Navigating The Tapestry Of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide To The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map
Navigating the Tapestry of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map

Kentucky, a state renowned for its rolling hills and bluegrass music, holds a rich and complex history deeply intertwined with its Indigenous peoples. The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map serves as a visual testament to this legacy, offering a window into the diverse cultural tapestry that has shaped the state’s identity. Understanding the map’s significance requires delving into the history of the tribes who once called this land home, their enduring cultural practices, and the challenges they have faced throughout the years.
A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Past
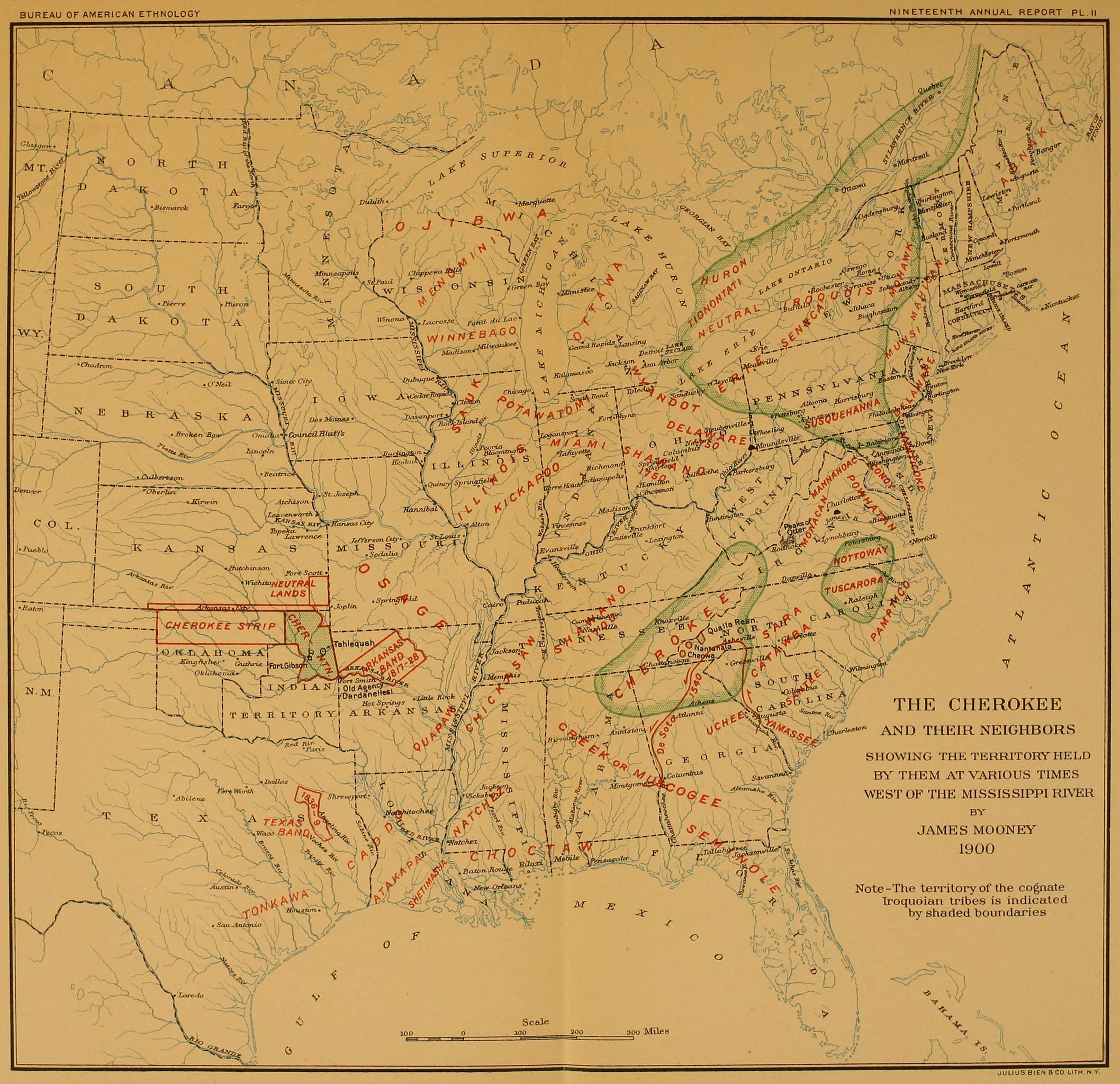
Kentucky’s Indigenous history predates European settlement by centuries. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was inhabited by various Native American groups long before the arrival of European explorers. The map, therefore, becomes a tool for understanding the spatial distribution of these tribes and their interactions with the environment.
Pre-Colonial Kentucky: A Mosaic of Tribes
Prior to European contact, the land that is now Kentucky was inhabited by a diverse range of Indigenous peoples. The most prominent groups included:
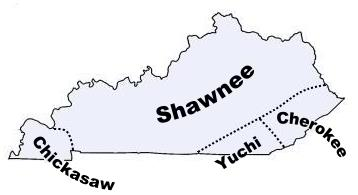
- The Shawnee: Known for their skilled warriors and adaptable lifestyle, the Shawnee inhabited the Ohio Valley, including portions of present-day Kentucky. Their presence was significant in shaping the region’s history and influencing relations with European settlers.
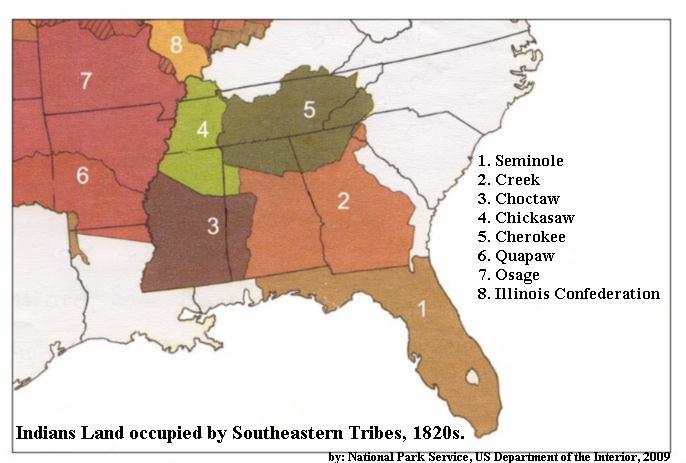
- The Cherokee: Holding vast territories in the southeastern United States, the Cherokee had a presence in eastern Kentucky, primarily along the Cumberland Mountains. They were known for their sophisticated political system, cultural traditions, and resilience in the face of forced removal.
- The Chickasaw: Primarily located in present-day Mississippi and Alabama, the Chickasaw had hunting grounds that extended into western Kentucky. Their influence in the region was significant, particularly in trade and diplomacy with other tribes.
- The Miami: These tribes were known for their agricultural skills and strong political organization. Their presence in Kentucky, though less extensive than other tribes, was marked by their strategic alliances and interactions with neighboring groups.
- The Delaware: The Delaware, or Lenape, were a powerful tribe with a significant presence in the Ohio Valley. Their influence extended into Kentucky, where they engaged in trade and established relationships with other tribes.
The Impact of European Colonization: Dispossession and Resilience
The arrival of European settlers in the 18th century brought about profound changes for the Indigenous peoples of Kentucky. Land encroachment, disease, and forced removal significantly impacted their populations and cultural practices. The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map, in this context, becomes a reminder of the displacement and hardship endured by these communities.
- The Treaty of Greenville (1795): This treaty, signed between the United States and several Native American tribes, including the Shawnee, Cherokee, and Delaware, ceded large tracts of land in the Ohio Valley, including portions of Kentucky, to the United States. This treaty marked a significant turning point in the relationship between the tribes and the US government.
- The Trail of Tears (1830s): The forced removal of the Cherokee from their ancestral lands in the Southeast, including those in Kentucky, had a devastating impact on their community. This forced relocation, known as the Trail of Tears, stands as a stark reminder of the injustices faced by Indigenous peoples.
The Enduring Legacy: Cultural Persistence and Revitalization
Despite the challenges they have faced, the Indigenous peoples of Kentucky have maintained their cultural traditions and identities. Today, several federally recognized tribes, including the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, the Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma, and the Miami Tribe of Oklahoma, have descendants with roots in Kentucky. Their stories, traditions, and cultural practices continue to enrich the state’s cultural tapestry.
The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map: A Gateway to Understanding
The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the state’s Indigenous heritage. It provides a visual representation of the historical presence of these tribes and their connection to the land. By studying the map, we can gain insights into:
- The spatial distribution of different tribes: The map helps us visualize the areas where specific tribes lived and interacted with each other.
- The historical significance of specific locations: Certain places on the map might hold cultural or historical significance for different tribes, highlighting the importance of these locations in their stories.
- The impact of colonization on Indigenous communities: The map can illustrate how European settlement and expansion led to the displacement and forced removal of Native American tribes.
- The ongoing efforts of tribal nations to preserve their heritage: The map serves as a reminder of the resilience and cultural persistence of Indigenous peoples in Kentucky.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the federally recognized tribes with historical ties to Kentucky?
While there are no federally recognized tribes currently residing in Kentucky, several tribes with historical ties to the state are federally recognized, including the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, the Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma, and the Miami Tribe of Oklahoma.
2. How can I learn more about the history of Indigenous peoples in Kentucky?
Several resources are available for exploring the history of Indigenous peoples in Kentucky. These include:
- The Kentucky Historical Society: This organization houses a vast collection of resources related to Kentucky’s history, including information about Indigenous peoples.
- The Kentucky Department of Libraries and Archives: This department provides access to historical documents, photographs, and maps related to Kentucky’s Indigenous history.
- Local museums and historical societies: Numerous museums and historical societies across Kentucky offer exhibits and programs dedicated to the state’s Indigenous heritage.
3. What are the ongoing efforts to preserve Indigenous cultural practices in Kentucky?
Several initiatives are underway to preserve and celebrate Indigenous culture in Kentucky. These include:
- The Kentucky Native American Heritage Commission: This commission works to promote awareness and understanding of Kentucky’s Indigenous history and culture.
- Tribal cultural centers and museums: Many tribes across the country maintain cultural centers and museums dedicated to preserving their traditions and sharing them with the public.
- Educational programs: Several schools and educational institutions in Kentucky offer programs and courses focused on Indigenous history and culture.
Tips for Engaging with the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map
- Explore the map with a historical perspective: Consider the map as a window into the past, understanding the context of the time period and the events that shaped the lives of Indigenous peoples.
- Identify key locations and their significance: Pay attention to specific locations on the map that hold cultural or historical importance for different tribes.
- Connect the map to broader historical narratives: Relate the information on the map to broader historical events, such as the Treaty of Greenville or the Trail of Tears, to understand the impact of colonization on Indigenous communities.
- Engage with local resources: Visit museums, historical societies, and cultural centers in Kentucky to learn more about the state’s Indigenous heritage.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Shared History
The Kentucky Indian Tribes Map serves as a powerful reminder of the complex and multifaceted history of Indigenous peoples in the state. It is a tool for understanding the diverse cultural tapestry that has shaped Kentucky’s identity, acknowledging the contributions and challenges faced by these communities. By engaging with the map, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacy of Indigenous peoples in Kentucky and work towards a future that honors their history and celebrates their cultural resilience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Kentucky’s Indigenous Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to the Kentucky Indian Tribes Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!