Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map Of Abundance And Opportunity
Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map of Abundance and Opportunity
Related Articles: Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map of Abundance and Opportunity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map of Abundance and Opportunity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map of Abundance and Opportunity
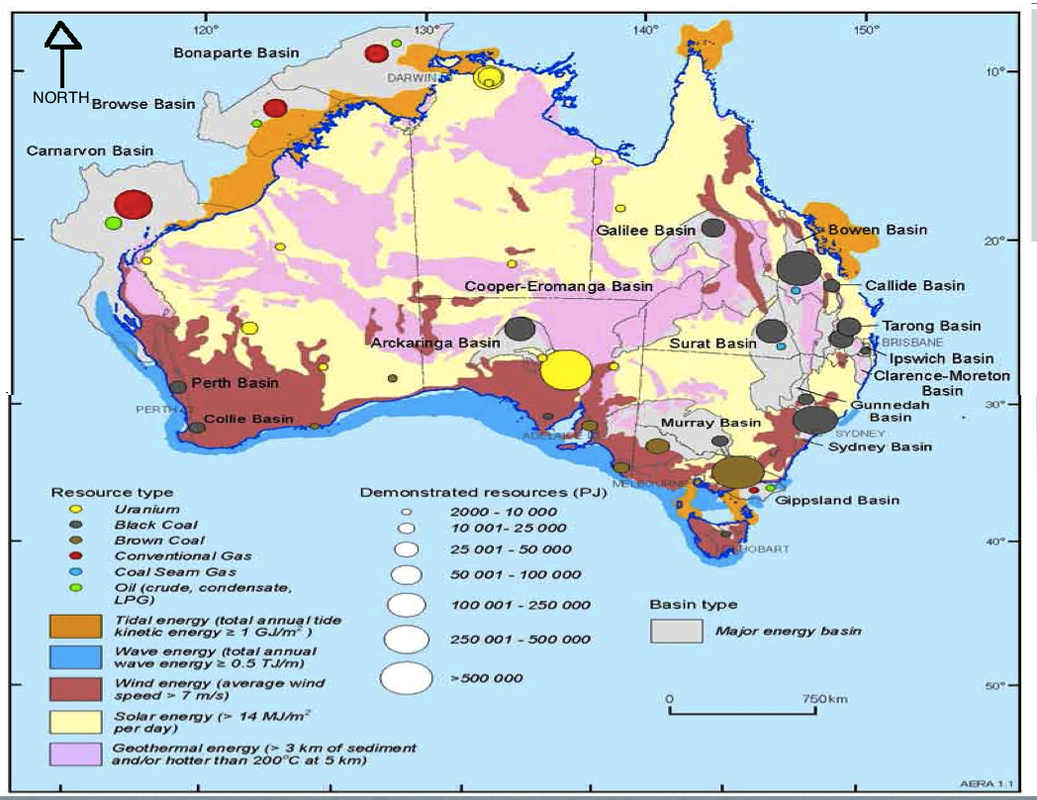
Australia, the world’s sixth-largest country, is a land of immense natural wealth. Its vast and diverse landscape harbors a treasure trove of resources that contribute significantly to its economy and global trade. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of Australia’s natural resources, exploring their distribution, significance, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
A Diverse Landscape, A Rich Resource Base
Australia’s geological history, characterized by tectonic activity and ancient landmasses, has sculpted a landscape teeming with mineral deposits, energy sources, and agricultural potential. The country’s natural resources map is a vibrant testament to this geological legacy, showcasing a remarkable array of commodities:
Mineral Resources:
- Iron Ore: Australia is the world’s largest exporter of iron ore, with vast deposits concentrated in Western Australia’s Pilbara region. This ferrous metal is a vital ingredient in steel production, underpinning global infrastructure development.
- Coal: Australia boasts significant reserves of both thermal and coking coal, primarily located in New South Wales, Queensland, and Victoria. These resources fuel power generation and are crucial for steelmaking.
- Bauxite: Australia is a major producer of bauxite, the raw material for aluminum production. Deposits are concentrated in Western Australia and Queensland, supplying a global market hungry for this lightweight and versatile metal.
- Gold: Australia is a renowned gold producer, with significant deposits in Western Australia, Victoria, and Queensland. The country’s gold mines contribute to its economic prosperity and are a symbol of its mining heritage.
- Copper: Australia is a leading producer of copper, a vital metal used in numerous industries, including construction, electronics, and transportation. Deposits are found in various states, including Queensland, Western Australia, and South Australia.
- Other Minerals: Australia’s mineral wealth extends beyond these key commodities, encompassing resources like nickel, zinc, lead, manganese, uranium, and rare earth elements. These diverse mineral deposits contribute to the country’s economic diversification and global supply chains.
Energy Resources:
- Coal-Fired Power: Coal remains a significant energy source in Australia, contributing to the country’s electricity generation. While the nation is transitioning towards renewable energy sources, coal continues to play a role in meeting energy demands.
- Natural Gas: Australia possesses substantial reserves of natural gas, primarily in Queensland and Western Australia. This clean-burning fossil fuel is used for electricity generation, industrial processes, and domestic consumption.
- Renewable Energy: Australia is blessed with abundant renewable energy resources, including solar, wind, and hydro power. The country is investing heavily in developing these sustainable energy sources to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Agricultural Resources:
- Arable Land: Australia possesses vast tracts of arable land, suitable for cultivating a wide range of crops. Wheat, barley, cotton, and sugar cane are among the major agricultural commodities produced in the country.
- Livestock: Australia is a major producer of livestock, particularly beef, sheep, and dairy products. The country’s vast grazing lands provide ample space for livestock farming, contributing significantly to the global food supply.
- Fisheries: Australia’s extensive coastline and surrounding waters harbor a rich diversity of marine life, supporting a thriving fishing industry. The country is a major exporter of seafood, including prawns, tuna, and lobster.
Navigating the Resource Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
While Australia’s natural resource endowment presents immense economic potential, it also presents challenges that require careful management and sustainable practices:
- Environmental Impact: Mining and energy extraction can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat loss, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable resource management practices are essential to minimize these impacts and protect the environment.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses a significant threat to Australia’s natural resources, impacting water availability, agricultural productivity, and coastal ecosystems. The country is actively working to mitigate climate change through renewable energy development and carbon emissions reduction.
- Global Market Volatility: Fluctuations in global commodity prices can impact the profitability of Australia’s resource industries. Diversification and value-adding activities are crucial to mitigate price volatility and ensure long-term economic stability.
- Indigenous Land Rights: Indigenous communities have traditional land ownership and cultural connections to many resource-rich areas. Respecting Indigenous rights and engaging in meaningful consultation is essential for responsible resource development.
Navigating the Future: A Focus on Sustainability
Australia is increasingly prioritizing sustainable resource management to ensure the long-term viability of its natural wealth. This involves:
- Investing in Renewable Energy: Australia is actively transitioning towards a renewable energy future, investing in solar, wind, and hydro power projects. This shift will reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Promoting Circular Economy Principles: The country is embracing circular economy principles, promoting resource reuse, recycling, and waste reduction. This approach minimizes environmental impact and maximizes resource efficiency.
- Investing in Research and Development: Australia is supporting research and development in areas such as resource extraction technology, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture. These investments will drive innovation and create new opportunities for the resource sector.
- Strengthening International Collaboration: Australia is engaging in international collaborations to address global challenges related to resource management, climate change, and sustainable development.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Australia’s Resource Map
Q: What is the primary economic driver in Australia?
A: Australia’s economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources. Mining and energy extraction are major contributors to GDP, employment, and export earnings.
Q: How does Australia’s natural resource map contribute to its global standing?
A: Australia’s abundant resources make it a significant player in global commodity markets. The country is a major exporter of minerals, energy, and agricultural products, contributing to global supply chains and economic growth.
Q: What are the environmental concerns associated with resource extraction in Australia?
A: Resource extraction activities can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat loss, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable practices are essential to minimize these impacts and protect the environment.
Q: How is Australia addressing climate change in relation to its resource sector?
A: Australia is actively investing in renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and implementing carbon reduction measures to mitigate climate change and ensure the sustainability of its resource sector.
Q: How does Indigenous land ownership influence resource development in Australia?
A: Indigenous communities have traditional land ownership and cultural connections to many resource-rich areas. Respecting Indigenous rights and engaging in meaningful consultation is essential for responsible resource development.
Tips for Understanding Australia’s Resource Map
- Explore Online Resources: Websites like the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) and the Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources (DISER) provide comprehensive data and information on Australia’s natural resources.
- Consult Resource Maps: Utilize online maps and interactive platforms to visualize the distribution of different resources across Australia.
- Read Industry Reports: Stay informed about the latest trends, challenges, and opportunities in Australia’s resource sector by reading industry reports and publications.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Participate in discussions and forums to understand the perspectives of different stakeholders, including Indigenous communities, environmental groups, and industry representatives.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Abundance, A Future of Sustainability
Australia’s natural resource map is a testament to its geological history and a reflection of its economic potential. The country’s diverse landscape harbors a wealth of minerals, energy sources, and agricultural resources that contribute significantly to its prosperity and global standing. However, responsible resource management and sustainable practices are crucial to ensure the long-term viability of these assets and address the challenges posed by environmental concerns and climate change. By embracing innovation, investing in renewable energy, and promoting circular economy principles, Australia can continue to leverage its natural wealth while safeguarding its environment for future generations.




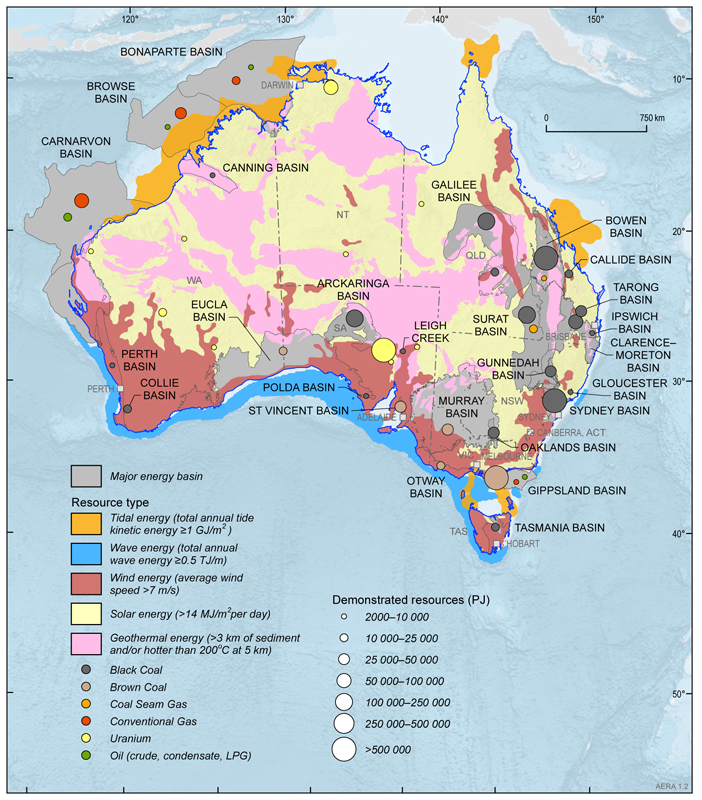

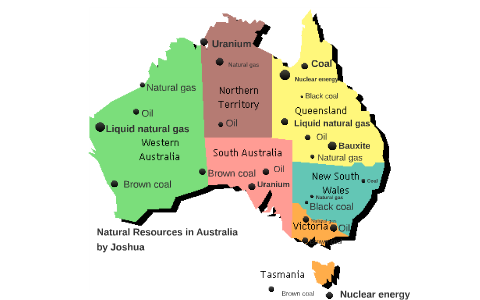
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Australia’s Natural Resource Endowment: A Map of Abundance and Opportunity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!