Mapping The Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory And Its Significance
Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance
Related Articles: Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance
- 3.1 Defining Inuit Territory: A Complex Landscape
- 3.2 Mapping the Inuit Experience: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives
- 3.3 The Importance of Mapping Inuit Territory: A Multifaceted Perspective
- 3.4 FAQs on Inuit Territory Mapping
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding Inuit Territory
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Tapestry of Resilience and Cultural Heritage
- 4 Closure
Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance
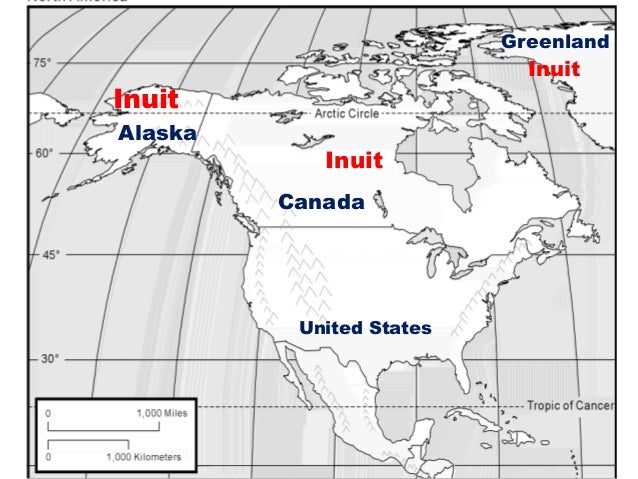
The Arctic, a vast and unforgiving landscape, is home to a unique and resilient people – the Inuit. Their ancestral lands, spanning across vast stretches of northern Canada, Greenland, Alaska, and Russia, hold profound cultural, historical, and ecological significance. Understanding the intricate tapestry of Inuit territory is crucial for appreciating their enduring connection to the land and the challenges they face in the 21st century.
Defining Inuit Territory: A Complex Landscape
Inuit territory is not a singular, clearly defined geographical entity. It encompasses a vast, interconnected network of lands and waters, each holding unique cultural and ecological significance. The precise boundaries of Inuit territory are often fluid, evolving over generations and influenced by historical events, treaty agreements, and contemporary political realities.
Key Features of Inuit Territory:
- Landscapes: The Inuit inhabit diverse landscapes, including vast tundra, ice-covered seas, rugged mountains, and fertile river valleys. These environments provide sustenance and resources for their traditional way of life.
- Sea Ice: The Arctic sea ice, a crucial element of the Inuit ecosystem, serves as a hunting ground, a travel route, and a vital component of their cultural identity. Its rapid decline due to climate change presents a significant threat to their livelihoods and traditions.
- Wildlife: The Arctic is rich in wildlife, including caribou, seals, polar bears, walrus, and fish. These animals are central to Inuit culture and provide sustenance, clothing, and tools.
- Traditional Knowledge: Inuit possess an extensive body of knowledge about the Arctic environment, its resources, and its intricate ecosystems. This knowledge, passed down through generations, is crucial for navigating the challenges of life in the Arctic.
Mapping the Inuit Experience: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives
Mapping Inuit territory involves more than just delineating geographical boundaries. It encompasses a deeper understanding of their historical struggles, cultural expressions, and contemporary challenges.
Historical Context:
- Pre-Colonial Era: Prior to European contact, the Inuit had established distinct cultural regions, each with its unique language, customs, and hunting practices. Their territory was defined by the movement of wildlife, seasonal migrations, and the shared knowledge of the land.
- Colonial Era: European colonization brought significant changes to Inuit territory. Land claims were asserted, resources were exploited, and traditional ways of life were disrupted. This period saw the displacement of Inuit communities and the imposition of foreign laws and practices.
- Treaty Negotiations: In the 20th century, Inuit began negotiating land claims with governments, aiming to secure recognition of their rights and ownership of their traditional territories. These treaties, while acknowledging Inuit rights, often fell short of fully recognizing their ancestral claims.
Contemporary Challenges:
- Climate Change: The Arctic is experiencing the most rapid warming on Earth, impacting sea ice, wildlife, and Inuit communities. Melting sea ice disrupts traditional hunting practices, while rising temperatures threaten the permafrost, impacting infrastructure and cultural sites.
- Resource Development: The Arctic holds significant mineral and energy resources, attracting global attention. Development activities can threaten Inuit lands, resources, and cultural heritage.
- Self-Determination: Inuit communities are increasingly advocating for self-determination, seeking greater control over their lands, resources, and governance. This struggle involves asserting their cultural identity and ensuring their rights are respected.
The Importance of Mapping Inuit Territory: A Multifaceted Perspective
Mapping Inuit territory serves several crucial purposes:
- Cultural Preservation: Accurate maps can help document and preserve Inuit cultural heritage, including traditional knowledge, stories, and historical sites.
- Environmental Stewardship: Mapping Inuit territory can inform conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of sensitive ecosystems and the sustainable management of resources.
- Economic Development: Mapping can facilitate sustainable economic development that respects Inuit rights and values, promoting opportunities within their traditional territories.
- Political Recognition: Mapping Inuit territory can contribute to the recognition of their land claims and their right to self-determination.
FAQs on Inuit Territory Mapping
1. What is the difference between Inuit territory and Inuit land claims?
Inuit territory refers to the vast geographical areas traditionally inhabited by Inuit communities. Inuit land claims, on the other hand, are legal claims made by Inuit organizations seeking recognition of their rights to specific areas of land and resources. These claims are often based on historical use and occupation of the territory.
2. How do Inuit territories differ across the Arctic region?
Inuit territories vary significantly across the Arctic, reflecting differences in language, culture, and historical experiences. For example, the Inuit of Greenland have a distinct cultural heritage and political status compared to those in Canada or Alaska.
3. What are the challenges of mapping Inuit territory?
Mapping Inuit territory presents several challenges:
- Accessibility: The Arctic is a remote and challenging environment, making access difficult and expensive.
- Data Collection: Gathering accurate data on traditional knowledge, cultural sites, and environmental conditions can be complex.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Mapping must be conducted with respect for Inuit cultural values and traditions, ensuring their voices are heard and their knowledge is incorporated.
4. What is the role of technology in mapping Inuit territory?
Technology plays a crucial role in mapping Inuit territory, enabling:
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and aerial imagery provide valuable data on land cover, sea ice, and environmental changes.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows for the creation of interactive maps, integrating diverse data sources and enabling analysis of spatial patterns.
- Community Engagement: Technology can facilitate collaboration with Inuit communities, enabling them to contribute their knowledge and perspectives.
Tips for Understanding Inuit Territory
- Engage with Inuit Communities: Seek out opportunities to learn from Inuit elders, artists, and community leaders.
- Explore Inuit Art and Culture: Immerse yourself in Inuit art, literature, and music to gain a deeper understanding of their worldview.
- Support Organizations Advocating for Inuit Rights: Contribute to organizations working to protect Inuit lands, resources, and cultural heritage.
- Stay Informed about Arctic Issues: Follow news and research related to climate change, resource development, and Inuit self-determination.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Resilience and Cultural Heritage
Mapping Inuit territory is not just about delineating geographical boundaries; it’s about understanding the intricate tapestry of their cultural heritage, historical struggles, and contemporary challenges. It’s about recognizing their enduring connection to the land, their resilience in the face of adversity, and their commitment to preserving their traditions for future generations. By acknowledging the importance of Inuit territory and supporting their efforts for self-determination, we can contribute to a more equitable and sustainable future for the Arctic and its people.


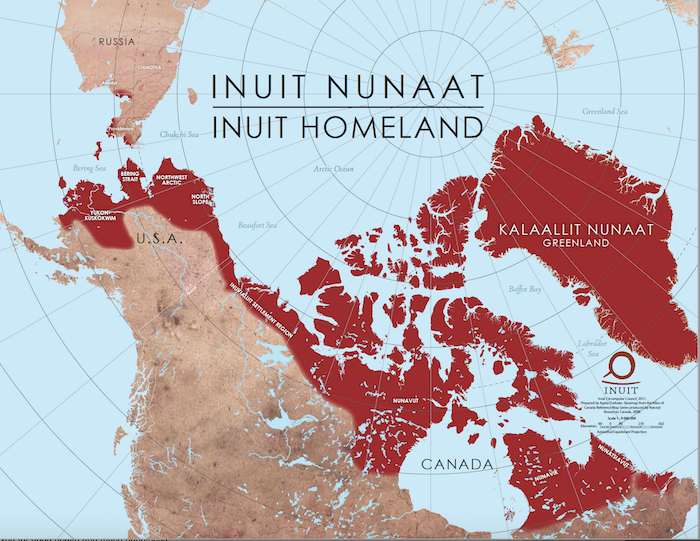
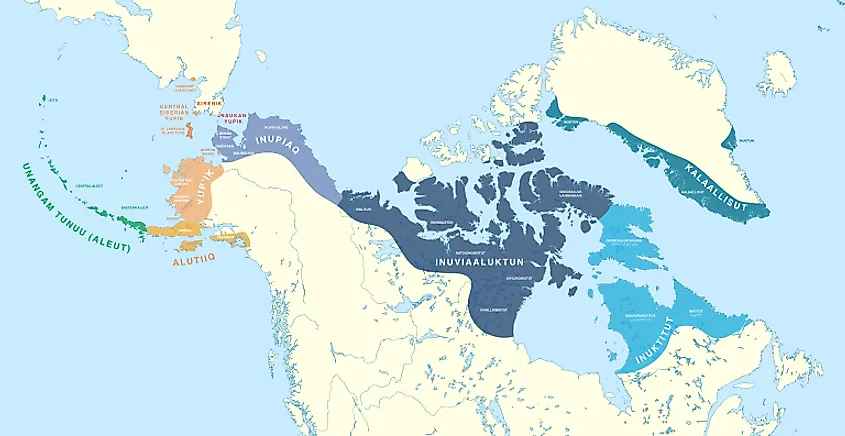
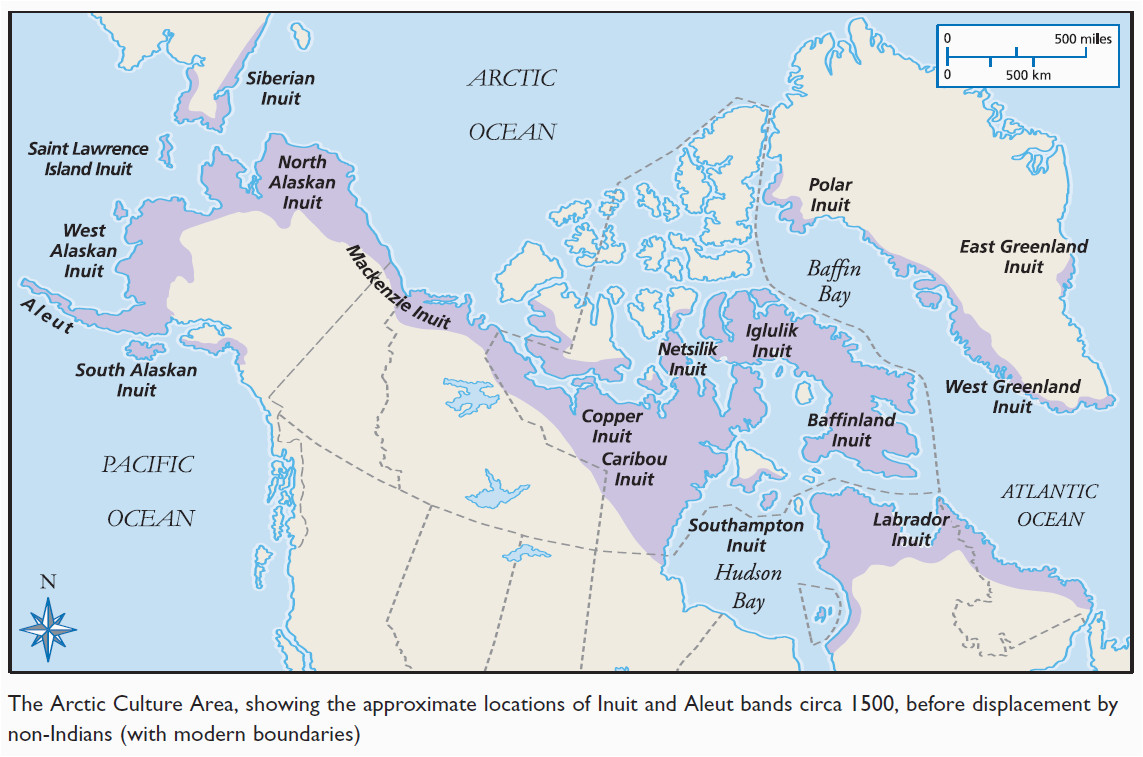



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Arctic: Understanding Inuit Territory and its Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!