file sizes without compromising data integrity.
- Consider Data Subsetting: Extract only the relevant data for a specific analysis or area of interest, creating lighter maps for efficient processing.
- Experiment with Different Techniques: Explore various data optimization techniques to find the most effective approach for your specific needs.
Conclusion
Map weight is a fundamental aspect of GIS, significantly impacting performance, storage requirements, and user experience. By carefully managing map weight through data optimization strategies, GIS professionals can ensure efficient workflows, enhance user experiences, and maximize the value of spatial data.
Understanding the interplay between map weight and data richness is crucial for developing effective GIS applications that balance performance with accuracy and deliver valuable insights from spatial information.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Weight in Geographic Information Systems. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!