Navigating The Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps For Agricultural Success
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps for Agricultural Success
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps for Agricultural Success
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps for Agricultural Success. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps for Agricultural Success
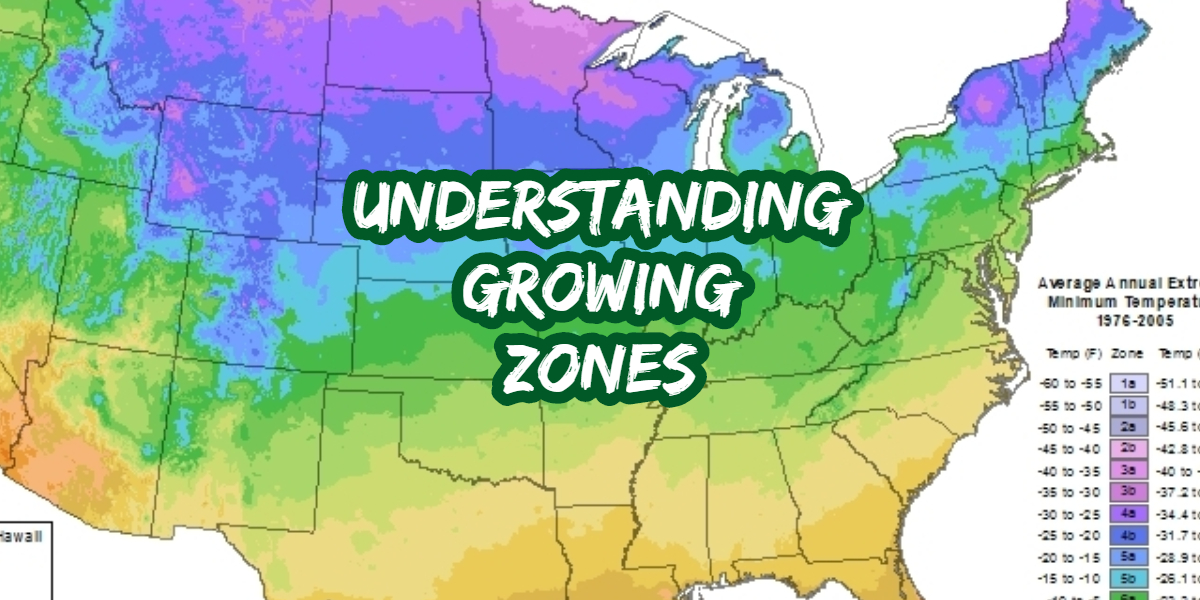
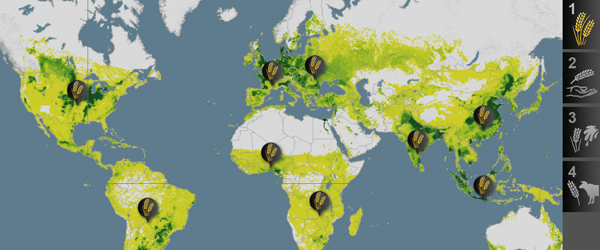
Farm zone maps, also known as agricultural zoning maps or land use maps, are essential tools for agricultural planning and management. They provide a visual representation of how land is allocated and utilized within a specific geographic area, offering valuable insights into the suitability of different regions for specific agricultural practices. By understanding the information contained within these maps, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding crop selection, livestock management, and overall farm operations.
Deciphering the Zones: Understanding the Data
Farm zone maps typically depict various zones based on factors like:
- Soil Type: Different soil types possess varying levels of fertility, drainage, and suitability for different crops. Maps may highlight areas with sandy, clay, or loam soils, each requiring different management practices.
- Climate: Climate zones are often represented, showcasing areas with distinct temperature ranges, rainfall patterns, and growing seasons. These factors influence the viability of specific crops and livestock.
- Topography: Land elevation, slope, and aspect (direction the land faces) are depicted, revealing areas prone to erosion, waterlogging, or excessive sunlight. These factors impact crop growth and water management.
- Water Availability: Access to water sources, such as rivers, lakes, or groundwater, is crucial for irrigation. Maps may indicate areas with limited water availability, highlighting potential challenges for certain agricultural practices.
- Infrastructure: Roads, transportation networks, and proximity to markets are depicted, highlighting areas with better access for transporting agricultural produce.
Benefits of Utilizing Farm Zone Maps
Farm zone maps offer a wide range of benefits for individuals and organizations involved in agriculture:
- Informed Decision-Making: Maps provide a comprehensive overview of land suitability, enabling farmers to select crops and livestock best suited to their specific location.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: By understanding the resource availability and limitations within each zone, farmers can allocate resources effectively, maximizing yield and minimizing waste.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying areas prone to specific hazards, such as flooding or drought, allows farmers to implement proactive measures to minimize potential losses.
- Sustainable Practices: Maps can help identify areas suitable for conservation practices, such as planting cover crops or implementing rotational grazing, promoting long-term soil health.
- Improved Market Access: Knowing the proximity to markets and transportation infrastructure helps farmers make informed decisions regarding crop selection and distribution.
- Land Use Planning: Government agencies and local authorities can utilize these maps to guide land use planning, ensuring sustainable agricultural practices and protecting natural resources.
- Investment Decisions: Investors and lenders can utilize these maps to assess the viability and potential profitability of agricultural projects, guiding investment decisions.
Types of Farm Zone Maps
Various types of farm zone maps cater to different needs:
- General Purpose Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of agricultural zones, encompassing multiple factors like soil type, climate, and topography.
- Crop-Specific Maps: These maps highlight areas suitable for specific crops, considering factors like temperature requirements, rainfall patterns, and soil fertility.
- Livestock-Specific Maps: These maps focus on areas suitable for different livestock breeds, considering factors like pasture availability, water access, and climate conditions.
- Environmental Sensitivity Maps: These maps identify areas with high environmental sensitivity, highlighting areas requiring special attention to minimize negative impacts on ecosystems.
Accessing Farm Zone Maps
Farm zone maps can be accessed through various sources:
- Government Agencies: National and local government agencies often create and maintain farm zone maps, making them available online or through physical copies.
- Research Institutions: Universities and agricultural research institutions may conduct studies and develop specialized farm zone maps for specific regions or crops.
- Private Companies: Private companies specializing in agricultural data analysis and mapping services offer customized farm zone maps tailored to specific needs.
- Online Platforms: Several online platforms provide access to farm zone maps, often offering interactive tools for exploring and analyzing data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Farm Zone Maps
Q: What are the limitations of farm zone maps?
A: While farm zone maps provide valuable information, they are based on average conditions and may not reflect localized variations within a zone. Factors like microclimate, soil variability, and specific management practices can influence the actual suitability of a particular area.
Q: How often are farm zone maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the source and the type of data used. Some maps are updated annually, while others may be updated less frequently. It is important to check the date of the map to ensure the information is current.
Q: Can I create my own farm zone map?
A: While creating a comprehensive farm zone map requires specialized expertise and data, you can utilize readily available resources like soil maps, climate data, and topographic information to create basic maps for your own farm.
Q: How can I use farm zone maps to improve my farm’s sustainability?
A: By understanding the environmental sensitivity of different zones, you can implement sustainable practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and conservation tillage to minimize soil erosion and protect water resources.
Tips for Utilizing Farm Zone Maps
- Cross-reference with Local Expertise: Consult with local farmers and agricultural experts to gain insights into specific conditions and practices within a particular zone.
- Consider Microclimate: Factor in local microclimate variations within a zone, as these can significantly influence crop growth and livestock health.
- Monitor Data Updates: Stay informed about updates to farm zone maps, as changes in land use, environmental conditions, and agricultural practices can impact their accuracy.
- Utilize Mapping Software: Explore mapping software and online platforms that offer interactive tools for visualizing and analyzing farm zone data.
Conclusion
Farm zone maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating the complex landscape of agriculture, providing essential information for informed decision-making and sustainable practices. By understanding the data contained within these maps, individuals and organizations can optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, and contribute to the long-term success and sustainability of agricultural operations. As technology advances and data collection improves, farm zone maps will continue to evolve, offering even more comprehensive and detailed insights into the agricultural potential of different regions.



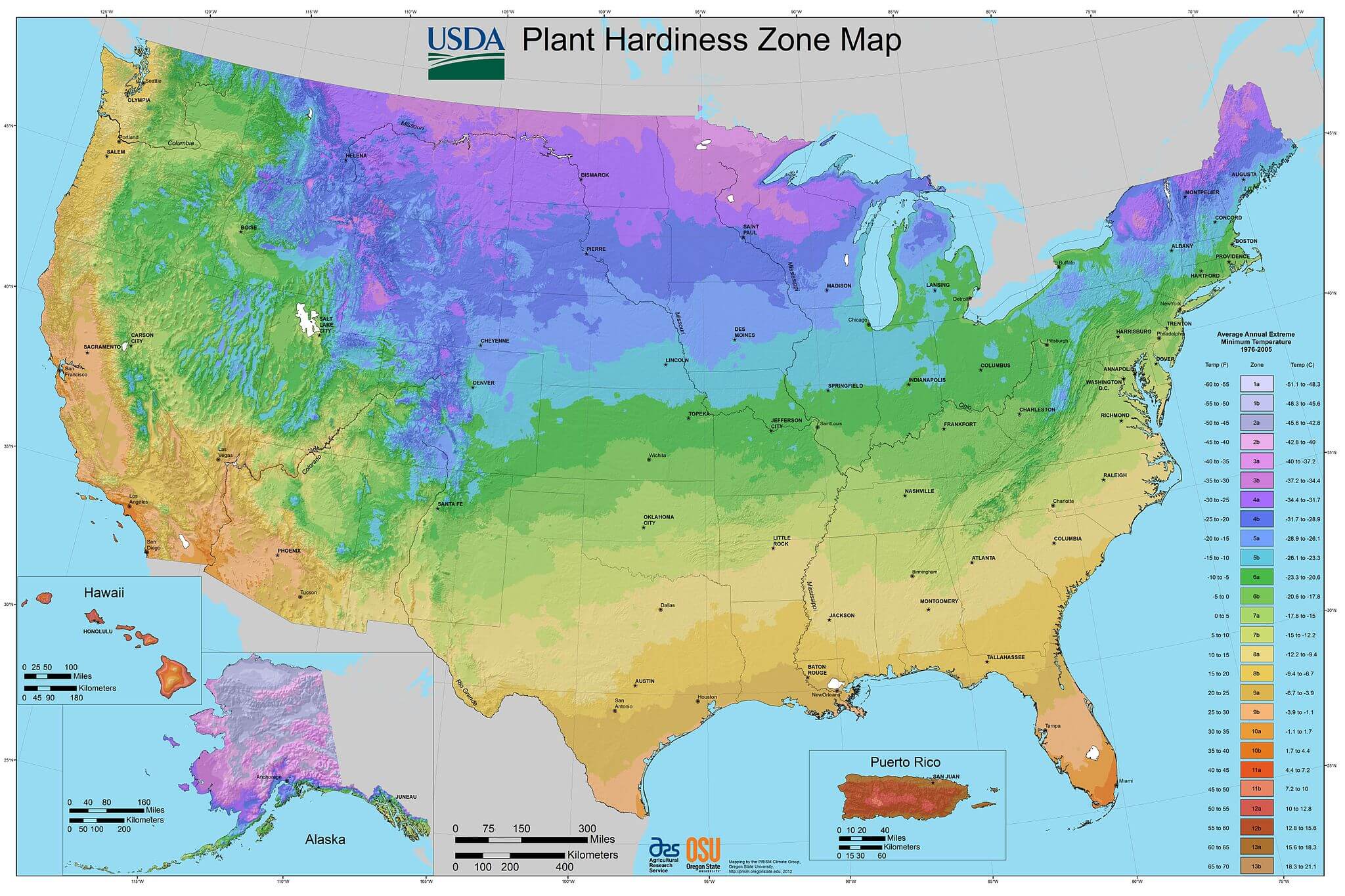
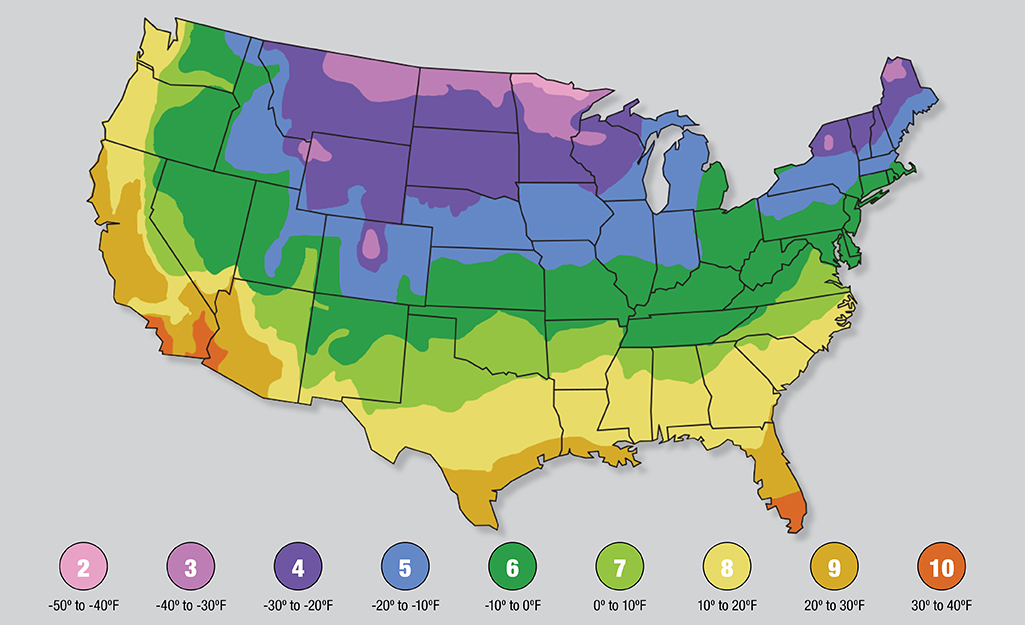
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Farm Zone Maps for Agricultural Success. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!