Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Sudan’s States
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan’s States
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan’s States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan’s States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan’s States
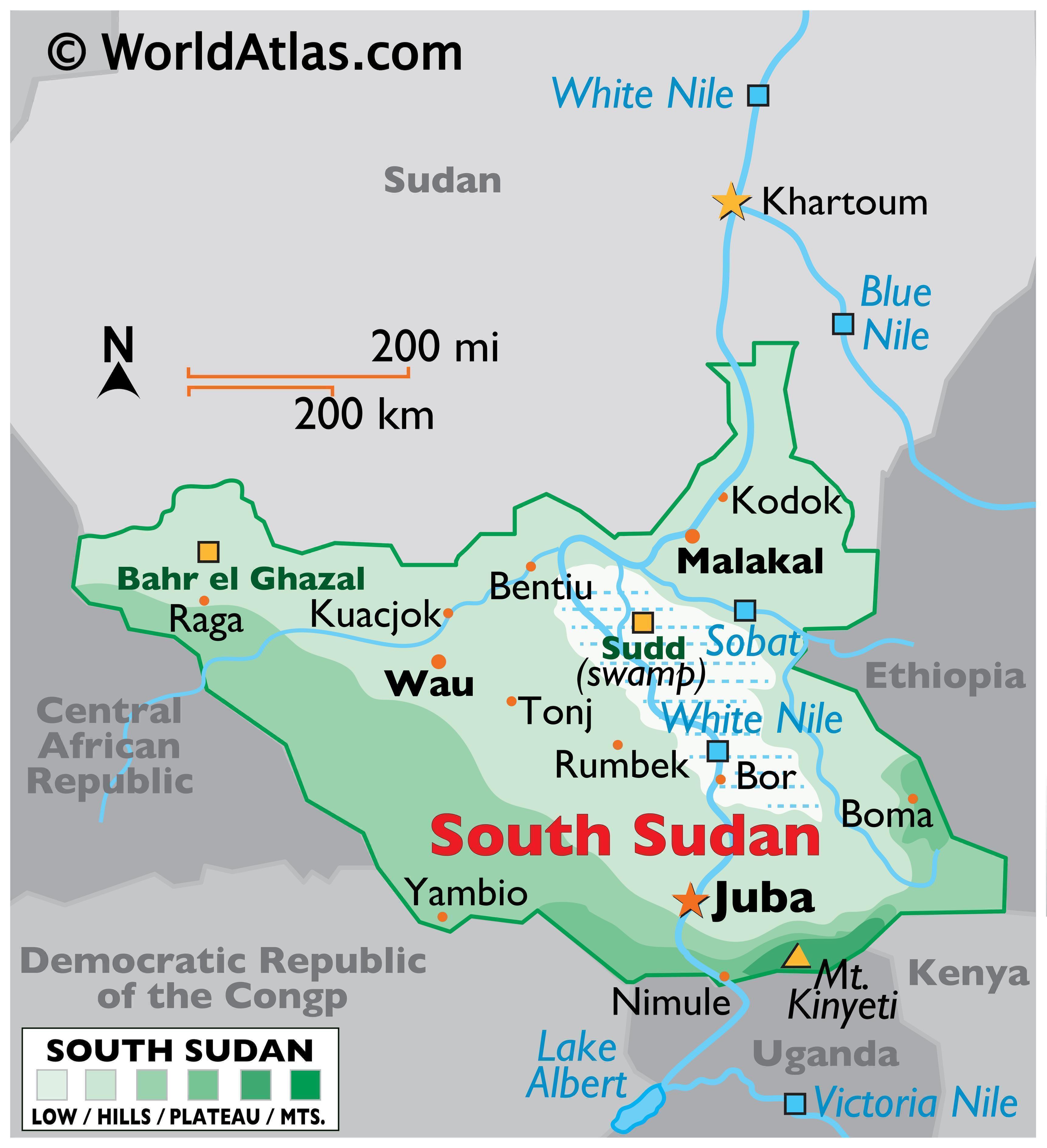
South Sudan, a young nation in East Africa, is a land of vast plains, fertile river valleys, and diverse cultures. Understanding its administrative structure is crucial for navigating its political, social, and economic landscape. The country’s map is divided into ten states, each with its unique history, geography, and cultural identity.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of each state, exploring its key features, challenges, and potential.
A Glimpse into South Sudan’s States:
1. Central Equatoria:
- Location: Located in the south-central region, bordering Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Key Features: The state is home to Juba, the capital city, and is known for its fertile land, abundant rainfall, and diverse ethnic groups.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to urbanization, environmental degradation, and the influx of refugees from neighboring countries.
- Potential: Central Equatoria holds significant potential for agriculture, tourism, and trade due to its strategic location and natural resources.
2. Eastern Equatoria:
- Location: Situated in the south-eastern region, bordering Kenya, Uganda, and Ethiopia.
- Key Features: The state boasts a diverse landscape ranging from mountains to plains and is home to the Imatong Mountains, a significant ecological reserve.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, limited infrastructure, and a lack of access to basic services.
- Potential: Eastern Equatoria holds potential for ecotourism, agriculture, and livestock farming due to its natural resources and proximity to neighboring countries.
3. Jonglei:
- Location: Situated in the south-eastern region, bordering Ethiopia and the states of Upper Nile and Central Equatoria.
- Key Features: The state is known for its vast wetlands, including the Sudd, the world’s largest swamp, and is home to diverse wildlife.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, cattle raiding, and limited access to education and healthcare.
- Potential: Jonglei holds potential for livestock farming, fisheries, and ecotourism due to its natural resources and vast land.
4. Lakes:
- Location: Situated in the south-western region, bordering the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Key Features: The state is known for its numerous lakes, including Lake No, and is home to the Dinka ethnic group.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, cattle raiding, and limited access to basic services.
- Potential: Lakes holds potential for agriculture, fishing, and livestock farming due to its fertile land and abundant water resources.
5. Northern Bahr el Ghazal:
- Location: Situated in the north-western region, bordering Sudan.
- Key Features: The state is known for its vast plains, fertile land, and the presence of the Bahr el Ghazal River.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to drought, desertification, and limited access to education and healthcare.
- Potential: Northern Bahr el Ghazal holds potential for agriculture, livestock farming, and oil exploration due to its natural resources and proximity to Sudan.
6. Unity:
- Location: Situated in the north-eastern region, bordering Sudan and Ethiopia.
- Key Features: The state is known for its oil fields and is home to the Nuer ethnic group.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, oil extraction, and limited access to basic services.
- Potential: Unity holds potential for oil production, agriculture, and livestock farming due to its natural resources and strategic location.
7. Upper Nile:
- Location: Situated in the north-eastern region, bordering Sudan and Ethiopia.
- Key Features: The state is known for its fertile land, the presence of the Nile River, and the diversity of its ethnic groups.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, limited access to education and healthcare, and the impact of climate change.
- Potential: Upper Nile holds potential for agriculture, fisheries, and tourism due to its natural resources and strategic location.
8. Warrap:
- Location: Situated in the north-western region, bordering Sudan.
- Key Features: The state is known for its fertile land, the presence of the Bahr el Ghazal River, and the Dinka ethnic group.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to drought, desertification, and limited access to education and healthcare.
- Potential: Warrap holds potential for agriculture, livestock farming, and trade due to its natural resources and proximity to Sudan.
9. Western Bahr el Ghazal:
- Location: Situated in the west-central region, bordering Sudan and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Key Features: The state is known for its fertile land, the presence of the Bahr el Ghazal River, and the diversity of its ethnic groups.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, limited access to education and healthcare, and the impact of climate change.
- Potential: Western Bahr el Ghazal holds potential for agriculture, livestock farming, and trade due to its natural resources and strategic location.
10. Western Equatoria:
- Location: Situated in the south-western region, bordering the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Key Features: The state is known for its mountainous terrain, abundant rainfall, and the diversity of its ethnic groups.
- Challenges: The state faces challenges related to inter-tribal conflicts, limited access to education and healthcare, and the impact of climate change.
- Potential: Western Equatoria holds potential for agriculture, tourism, and mining due to its natural resources and proximity to the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Understanding the Importance of South Sudan’s States:
The division of South Sudan into states is essential for effective governance, development, and representation of diverse communities. Each state has a unique character, reflecting its history, geography, and cultural heritage. By understanding the specific needs and challenges of each state, the government can develop targeted policies and initiatives for promoting sustainable development, fostering peace, and improving the lives of its citizens.
FAQs about South Sudan’s States:
Q: What is the largest state in South Sudan?
A: Jonglei is the largest state in South Sudan, covering a vast area of wetlands and savanna.
Q: Which state is the most populated in South Sudan?
A: Central Equatoria is the most populated state in South Sudan, with Juba, the capital city, located within its borders.
Q: What is the main economic activity in each state?
A: The main economic activities in each state vary based on their natural resources and geographical characteristics. For example, oil production is significant in Unity, while agriculture and livestock farming dominate in states like Jonglei and Warrap.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by the states in South Sudan?
A: The states of South Sudan face a multitude of challenges, including inter-tribal conflicts, limited infrastructure, lack of access to basic services, and the impact of climate change.
Q: What are the potential opportunities for development in each state?
A: Each state in South Sudan holds unique potential for development. For example, Central Equatoria has potential for tourism and trade, while Jonglei offers opportunities for livestock farming and ecotourism.
Tips for Navigating South Sudan’s States:
- Research thoroughly: Before traveling to a specific state, it is crucial to research its current security situation, cultural norms, and any travel advisories.
- Seek local guidance: Engaging with local communities and seeking guidance from experienced individuals can provide valuable insights into navigating specific areas.
- Respect cultural sensitivities: South Sudan is a diverse country with various cultural practices and traditions. Respecting local customs and beliefs is essential for fostering positive interactions.
- Be prepared for challenges: Traveling in South Sudan can present challenges related to infrastructure, communication, and access to basic services. Be prepared for potential difficulties and pack accordingly.
Conclusion:
South Sudan’s map is a reflection of its diverse landscape, vibrant cultures, and complex history. Understanding its states is crucial for navigating the country’s political, social, and economic landscape. Each state presents unique opportunities for development and faces distinct challenges. By acknowledging the specific needs and potential of each state, South Sudan can work towards a future of peace, prosperity, and sustainable development for all its citizens.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1145399314-e930d03d09f54eac8af43203b195a987.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan’s States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!