Navigating The Holy Land In Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture
Navigating the Holy Land in Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture
Related Articles: Navigating the Holy Land in Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Holy Land in Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Holy Land in Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture

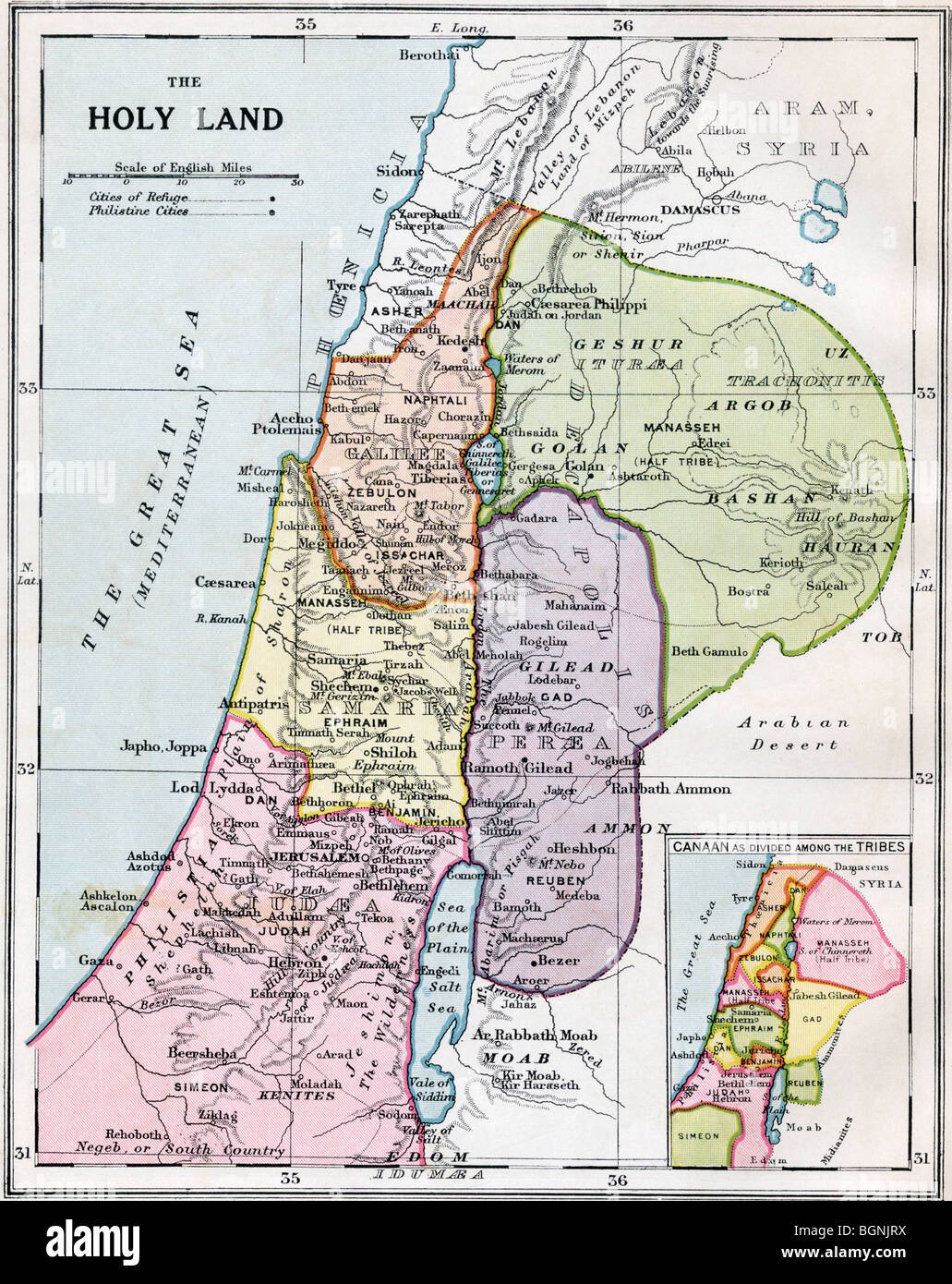
The Holy Land, a region steeped in history and religious significance, holds a profound place in the narratives of the Bible. Understanding its geography during biblical times is crucial for appreciating the context, events, and characters that shaped the stories we hold dear. This article delves into the map of the Holy Land in biblical times, exploring its physical features, key locations, and the impact of its geography on the lives of its inhabitants.
The Physical Landscape:
The Holy Land, encompassing modern-day Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and parts of Syria, is a land of diverse landscapes. The region is characterized by:
- The Mediterranean Coast: A narrow coastal plain, often fertile and dotted with ancient cities like Jaffa and Caesarea Maritima.
- The Coastal Plain: A fertile region, often referred to as the "Shephelah," stretching inland from the coast, offering agricultural potential.
- The Central Highlands: A mountainous region, home to Jerusalem and Hebron, with rugged terrain and strategic importance.
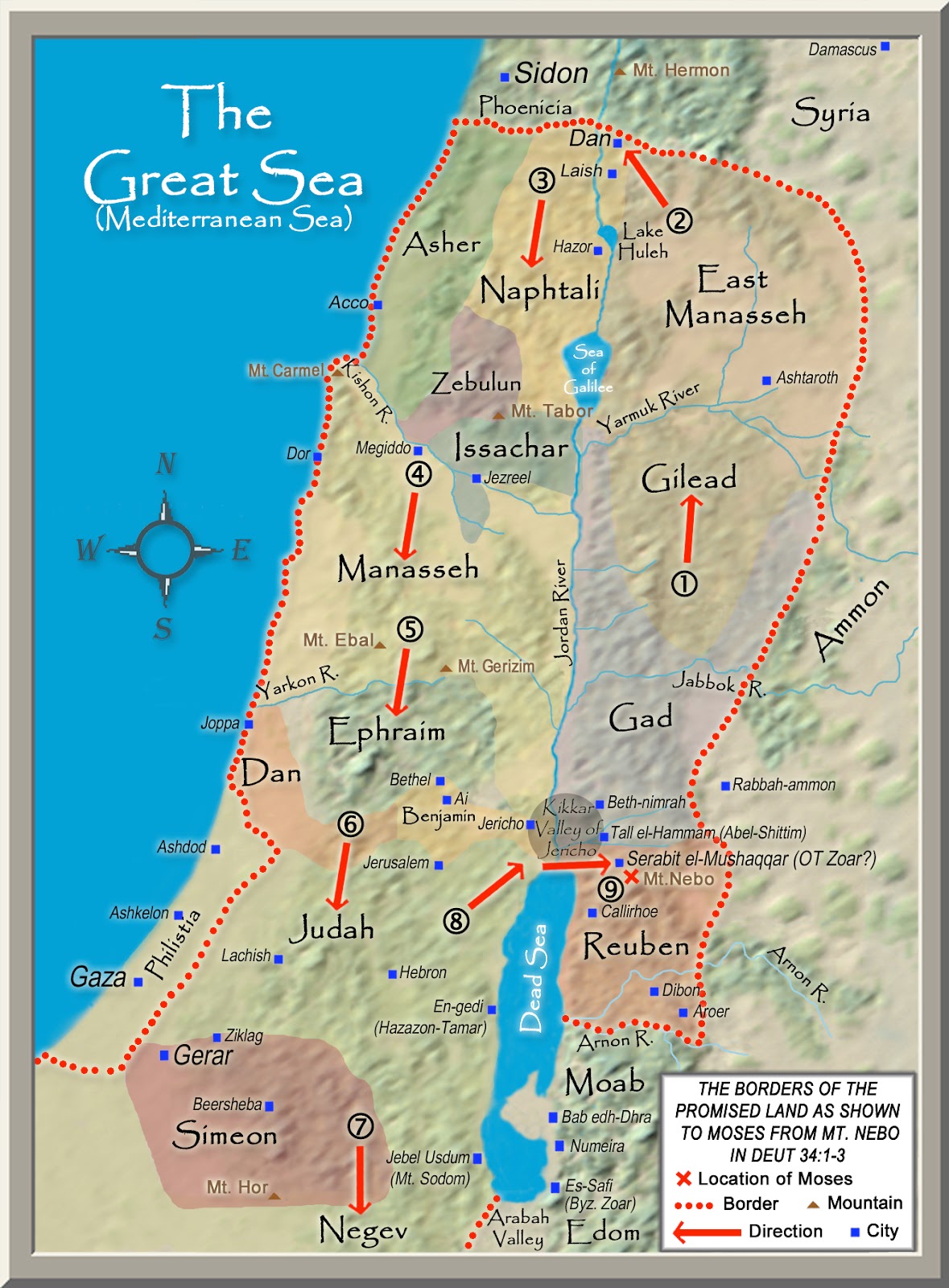
- The Jordan Rift Valley: A deep geological fault, running from north to south, containing the Jordan River and the Dead Sea, a unique and challenging landscape.
- The Transjordan: The eastern side of the Jordan River, comprising the Gilead and Moab regions, known for its rolling hills and fertile plains.
- The Negev Desert: A vast, arid region in the south, sparsely populated, but offering important trade routes.
Key Locations and Their Significance:
The Holy Land, with its diverse geography, provided a backdrop for numerous biblical events and narratives. Understanding the locations and their significance is essential for appreciating the context of the stories:
- Jerusalem: The "City of David," a central location in the Bible, serving as the capital of the united kingdom of Israel and later as the center of Jewish religious life. It is the location of the Temple Mount, a site of immense spiritual importance.
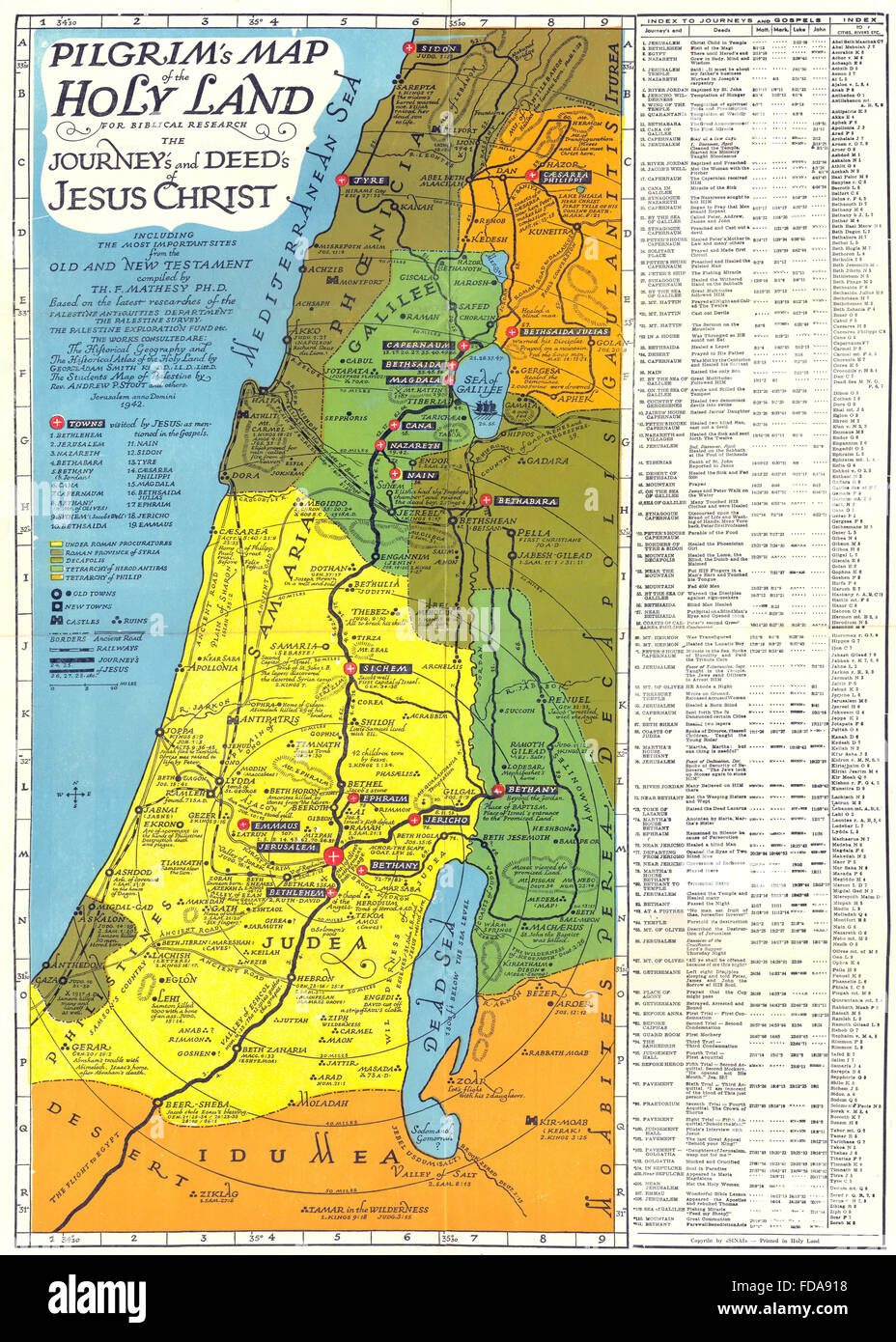
- Bethlehem: The birthplace of Jesus Christ, situated in the Judean hills, a small town that holds profound significance for Christians.
- Nazareth: The hometown of Jesus, located in Galilee, a region known for its diverse population and agricultural richness.
- Galilee: A region in the north, known for its fertile plains and its role in the ministry of Jesus.
- Samaria: A region in the north, often contested between Israel and Judah, known for its mixed population and its role in the story of the Northern Kingdom.
- Caesarea Maritima: A coastal city built by Herod the Great, serving as a Roman administrative center, a testament to the Roman influence in the region.
The Impact of Geography on Life in Biblical Times:
The Holy Land’s diverse geography played a crucial role in shaping the lives of its inhabitants, influencing:
- Agriculture and Trade: The fertile regions of the coastal plain and Galilee supported agriculture, while the strategic location of the Holy Land facilitated trade routes connecting the Mediterranean world with the East.
- Political Boundaries and Conflicts: The diverse landscape, with its natural barriers, contributed to the formation of kingdoms and the development of distinct cultural identities, often leading to conflicts and territorial disputes.
- Religious Practices and Beliefs: The presence of mountains, rivers, and deserts influenced religious beliefs and practices, with these natural features often imbued with spiritual significance.
- Social Structure and Daily Life: The geography influenced the development of different communities, each adapted to its specific environment, shaping their social structures and daily life.
FAQs on the Map of the Holy Land in Biblical Times:
1. What was the main difference between the Northern Kingdom (Israel) and the Southern Kingdom (Judah) in terms of geography?
The Northern Kingdom (Israel) occupied the more fertile regions of Galilee and the northern Shephelah, while the Southern Kingdom (Judah) encompassed the central highlands, including Jerusalem and the Negev Desert. This difference in geography contributed to their differing economic and political development.
2. How did the Jordan River and the Dead Sea influence the lives of the people living in the region?
The Jordan River served as a vital water source and a natural boundary, while the Dead Sea, with its unique properties, offered opportunities for salt production and trade. Both features played significant roles in the cultural and economic life of the region.
3. What was the significance of the coastal plain in biblical times?
The coastal plain, with its fertile land and access to the Mediterranean Sea, was crucial for agriculture, trade, and communication. It served as a hub for connecting the Holy Land with the wider world.
4. Why was Jerusalem considered a strategic location?
Jerusalem, situated in the central highlands, offered strategic advantages due to its elevated position and its control over important trade routes. Its location contributed to its importance as a religious and political center.
5. How did the geography of the Holy Land influence the development of different cultures and communities?
The diverse landscape, with its fertile plains, mountainous regions, and deserts, led to the development of distinct cultures and communities, each adapted to its specific environment. This diversity contributed to the rich tapestry of the Holy Land’s history.
Tips for Studying the Map of the Holy Land in Biblical Times:
- Use a reliable map: Choose a map specifically designed for biblical times, providing accurate geographical information and historical context.
- Focus on key locations: Identify and understand the significance of key locations mentioned in the Bible, tracing their development and importance throughout history.
- Consider the impact of geography: Analyze how the diverse landscapes influenced the lives of the people, their agriculture, trade, politics, and religious beliefs.
- Connect the map with the Bible: Use the map as a tool to visualize the stories and events described in the Bible, gaining a deeper understanding of their context.
- Explore historical resources: Consult historical texts, archaeological findings, and scholarly works to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the Holy Land’s geography and its impact on biblical narratives.
Conclusion:
The map of the Holy Land in biblical times offers a window into a world rich in history, faith, and cultural diversity. Understanding the physical features, key locations, and the impact of geography on the lives of its inhabitants is crucial for appreciating the context and significance of the biblical narratives. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the stories, characters, and events that shaped the Holy Land and its enduring legacy.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Holy Land in Biblical Times: A Geographical Journey Through Scripture. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!