A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring The Significance Of Its Rivers
A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring the Significance of its Rivers
Related Articles: A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring the Significance of its Rivers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring the Significance of its Rivers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring the Significance of its Rivers

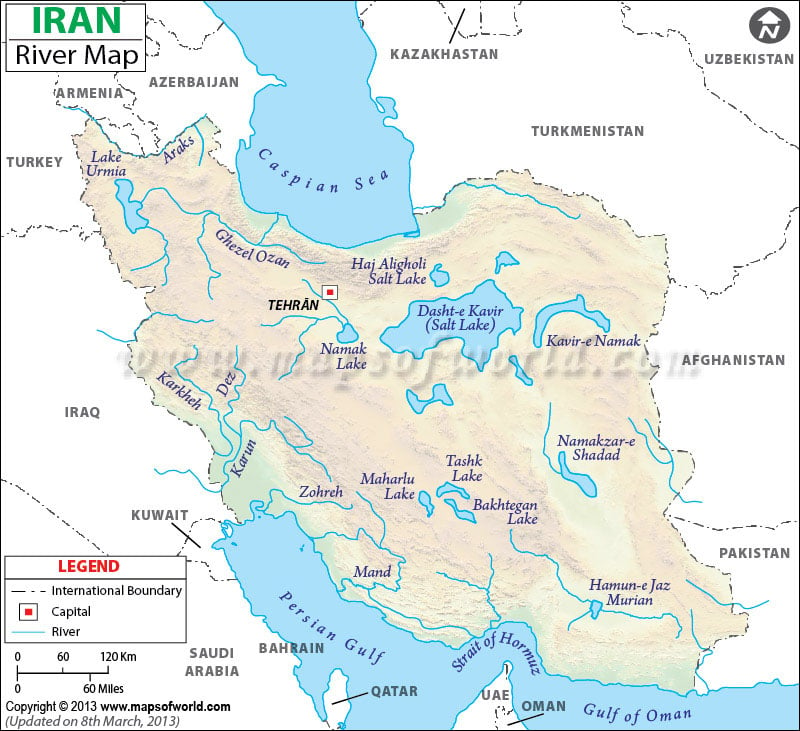
Iran, a landlocked nation nestled in the heart of the Middle East, possesses a unique geographical landscape sculpted by the interplay of mountains, deserts, and, crucially, its network of rivers. These waterways, while not as extensive as those found in other regions, play a vital role in shaping the country’s ecology, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding the characteristics and significance of Iran’s rivers provides valuable insight into the nation’s past, present, and future.
The River Systems of Iran: A Diverse Tapestry
Iran’s river systems can be categorized into two primary types:
- Endorheic basins: These rivers flow into inland lakes or salt flats, ultimately terminating without reaching the sea. They are largely concentrated in the central plateau, where arid conditions prevail.
- Exoreic basins: These rivers flow towards the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, or the Caspian Sea. They are found primarily in the western and northern regions, where rainfall is more abundant.
Major Rivers of Iran:
1. The Karun River:
- Source: Zagros Mountains
- Length: 950 km
- Discharge: 1,000 m³/s
- Significance: The longest and most voluminous river in Iran, the Karun is a vital source of irrigation for agriculture in Khuzestan province. It also serves as a crucial source of drinking water for the region and is home to a diverse ecosystem. The Karun River is also a key source of hydroelectric power, with the Karun-3 dam being a major contributor to Iran’s energy grid.
2. The Zayandeh Rud River:
- Source: Zagros Mountains
- Length: 400 km
- Discharge: 150 m³/s
- Significance: The Zayandeh Rud, meaning "life-giving river," is a lifeline for the city of Isfahan and its surrounding agricultural areas. It is a source of irrigation and drinking water, as well as a popular recreational destination. The river’s flow has been significantly impacted by drought and dam construction, leading to concerns over its sustainability.
3. The Aras River:
- Source: Armenian Highlands
- Length: 1,072 km
- Discharge: 150 m³/s
- Significance: The Aras River forms a natural border between Iran and Azerbaijan. It is a vital source of irrigation and hydroelectric power for both countries. The Aras River is also a significant habitat for numerous fish species and migratory birds.
4. The Sefid Rud River:
- Source: Alborz Mountains
- Length: 700 km
- Discharge: 100 m³/s
- Significance: The Sefid Rud, meaning "white river," is the largest river in the Caspian Sea basin. It is a crucial source of irrigation and hydroelectric power for the region. The Sefid Rud is also a popular destination for whitewater rafting and kayaking.
5. The Helmand River:
- Source: Hindu Kush Mountains
- Length: 1,150 km
- Discharge: 1,500 m³/s
- Significance: While the Helmand River flows primarily through Afghanistan, it forms a crucial part of the Sistan Basin, a shared border region between Iran and Afghanistan. The river is a source of irrigation for both countries, but its flow has been impacted by drought and dam construction, leading to tensions over water resources.
The Importance of Iran’s Rivers
Beyond their obvious role in supplying water for agriculture, drinking, and industry, Iran’s rivers hold profound significance:
- Ecological Importance: The rivers support a rich and diverse ecosystem, providing habitat for numerous fish species, birds, and other wildlife. They also play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the surrounding environment by regulating water levels, replenishing groundwater, and preventing soil erosion.
- Economic Significance: Rivers are essential for the development of agriculture, industry, and tourism in Iran. They provide irrigation for vast areas of farmland, supply water for industrial processes, and offer recreational opportunities for tourists.
- Cultural Significance: Rivers have long played a central role in Iranian culture and history. They are often depicted in art, literature, and poetry, and they are revered as symbols of life and fertility. Many ancient cities and settlements were established along riverbanks, and these waterways have been vital trade routes for centuries.
- Political Significance: The sharing of water resources between Iran and its neighboring countries, particularly in the arid regions, can be a source of tension and conflict. The equitable management of these shared resources is crucial for regional stability and cooperation.
Challenges Facing Iran’s Rivers
Despite their importance, Iran’s rivers face numerous challenges:
- Drought and Climate Change: Iran is experiencing increasing periods of drought, which significantly impact river flow and water availability. Climate change is exacerbating these trends, leading to concerns over the long-term sustainability of water resources.
- Dam Construction: The construction of numerous dams across Iran’s rivers has altered flow patterns and impacted downstream ecosystems. While dams provide benefits in terms of irrigation and hydroelectric power, they can also lead to ecological damage and social displacement.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities, as well as urban waste disposal, are contributing to pollution in many Iranian rivers. This pollution poses serious risks to human health and the environment.
- Overexploitation: The over-extraction of water for irrigation and other uses has led to the depletion of groundwater resources and the decline of river flow. This unsustainable water management practices threaten the long-term health of Iran’s rivers.
Addressing the Challenges
To ensure the sustainable management of Iran’s rivers, a multi-faceted approach is required:
- Water Conservation: Implementing efficient irrigation techniques, reducing water waste in urban areas, and promoting water-saving practices are essential for conserving water resources.
- Integrated Water Resource Management: Adopting a comprehensive approach to water resource management, considering the needs of all users and the environmental impacts of water use, is crucial for ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Environmental Protection: Strengthening environmental regulations, enforcing pollution control measures, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices are vital for protecting the ecological integrity of Iran’s rivers.
- Regional Cooperation: Collaborative efforts between Iran and its neighboring countries are essential for managing shared water resources and ensuring the equitable distribution of water.
FAQs on Iran’s Rivers:
1. What is the longest river in Iran?
The Karun River is the longest river in Iran, spanning approximately 950 km.
2. What is the most important river in Iran?
All rivers in Iran play a vital role in the country’s ecosystem and economy. However, the Karun River, due to its length, discharge, and importance for agriculture and hydroelectric power, is often considered the most important.
3. How do dams impact Iran’s rivers?
Dams can provide benefits in terms of irrigation and hydroelectric power generation. However, they can also alter river flow patterns, fragment ecosystems, and impact downstream water availability.
4. What are the main threats to Iran’s rivers?
The main threats to Iran’s rivers include drought, climate change, dam construction, pollution, and overexploitation.
5. How can Iran address the challenges facing its rivers?
Iran can address these challenges by implementing water conservation measures, promoting sustainable water management practices, strengthening environmental regulations, and fostering regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding Iran’s Rivers:
- Explore the Geography: Studying maps and satellite images of Iran can provide a better understanding of the country’s river systems and their geographic context.
- Read about Iranian History: Learning about Iran’s history, particularly its ancient civilizations, can reveal the importance of rivers in shaping the country’s cultural and economic development.
- Visit Iranian Rivers: Experiencing Iran’s rivers firsthand can provide valuable insights into their beauty, significance, and the challenges they face.
- Engage with Local Communities: Talking to people who live near Iranian rivers can provide valuable perspectives on the impact of water resources on their lives and livelihoods.
Conclusion:
Iran’s rivers are vital arteries that flow through the country’s landscape, nourishing its people, its economy, and its culture. Understanding the characteristics, importance, and challenges facing these waterways is crucial for ensuring their long-term sustainability and the well-being of the Iranian people. By promoting responsible water management practices, fostering regional cooperation, and embracing sustainable development, Iran can safeguard its precious water resources for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Iran’s Waterways: Exploring the Significance of its Rivers. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!