Charting The World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide To Wildlife Maps
Charting the World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide to Wildlife Maps
Related Articles: Charting the World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide to Wildlife Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide to Wildlife Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide to Wildlife Maps
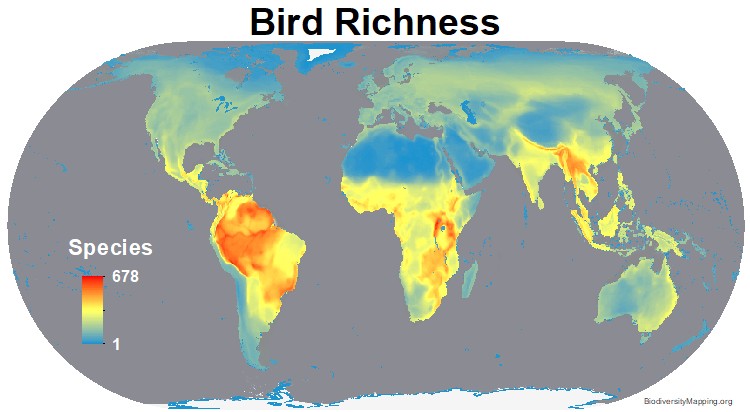
The Earth’s biodiversity is a tapestry woven from countless species, each playing a vital role in the intricate web of life. Understanding the distribution and abundance of these species is crucial for conservation efforts, scientific research, and informed decision-making. This is where wildlife maps come into play, providing a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing the complex patterns of life across the globe.
The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Patterns of Life
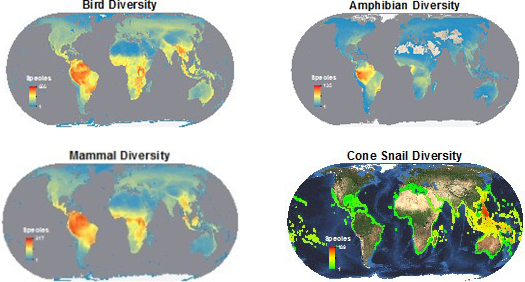
Wildlife maps are not merely static representations of species locations; they are dynamic tools that offer a glimpse into the intricate relationships between species, their habitats, and the environmental factors that influence their distribution. By visualizing data on species richness, population density, habitat ranges, and migration patterns, these maps provide a comprehensive understanding of biodiversity and its dynamics.
Types of Wildlife Maps: A Diverse Toolkit
The world of wildlife maps is as diverse as the species they represent. Different types of maps serve specific purposes, each providing valuable insights into the state of biodiversity.
- Species Distribution Maps: These maps depict the geographical areas where specific species are found, providing a clear picture of their current range and potential for expansion or contraction. This information is crucial for understanding the factors driving species distribution and predicting potential threats.
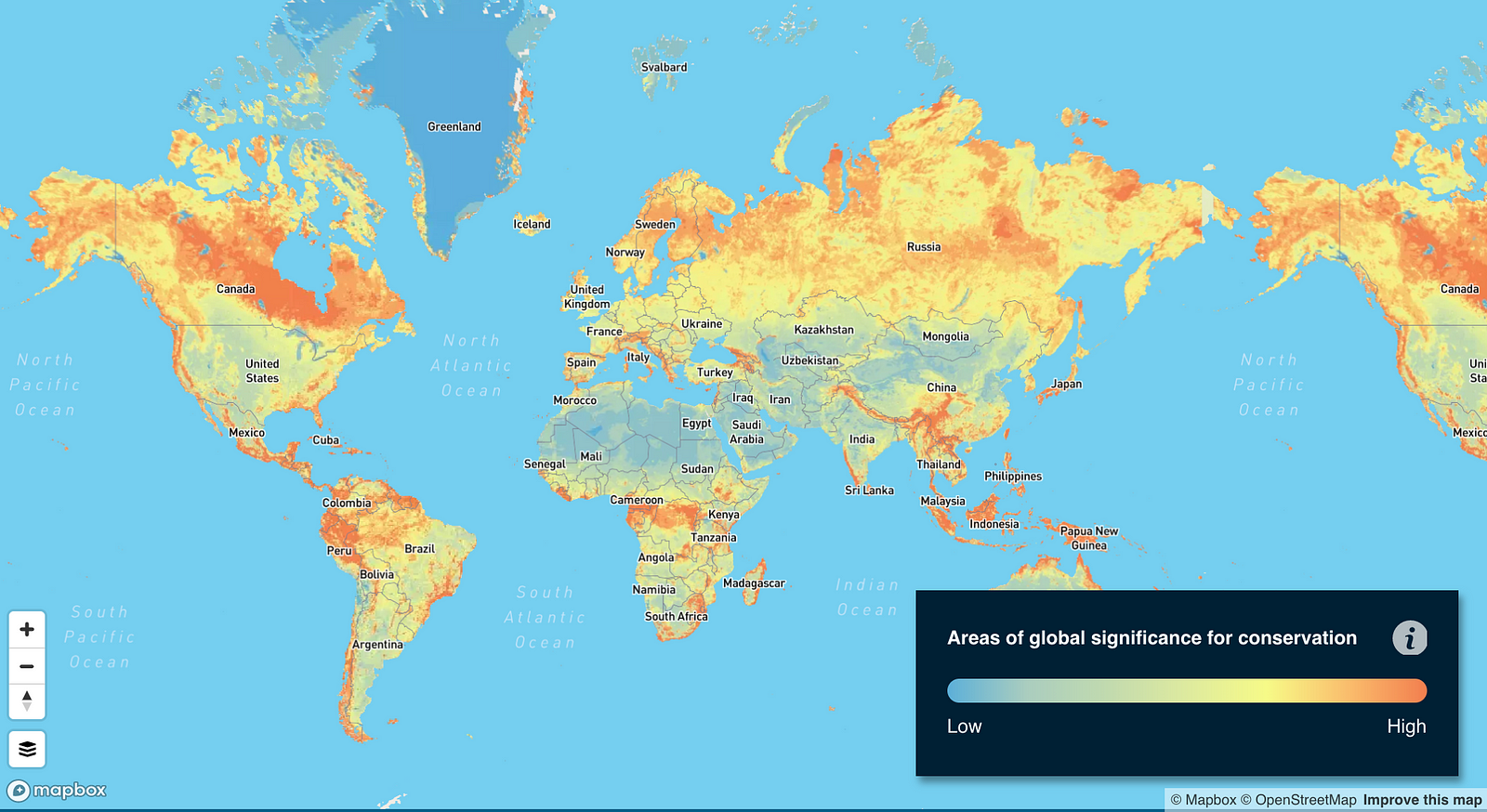
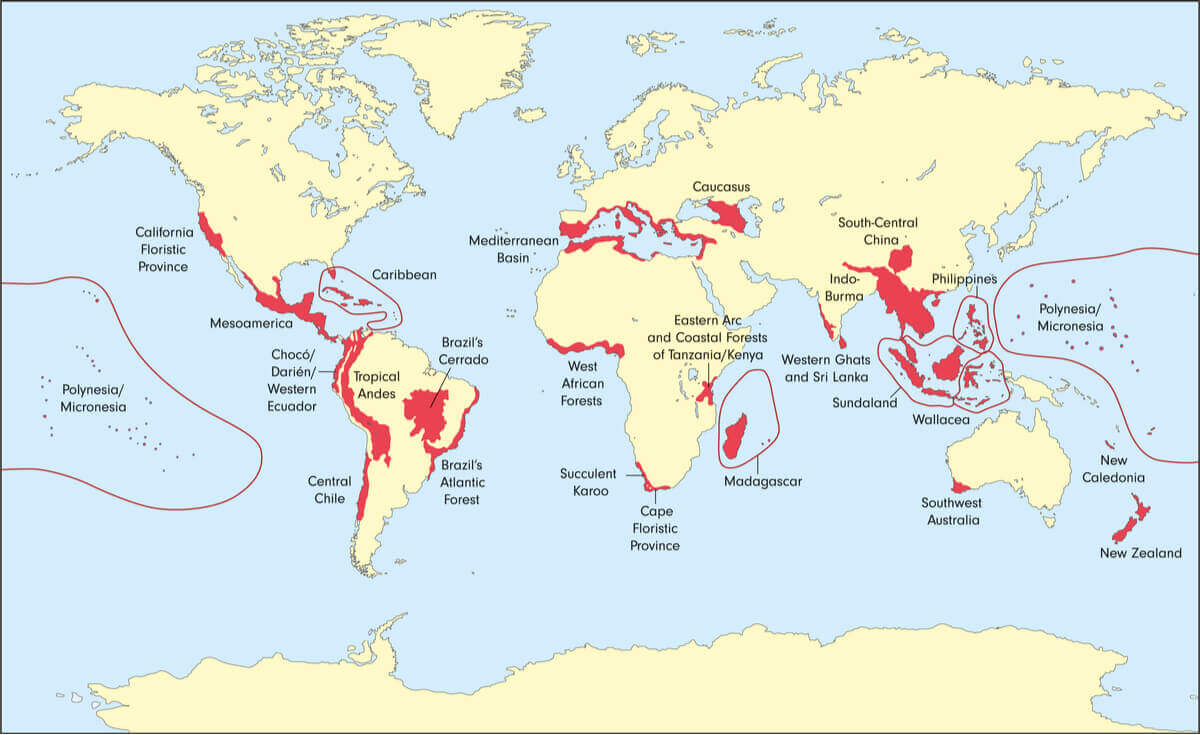
- Biodiversity Hotspot Maps: These maps highlight regions with exceptionally high concentrations of endemic species, often facing significant threats. These hotspots serve as focal points for conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of unique and vulnerable biodiversity.
- Habitat Suitability Maps: These maps predict the suitability of different areas for specific species based on environmental variables such as climate, vegetation, and elevation. They help identify areas with optimal conditions for species survival and guide habitat restoration and management strategies.
- Migration Route Maps: These maps track the movements of migratory species, revealing their seasonal journeys and the ecological corridors they rely on. Understanding these patterns is essential for protecting migratory routes from human disturbances and ensuring the long-term viability of these species.
- Conservation Status Maps: These maps visually depict the conservation status of different species, indicating their level of threat and urgency for conservation action. This information is critical for prioritizing conservation efforts and directing resources towards species most in need.
The Importance of Wildlife Maps: A Foundation for Conservation
Wildlife maps play a pivotal role in conservation efforts, serving as a foundation for informed decision-making and effective action.
- Targeted Conservation Efforts: By identifying areas with high biodiversity and vulnerable species, maps guide conservationists towards targeted interventions. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to the areas where they will have the greatest impact.
- Habitat Management and Restoration: Maps help identify suitable habitats for species and guide efforts to restore degraded ecosystems. This information is crucial for creating corridors that connect fragmented habitats, facilitating species movement and promoting genetic diversity.
- Species Monitoring and Management: Maps provide a framework for tracking changes in species distribution and abundance over time. This information is vital for identifying threats, evaluating the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and adapting management plans as needed.
- Policy and Decision-Making: Maps provide a visual representation of the complex interactions between humans and the natural world. This information informs policy decisions regarding land use, resource management, and environmental regulations, ensuring that biodiversity considerations are integrated into development plans.
Beyond Conservation: Applications in Research and Education
The utility of wildlife maps extends beyond conservation, playing a vital role in scientific research and public education.
- Scientific Research: Maps provide a basis for understanding species distribution, habitat requirements, and population dynamics. This information is crucial for ecological research, climate change modeling, and developing strategies for mitigating human impacts on biodiversity.
- Public Education and Awareness: Maps serve as powerful tools for communicating the importance of biodiversity and raising awareness about conservation issues. By visualizing the distribution of endangered species and threatened ecosystems, maps can engage the public and inspire action.
FAQs about Wildlife Maps
1. How are wildlife maps created?
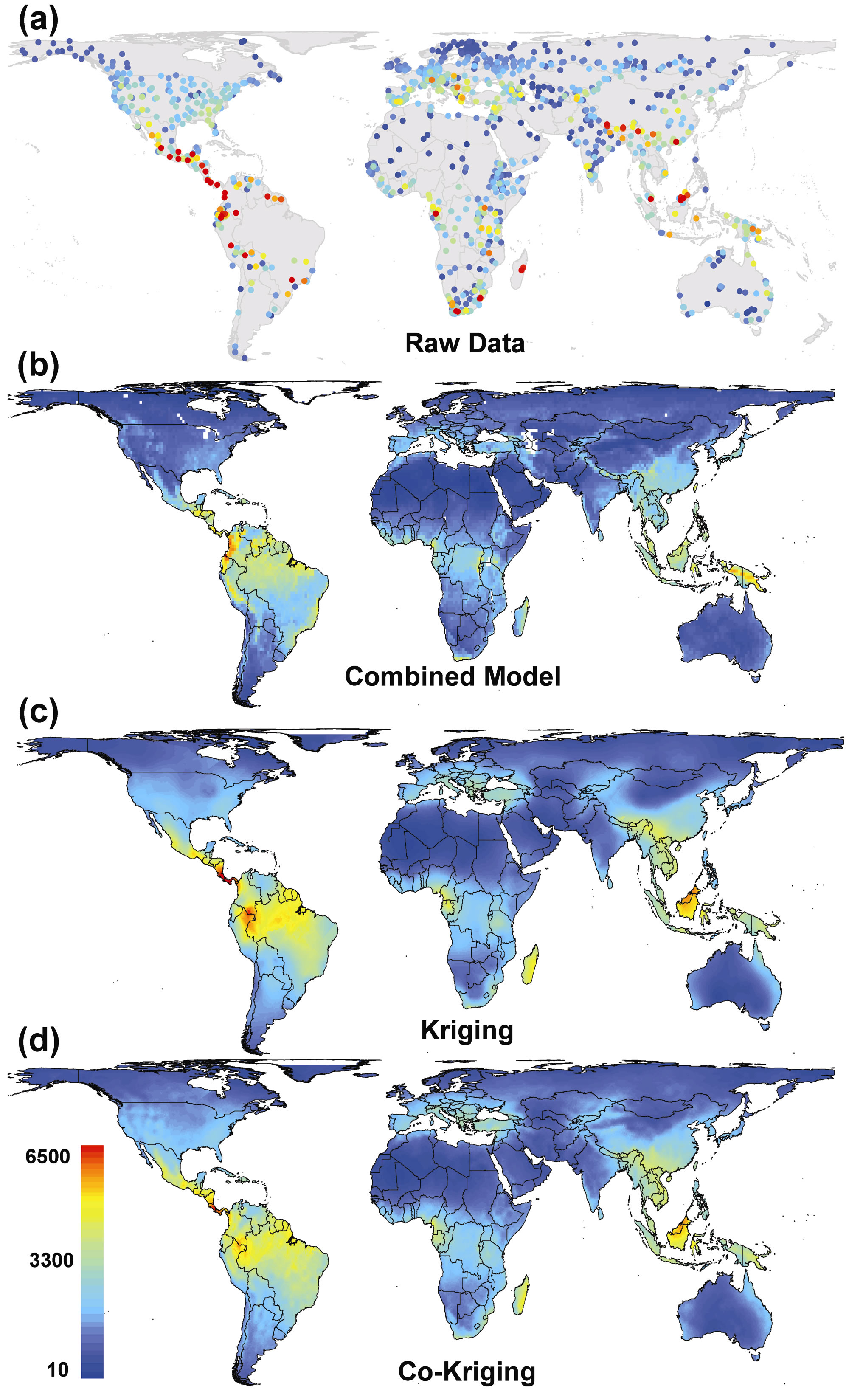
Wildlife maps are created using a combination of data sources, including:
- Species Occurrence Data: This data comes from field observations, museum records, and citizen science initiatives, providing information on the locations where species have been observed.
- Remote Sensing Data: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide information on habitat types, vegetation cover, and land use patterns, which are crucial for predicting species distribution and habitat suitability.
- Environmental Data: Climate data, elevation maps, and soil information provide insights into the environmental conditions that influence species distribution and abundance.
- Modeling Techniques: Statistical and spatial modeling techniques are used to analyze data and predict species distribution based on environmental factors and known occurrence data.
2. What are the limitations of wildlife maps?
While wildlife maps are powerful tools, they have certain limitations:
- Data Availability: The accuracy of maps depends on the quality and availability of data. Data gaps can lead to incomplete or inaccurate representations of species distribution.
- Sampling Bias: Data collection efforts may be biased towards certain areas or species, leading to underrepresentation of certain species or regions.
- Dynamic Nature of Biodiversity: Biodiversity is constantly changing, and maps may not capture recent shifts in species distribution or abundance.
- Uncertainty in Predictions: Models used to predict species distribution are based on assumptions and may not always accurately reflect real-world conditions.
3. How can I access wildlife maps?
There are numerous resources for accessing wildlife maps, including:
- Government Agencies: Agencies such as the United States Fish and Wildlife Service and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration provide maps and data on species distribution and conservation status.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund and Conservation International develop and share maps related to biodiversity hotspots, endangered species, and conservation efforts.
- Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions often develop and publish maps related to their research projects.
- Online Platforms: Websites like the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and the IUCN Red List provide access to a vast amount of data and maps on species distribution and conservation status.
Tips for Using Wildlife Maps Effectively
- Understand the Data Sources: Before using a wildlife map, it is essential to understand the data sources and methods used to create it. This will help you evaluate the reliability and limitations of the map.
- Consider the Scale: Wildlife maps can be created at different scales, from local to global. Choose a map that is appropriate for your specific needs and the scale of your research or project.
- Combine Different Data Sources: Combining information from different maps and data sources can provide a more comprehensive understanding of biodiversity and its dynamics.
- Interpret with Caution: Wildlife maps are tools for visualizing data, not absolute representations of reality. Interpret the information with caution and consider potential biases and uncertainties.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Protecting Biodiversity
Wildlife maps are essential tools for understanding and protecting the Earth’s biodiversity. By visualizing the distribution and abundance of species, these maps provide insights into the complex patterns of life, guide conservation efforts, inform policy decisions, and raise public awareness. As the world faces increasing threats to biodiversity, wildlife maps will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring the survival of our planet’s rich and diverse life forms.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the World’s Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Guide to Wildlife Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!