A Comprehensive Guide To The Geography Of Norway, Sweden, And Denmark: Exploring The Scandinavian Peninsula And Beyond
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: Exploring the Scandinavian Peninsula and Beyond
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: Exploring the Scandinavian Peninsula and Beyond
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: Exploring the Scandinavian Peninsula and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: Exploring the Scandinavian Peninsula and Beyond
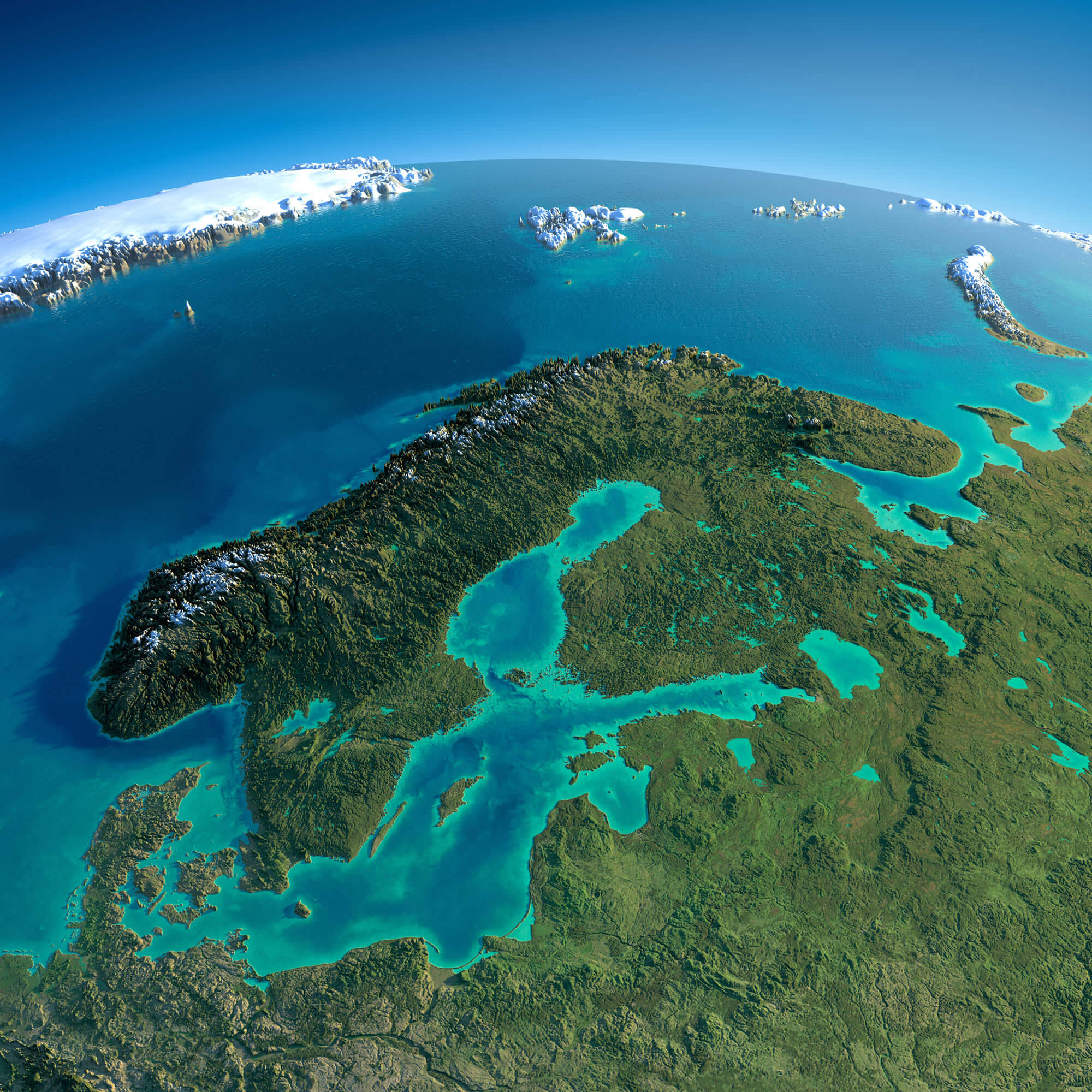
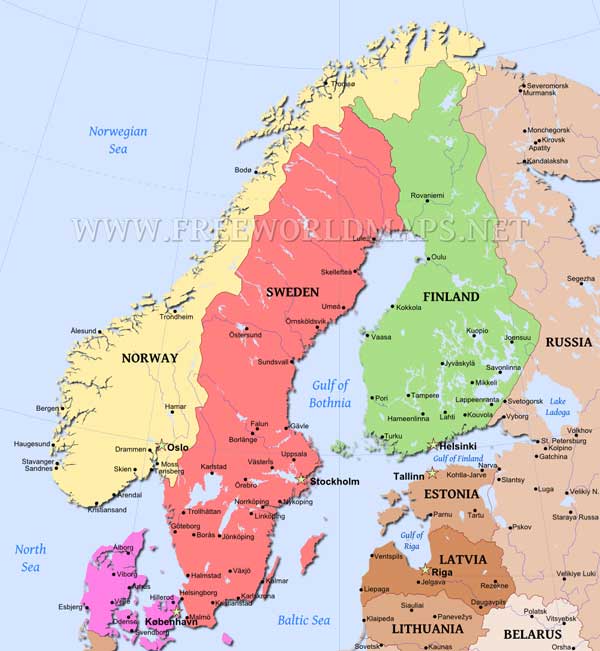
The Scandinavian Peninsula, a landmass cradled in Northern Europe, is home to three distinct nations: Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. While Denmark occupies its own peninsula, Jutland, the three countries share a rich history, cultural ties, and a landscape sculpted by the forces of nature. Understanding the geography of these nations provides valuable insight into their unique characteristics and the interconnectedness of their cultures.
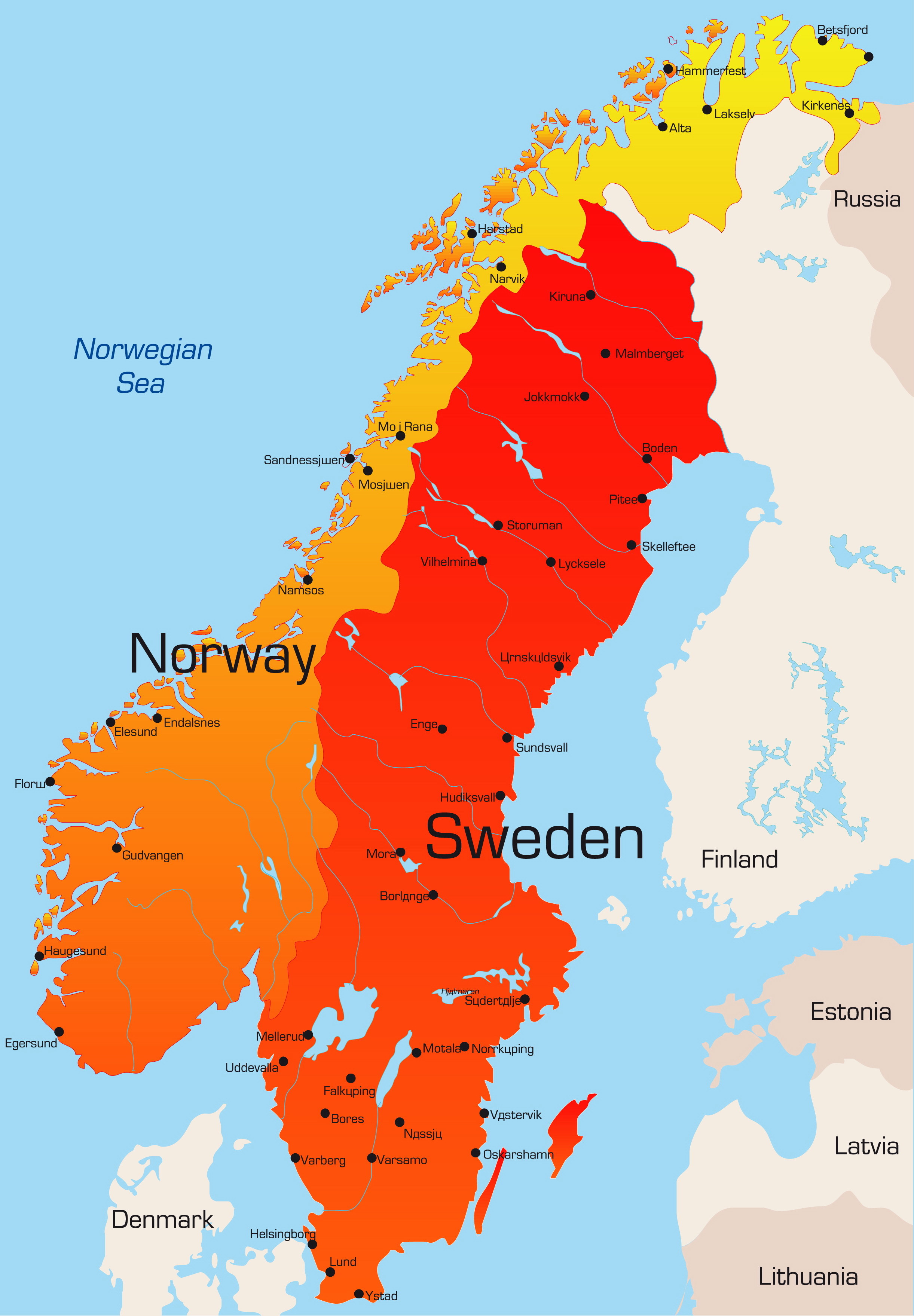
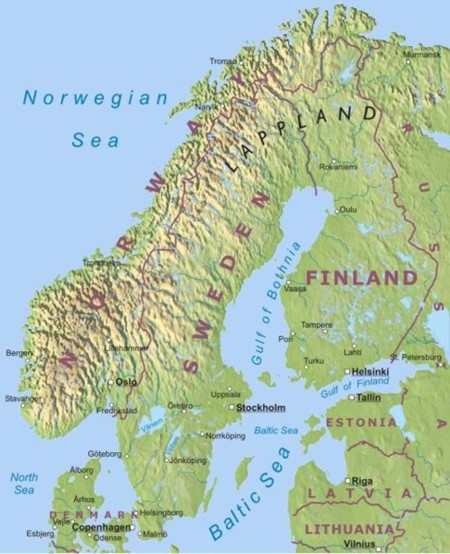
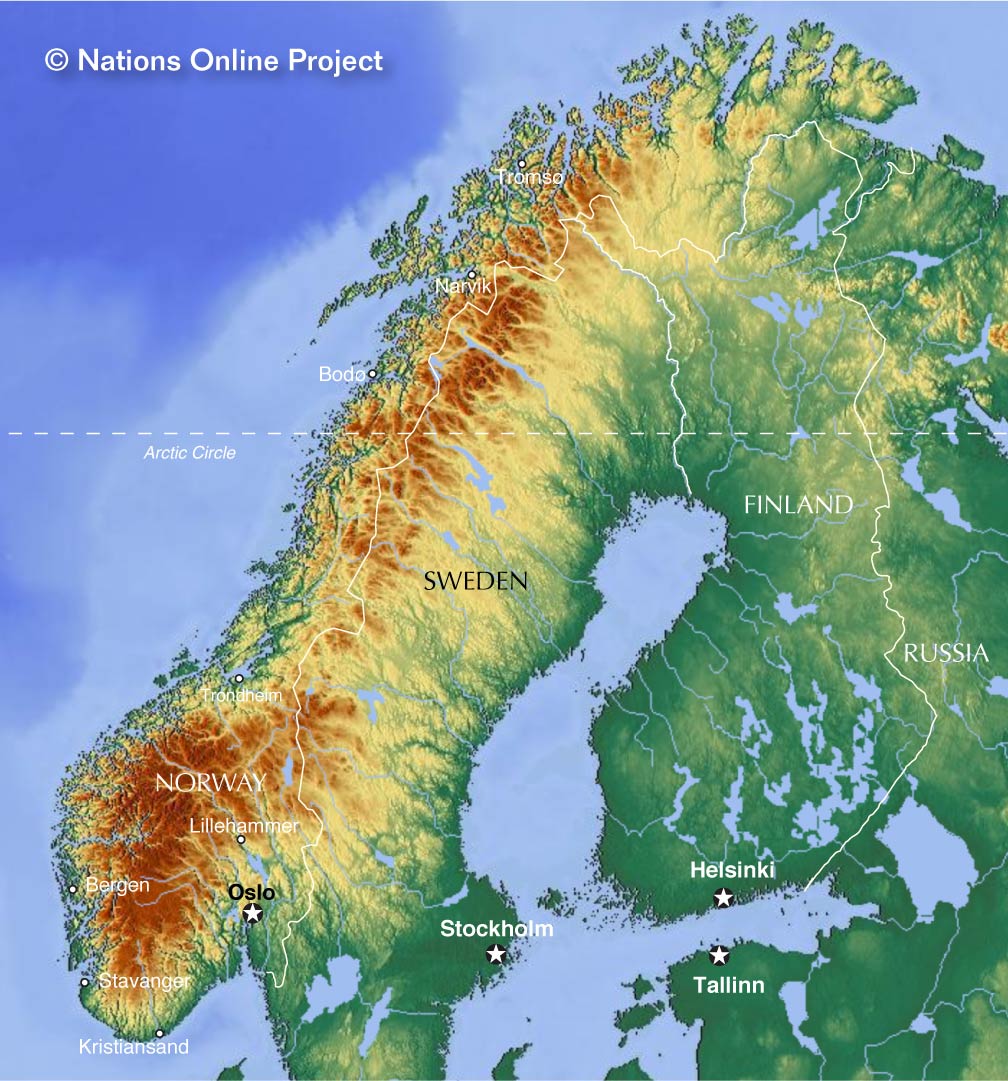
Norway: The Land of Fjords and Mountains
Norway, a country of rugged beauty, stretches along the western edge of the Scandinavian Peninsula. Its coastline, a tapestry of fjords, is a defining feature. Fjords, deep, narrow inlets carved by glaciers, create a dramatic landscape, drawing travelers from around the world. The country is also dominated by mountains, the most prominent being the Jotunheimen range, home to Norway’s highest peak, Galdhøpiggen.
Key Geographical Features of Norway:
- Fjords: The most iconic feature of Norway, fjords like Sognefjord, Geirangerfjord, and Hardangerfjord offer breathtaking views and opportunities for exploration.
- Mountains: The Scandinavian Mountains, a vast range stretching across the peninsula, dominate Norway’s landscape.
- Glaciers: Norway is home to numerous glaciers, including Jostedalsbreen, the largest glacier in continental Europe.
- Coastal Areas: The jagged coastline of Norway is punctuated by islands, skerries, and numerous fishing villages.
- Northern Lights: The aurora borealis, a celestial spectacle of dancing lights, is visible in the northern regions of Norway during winter.
Sweden: The Land of Lakes and Forests
Sweden, the largest country in Scandinavia, occupies the eastern portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. Its landscape is characterized by vast forests, numerous lakes, and rolling plains. The country’s interior is dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains, although they are less dramatic than those in Norway. Sweden’s lakes, known as "sjön," are a significant feature, with Lake Vänern and Lake Vättern being among the largest in Europe.
Key Geographical Features of Sweden:
- Lakes: Sweden is known as "The Land of a Thousand Lakes," with over 90,000 lakes scattered across its territory.
- Forests: Forests cover approximately 70% of Sweden, providing a vast and diverse ecosystem.
- Mountains: The Scandinavian Mountains, although lower than in Norway, contribute to Sweden’s varied topography.
- Coastal Areas: Sweden has a long coastline along the Baltic Sea, featuring numerous islands and archipelagos.
- Arctic Region: The northernmost region of Sweden, Lapland, is known for its unique Arctic landscape and the Sami indigenous culture.
Denmark: The Land of Islands and Jutland
Denmark, unlike Norway and Sweden, occupies its own peninsula, Jutland, and numerous surrounding islands. The country’s landscape is generally flat, with rolling hills and fertile agricultural land. The largest island is Zealand, home to Copenhagen, the capital city. Denmark’s coastline is characterized by sandy beaches, dunes, and sheltered inlets.
Key Geographical Features of Denmark:
- Jutland Peninsula: The largest landmass of Denmark, Jutland is known for its agricultural lands and flat topography.
- Islands: Denmark comprises 443 islands, of which 74 are inhabited. The most significant are Zealand, Funen, and Lolland.
- Coastal Areas: Denmark’s coastline is marked by beaches, dunes, and inlets, offering opportunities for seaside recreation.
- Wadden Sea: A unique ecosystem, the Wadden Sea is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, known for its tidal flats and abundant birdlife.
The Interconnectedness of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark
While distinct in their landscapes and cultures, Norway, Sweden, and Denmark share a deep historical and cultural connection. Their shared history, rooted in the Viking Age, has left its mark on their languages, customs, and traditions. The three nations also collaborate closely on various economic, political, and social issues, reflecting their shared interests and values.
The Importance of Understanding the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark
Understanding the geography of these three countries is crucial for various reasons:
- Economic Development: The landscape and natural resources play a significant role in the economic development of each country. Norway’s fjords, for instance, are crucial for tourism and fishing, while Sweden’s forests are essential for timber production.
- Cultural Identity: The geography of a country shapes its culture and identity. The rugged landscape of Norway has inspired a strong sense of independence and resilience, while Sweden’s vast forests have fostered a deep connection to nature.
- Environmental Sustainability: Understanding the geography of these countries is essential for promoting environmental sustainability. The challenges of climate change, for instance, are particularly relevant to the Nordic region, and require collaborative efforts to address.
- Tourism and Recreation: The diverse landscapes of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark offer a wealth of opportunities for tourism and recreation, from hiking and skiing in the mountains to sailing and kayaking in the fjords and lakes.
FAQs about the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark:
Q1: What is the highest mountain in Norway?
A1: The highest mountain in Norway is Galdhøpiggen, reaching a height of 2,469 meters (8,101 feet).
Q2: How many islands are there in Denmark?
A2: Denmark comprises 443 islands, of which 74 are inhabited.
Q3: What is the largest lake in Sweden?
A3: The largest lake in Sweden is Lake Vänern, with a surface area of 5,585 square kilometers (2,156 square miles).
Q4: What is the significance of the Wadden Sea?
A4: The Wadden Sea is a unique ecosystem, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, known for its tidal flats and abundant birdlife.
Q5: How do the fjords of Norway form?
A5: Fjords are deep, narrow inlets carved by glaciers during the last ice age. As glaciers retreated, they left behind these dramatic landscapes.
Tips for Exploring the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark:
- Visit National Parks: Explore the diverse landscapes of these countries by visiting their national parks, such as Jotunheimen National Park in Norway, Sarek National Park in Sweden, and Thy National Park in Denmark.
- Go Hiking or Skiing: Hike or ski through the mountains, experiencing the rugged beauty and challenging terrain.
- Take a Ferry or Boat Trip: Explore the fjords of Norway, the lakes of Sweden, or the islands of Denmark by ferry or boat.
- Visit Coastal Towns and Villages: Discover the charm of coastal towns and villages, experiencing local culture and cuisine.
- Learn about the History and Culture: Explore museums, historical sites, and cultural events to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s rich history and traditions.
Conclusion
The geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark plays a fundamental role in shaping their landscapes, cultures, and economies. From the dramatic fjords of Norway to the vast forests of Sweden and the islands of Denmark, these countries offer a diverse and captivating array of geographical features. Understanding their unique landscapes and the interconnectedness of their cultures provides valuable insight into the Scandinavian Peninsula and beyond. By appreciating the geographical diversity and historical ties of these nations, we can better understand the richness and complexity of the Nordic region.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: Exploring the Scandinavian Peninsula and Beyond. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!