India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling The Significance Of A Subtropical Nation
India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling the Significance of a Subtropical Nation
Related Articles: India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling the Significance of a Subtropical Nation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling the Significance of a Subtropical Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling the Significance of a Subtropical Nation
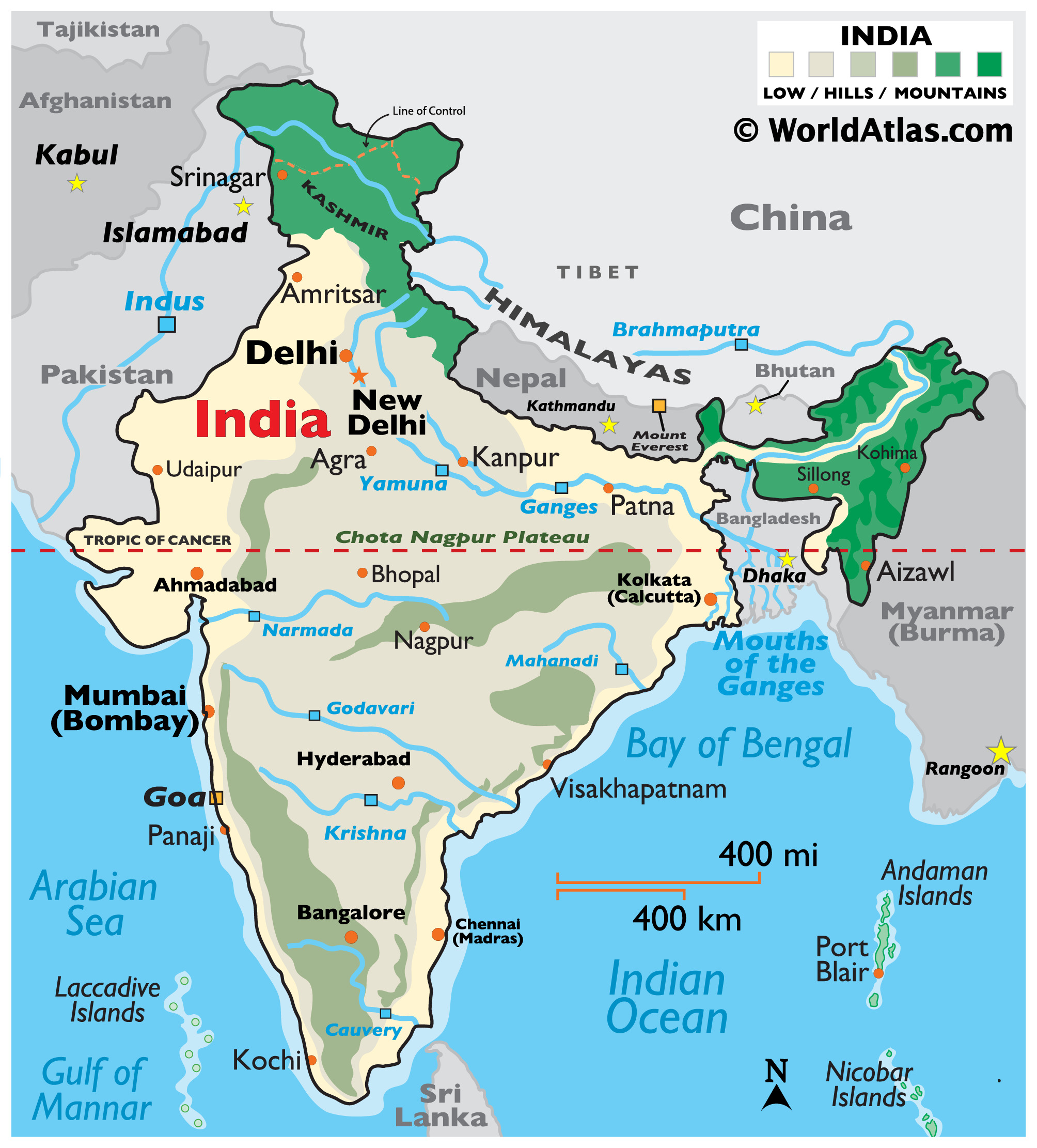
India, a land of diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage, occupies a unique position on the globe. Its location, straddling the Tropic of Cancer and situated primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, has profound implications for its climate, biodiversity, and overall geography. Understanding India’s position relative to the equator sheds light on the factors that shape its environment, influence its agriculture, and contribute to its rich tapestry of cultural and ecological diversity.
Understanding the Equator and its Significance
The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The equator is the Earth’s widest point and receives the most direct sunlight, leading to consistently warm temperatures throughout the year.
India’s Position Relative to the Equator
India, located in the Northern Hemisphere, lies south of the Tropic of Cancer, which runs through the middle of the country. This means that India is primarily situated in the subtropical zone. This unique position has a profound influence on India’s climate, biodiversity, and overall geography.
Key Implications of India’s Geographic Position
1. Climate:
- Subtropical Climate: India’s position south of the Tropic of Cancer results in a subtropical climate characterized by distinct seasons. The country experiences a hot and humid monsoon season from June to September, followed by a cool and dry winter season from December to February.
- Monsoon Winds: The monsoon winds, crucial for India’s agriculture, are driven by the differential heating of land and sea. The landmass of Asia heats up during the summer, creating low pressure, drawing in moist winds from the Indian Ocean, resulting in heavy rainfall.
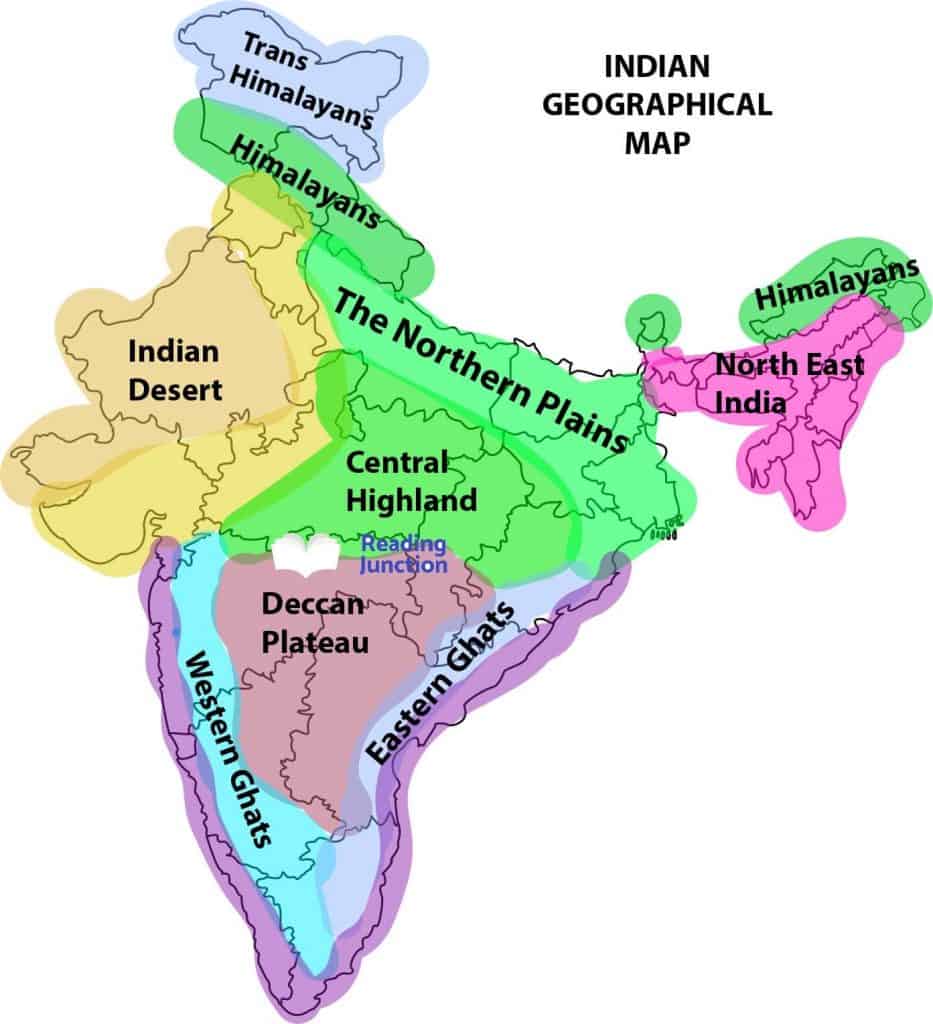
- Regional Variation: While the subtropical climate prevails across much of India, there are significant regional variations. The Himalayas in the north create a rain shadow effect, leading to drier conditions in the north-western parts of the country. The coastal areas experience a more humid climate due to the proximity to the ocean.
2. Biodiversity:
- Rich Ecosystem: India’s diverse ecosystems, ranging from snow-capped mountains to lush tropical rainforests, are a result of its geographic position. The country is home to a vast array of flora and fauna, including many endemic species.
- Endangered Species: The unique habitats of India, influenced by its proximity to the equator and the Himalayas, provide a sanctuary for numerous endangered species. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these species and their habitats.
3. Agriculture:
- Monsoon Dependence: The monsoon rains are crucial for India’s agriculture, providing much-needed irrigation for crops. However, the unpredictability of the monsoon can lead to droughts or floods, impacting agricultural production.
- Crop Diversity: India’s diverse climate zones support a wide range of crops, including rice, wheat, pulses, and fruits. The country is a major agricultural producer and exporter, contributing significantly to global food security.
4. Cultural Diversity:
- Influence on Traditions: India’s position south of the Tropic of Cancer has influenced its cultural traditions. The monsoon season, for instance, is celebrated with festivals and rituals in many parts of the country.
- Architectural Styles: The varying climatic conditions across India have influenced architectural styles. Houses in the north are built to withstand cold winters, while those in the south are designed for hot and humid weather.
FAQs about India’s Geographic Position
Q: Why is India not located on the equator?
A: India is located in the Northern Hemisphere, south of the Tropic of Cancer, which is approximately 23.5 degrees north of the equator. This position places India in the subtropical zone, influencing its climate and ecosystems.
Q: What are the advantages of India’s position south of the Tropic of Cancer?
A: India’s position south of the Tropic of Cancer provides several advantages, including:
- Rich biodiversity: The subtropical climate supports a wide range of plant and animal life, making India a biodiversity hotspot.
- Abundant rainfall: The monsoon rains are crucial for agriculture, providing irrigation and supporting a thriving agricultural sector.
- Diverse cultural traditions: The varying climatic conditions have shaped India’s cultural traditions, leading to a rich tapestry of festivals, languages, and customs.
Q: What are the challenges posed by India’s geographic position?
A: While India’s geographic position offers advantages, it also poses challenges:
- Unpredictable monsoon: The monsoon rains are crucial for agriculture but can be unpredictable, leading to droughts or floods.
- Climate change impacts: India is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events.
- Biodiversity conservation: The unique habitats of India are threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and poaching, requiring robust conservation efforts.
Tips for Understanding India’s Geographic Position
- Use maps and globes: Visualizing India’s location on a map or globe helps understand its position relative to the equator and other geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Websites and educational materials can provide detailed information about India’s geography, climate, and ecosystems.
- Travel to India: Experiencing India firsthand allows you to witness the diversity of its landscapes, cultures, and people, influenced by its unique geographic location.
Conclusion
India’s geographic position south of the Tropic of Cancer has profound implications for its climate, biodiversity, agriculture, and cultural traditions. Understanding this position provides valuable insights into the factors that shape India’s diverse landscape, its rich cultural heritage, and its role in the global ecosystem. By appreciating the significance of India’s unique location, we can better understand the challenges and opportunities facing this nation and contribute to its sustainable development.
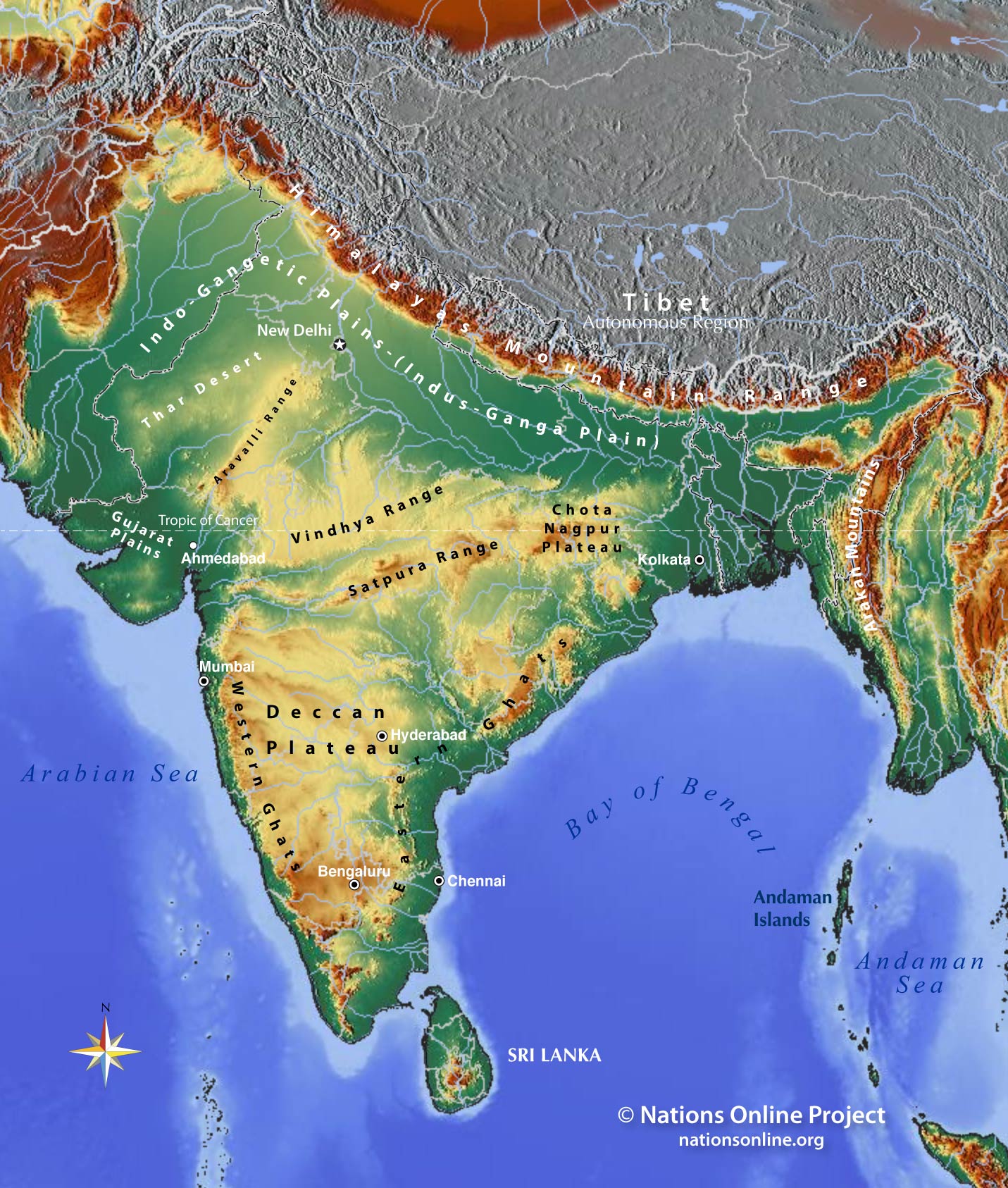


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into India’s Geographic Position: Unveiling the Significance of a Subtropical Nation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!