A Borderland Of Cultures: Exploring The States That Share A Frontier With Mexico
A Borderland of Cultures: Exploring the States that Share a Frontier with Mexico
Related Articles: A Borderland of Cultures: Exploring the States that Share a Frontier with Mexico
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Borderland of Cultures: Exploring the States that Share a Frontier with Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Borderland of Cultures: Exploring the States that Share a Frontier with Mexico

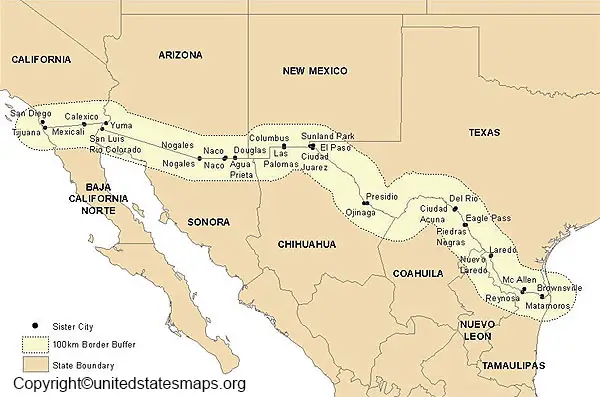
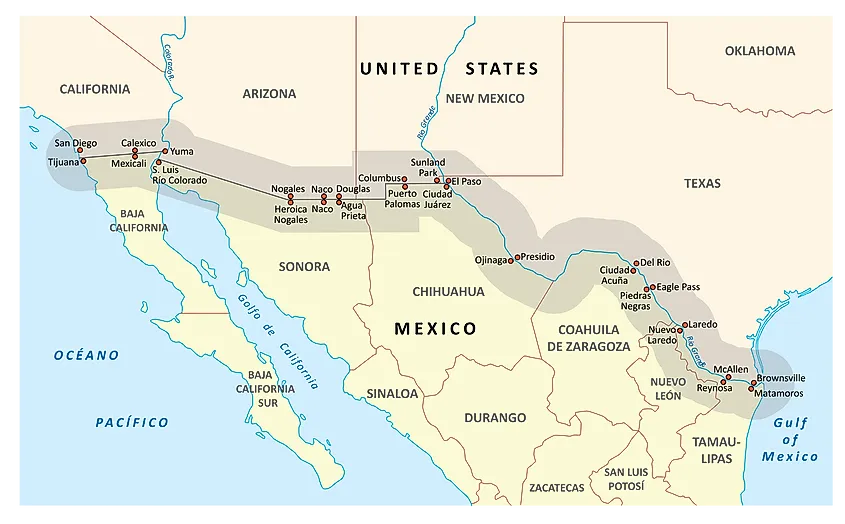
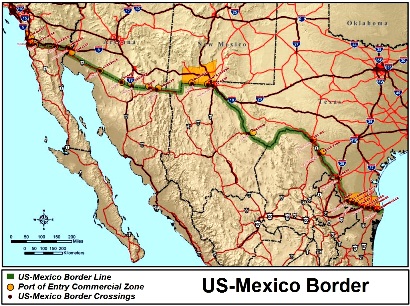
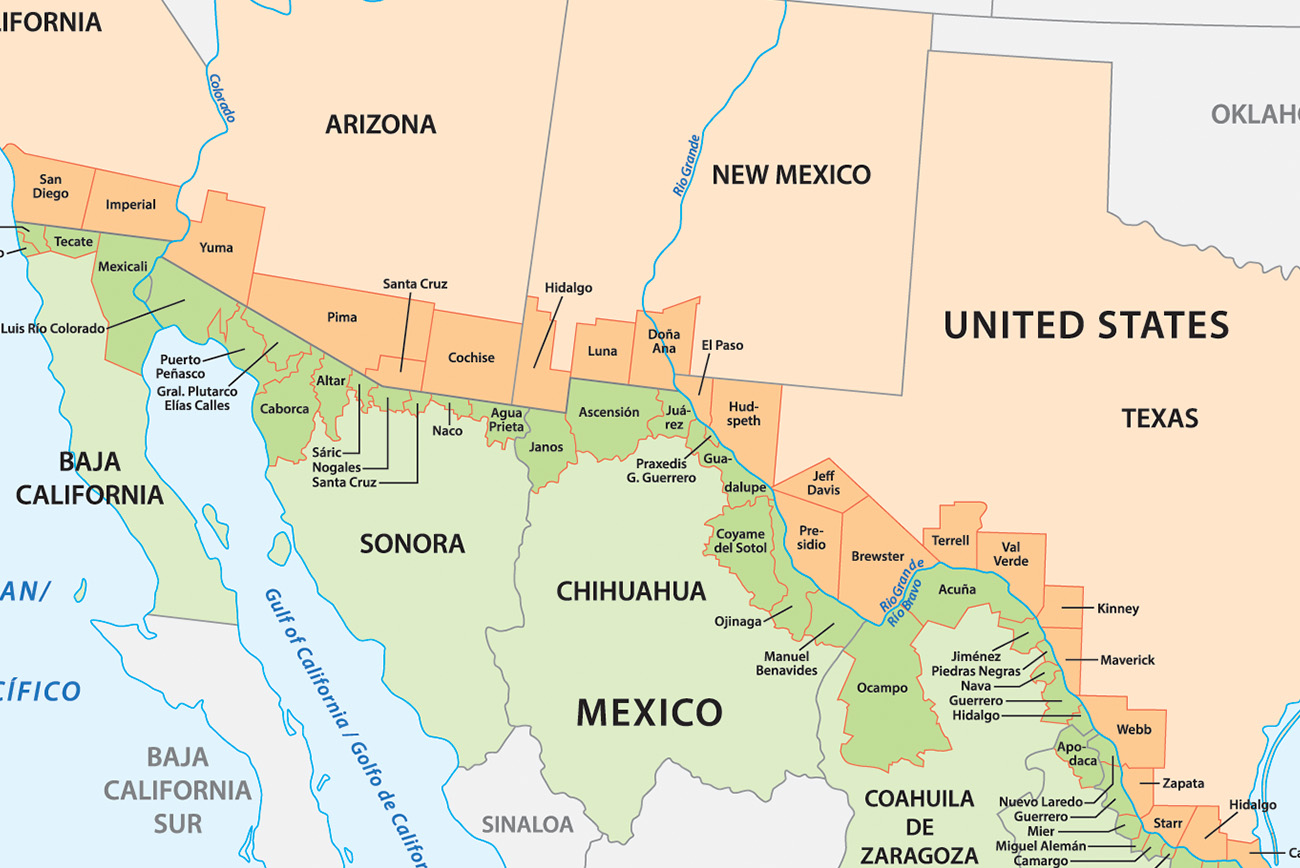
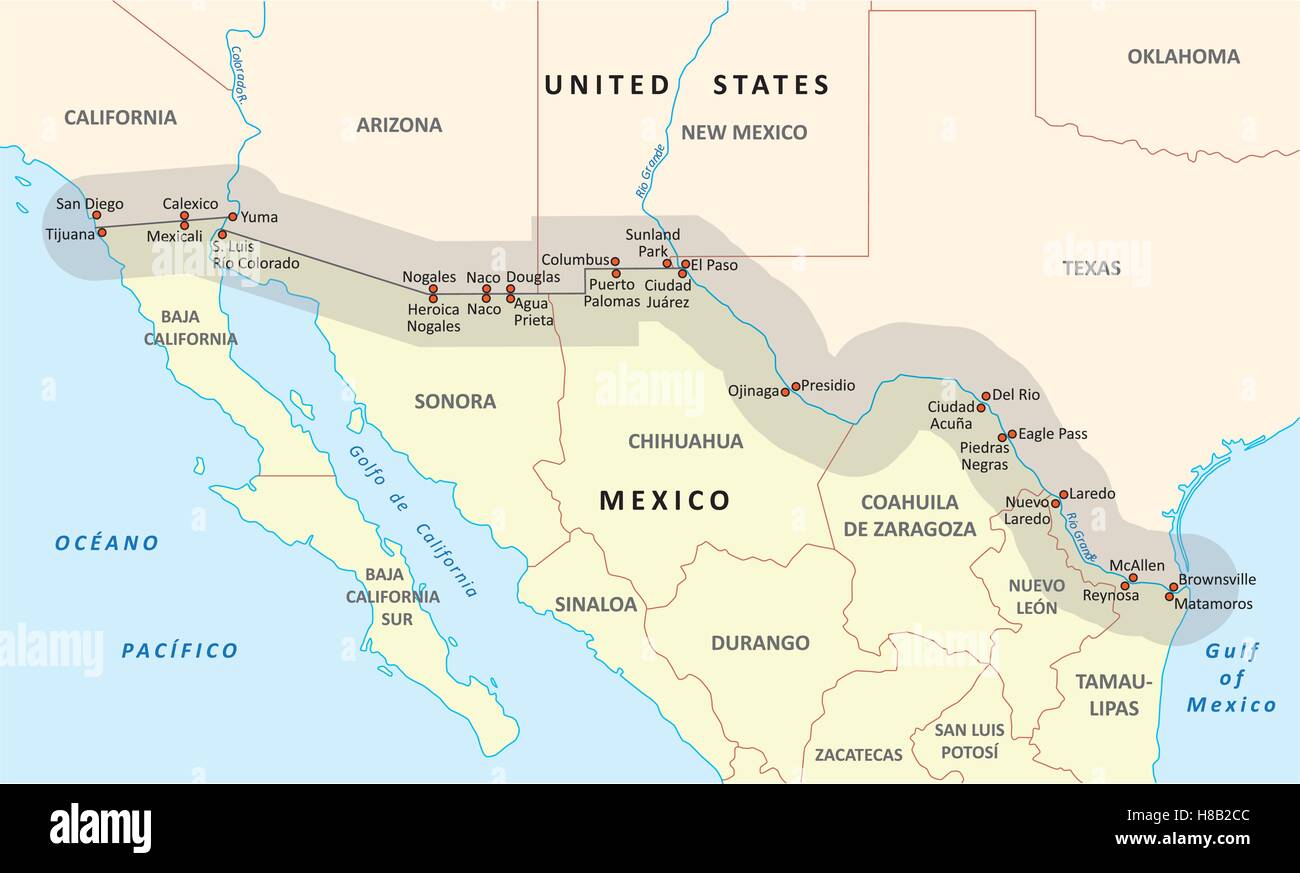
The United States and Mexico share a complex and dynamic relationship, one that is deeply intertwined with the geography of their shared border. This border, stretching over 1,954 miles from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico, is not just a physical boundary but a vibrant tapestry of cultures, histories, and economies. Understanding the states that directly interface with Mexico is crucial for comprehending the intricate dynamics of this relationship.
A Geographic Overview: The States that Border Mexico
The United States has four states that directly share a border with Mexico:
-
California: The largest of the border states, California boasts the longest stretch of the US-Mexico border, covering 141 miles. Its diverse landscape, from the bustling urban centers of San Diego and Los Angeles to the vast deserts of the Salton Sea, creates a unique environment for cross-border interactions.
-
Arizona: With 370 miles of border, Arizona is home to a rich history of cultural exchange and economic interdependence with Mexico. Its diverse geography, ranging from the towering peaks of the Grand Canyon to the Sonoran Desert, further emphasizes the diverse nature of the borderland.
-
New Mexico: The southernmost state in the US, New Mexico shares a 180-mile border with Mexico. Its history is deeply intertwined with Mexico, reflected in its Spanish colonial heritage and vibrant Hispanic culture.
-
Texas: The state with the second-longest border with Mexico (1,241 miles), Texas is a major economic and cultural hub for the region. Its diverse landscape, encompassing the sprawling plains of West Texas to the bustling cities of Houston and San Antonio, reflects the dynamic nature of the border.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Importance of the Border States
The states that border Mexico are not merely geographic entities but play a pivotal role in shaping the US-Mexico relationship. Their importance is multifaceted, encompassing economic, cultural, and political dimensions.
Economic Interdependence:
The US-Mexico border is a major economic engine, driving trade, investment, and employment in both countries. Border states serve as crucial gateways for goods and services, facilitating cross-border trade that benefits industries ranging from agriculture and manufacturing to tourism and technology.
-
Trade: The US-Mexico border is the busiest land border in the world, facilitating billions of dollars in trade annually. The border states play a crucial role in this exchange, serving as major hubs for manufacturing, agriculture, and energy production.
-
Investment: The border states are attractive destinations for foreign investment, particularly from Mexico. This investment fuels economic growth and job creation in the border region, further strengthening the economic ties between the two countries.
-
Tourism: The border states are popular destinations for both American and Mexican tourists, contributing significantly to the local economies. Tourism fosters cultural exchange and understanding, further strengthening the bond between the two countries.
Cultural Exchange and Diversity:
The border states are vibrant cultural melting pots, showcasing the rich tapestry of American and Mexican cultures. The constant exchange of ideas, traditions, and artistic expressions creates a unique cultural landscape that enriches the lives of residents on both sides of the border.
-
Hispanic Culture: The border states have a significant Hispanic population, reflecting the historical and cultural ties with Mexico. This cultural influence is evident in language, cuisine, music, and art, enriching the diverse tapestry of American culture.
-
Binational Communities: Many communities along the border straddle the US-Mexico divide, fostering close-knit relationships and a sense of shared identity. This binationalism fosters understanding and cooperation, contributing to a more harmonious relationship between the two countries.
Political and Security Considerations:
The border states face unique political and security challenges, navigating complex issues related to immigration, drug trafficking, and border security. These challenges require collaborative efforts between the US and Mexico to address shared concerns and promote security and stability in the border region.
-
Immigration: The border states are often the focal point of immigration debates, dealing with the complex issues of undocumented migration and border security. Finding solutions that address both security concerns and humanitarian needs requires collaboration and understanding.
-
Drug Trafficking: The border states are vulnerable to drug trafficking, posing a significant challenge to law enforcement agencies on both sides. Collaborative efforts between the US and Mexico are crucial to combat drug trafficking and protect communities from its harmful effects.
-
Border Security: The border states play a vital role in border security, working with federal agencies to enforce immigration laws and prevent illegal crossings. Balancing security concerns with the need for cross-border trade and cultural exchange requires careful consideration and diplomacy.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Border States
Q: What are the major industries in the border states?
A: The border states are home to a diverse range of industries, including:
- Agriculture: The fertile land along the border is ideal for agriculture, producing crops like cotton, citrus fruits, and vegetables.
- Manufacturing: The border states have a long history of manufacturing, with industries ranging from automotive and electronics to textiles and food processing.
- Tourism: The border states are popular tourist destinations, attracting visitors from both the US and Mexico. Tourism contributes significantly to the local economies, supporting hotels, restaurants, and attractions.
- Energy: The border states are home to significant energy resources, including oil, gas, and renewable energy sources. The energy sector plays a crucial role in the regional economy.
Q: What are the major cultural differences between the border states and other parts of the US?
A: The border states have a distinct cultural identity, shaped by their proximity to Mexico. This cultural influence is evident in:
- Language: Spanish is widely spoken in the border states, reflecting the historical and cultural ties with Mexico.
- Cuisine: Mexican cuisine is a staple in the border states, with a wide variety of dishes and flavors influenced by both Mexican and American traditions.
- Music: The border states are home to a vibrant music scene, blending traditional Mexican genres like mariachi with American influences.
- Art: The border states are known for their rich artistic heritage, showcasing a fusion of Mexican and American art forms.
Q: What are the challenges faced by the border states?
A: The border states face a number of challenges, including:
- Immigration: The issue of undocumented migration is a complex and sensitive topic, posing challenges for border security and social services.
- Drug Trafficking: The border states are vulnerable to drug trafficking, posing a significant threat to public safety and law enforcement.
- Economic Disparities: The border states often experience higher poverty rates and lower wages than other parts of the US, highlighting the need for economic development and opportunity.
- Environmental Issues: The border states face environmental challenges related to water scarcity, air pollution, and habitat loss, requiring collaborative efforts to address these issues.
Tips for Understanding the Border States
- Travel to the border states: Experiencing the border region firsthand provides a deeper understanding of its culture, history, and challenges.
- Engage with local communities: Connect with residents of the border states to learn about their perspectives and experiences.
- Explore cultural events and festivals: Attend events that celebrate the cultural diversity of the border region, such as music festivals, art exhibitions, and food festivals.
- Read books and articles: Learn about the history, culture, and politics of the border states through books, articles, and documentaries.
- Support organizations working on border issues: Contribute to organizations that address challenges related to immigration, economic development, and environmental protection in the border region.
Conclusion: A Region of Interdependence and Opportunity
The states that border Mexico are not simply geographic entities but crucial players in the US-Mexico relationship. They are economic powerhouses, cultural melting pots, and key players in addressing shared challenges. Understanding the dynamics of the border states is essential for comprehending the complex and multifaceted relationship between the US and Mexico. By fostering collaboration, promoting economic development, and celebrating cultural diversity, the border states can continue to play a vital role in shaping a more prosperous and harmonious future for both nations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Borderland of Cultures: Exploring the States that Share a Frontier with Mexico. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!